Abstract
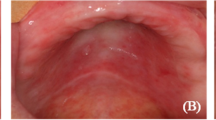
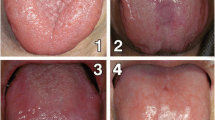
The aim of this study was to evaluate the correlation between frequency and phospholipase activity of Candida species and denture stomatitis according to Newton’s classification. Seventy-five complete denture wearers were evaluated for the presence of yeasts on the palatal mucosa by culture method. In addition, the number of yeast isolates producing phospholipase and amount of this enzyme were determined using egg yolk agar plate method. According to Newton’s classification, 25 denture wearers were with healthy palatal mucosa while 50 were with any types of denture stomatitis. The frequency of yeasts was linked to whether subjects had Type II or Type III, but not Type I denture stomatitis. Candida albicans was the most frequently isolated species in denture wearers with and without clinical signs of denture stomatitis and it was the only species produced phospholipase. Although the amount of phospholipase produced by the C. albicans isolates from denture wearers in control and Type II and III DS groups was not significantly different, there was statistically significant difference in the number of C. albicans isolates producing phospholipase between patients with and without clinical signs of DS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
TM Arendorf DM Walker (1987) ArticleTitleDenture stomatitis: a review J Oral Rehabil 14 217–227 Occurrence Handle3298586 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s3ltlGksA%3D%3D
BC Webb CJ Thomas MD Willcox DW Harty KW Knox (1998) ArticleTitleCandida-associated denture stomatitis. Aetiology and management: a review. Part 2. Oral diseases caused by Candida species Aust Dent J 43 160–166 Occurrence Handle9707778 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czntlSksA%3D%3D
I Espinoza R Rojas W Aranda J Gamonal (2003) ArticleTitlePrevalence of oral mucosal lesions in elderly people in Santiago, Chile J Oral Pathol Med 32 571–575 Occurrence Handle14632931 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3srlsVKltA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0714.2003.00031.x
MI MacEntee N Glick E Stolar (1998) ArticleTitleAge, gender, dentures and oral mucosal disorders Oral Dis 4 32–36 Occurrence Handle9655042 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czhvFWisw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1601-0825.1998.tb00252.x
PA Reichart (2000) ArticleTitleOral mucosal lesions in a representative cross-sectional study of aging Germans Commun Dent Oral Epidemiol 28 390–398 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvmt1Cltw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0528.2000.028005390.x
JD Shulman F Rivera-Hidalgo MM Beach (2005) ArticleTitleRisk factors associated with denture stomatitis in the United States J Oral Pathol Med 34 340–346 Occurrence Handle15946181 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2MzgtV2ktQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1600-0714.2005.00287.x
NS Dar-Odeh AA Shehabi (2003) ArticleTitleOral candidosis in patients with removable dentures Mycoses 46 187–191 Occurrence Handle12801360 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s3nsFKjsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1439-0507.2003.00871.x
J Barbeau J Séguin JP Goulet L Korinck Particlede SL Avon B Lalonde P Rompré N Deslauriers (2003) ArticleTitleReassessing the presence of Candida albicans in denture-related stomatitis Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 95 51–59 Occurrence Handle12539027
MJ McCullough BC Ross PC Reade (1996) ArticleTitleCandida albicans: a review of its history, taxonomy, epidemiology, virulence attributes and methods of strain differentiation Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 25 136–144 Occurrence Handle8727588 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28zitlOhsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0901-5027(96)80060-9
JE Cutler (1991) ArticleTitlePutative virulence factors of Candida albicans Annu Rev Microbiol 45 187–218 Occurrence Handle1741614 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XhsVOmtro%3D Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001155
MA Ghannoum KH Abu-Elteen (1990) ArticleTitlePathogenicity determinants of Candida Mycoses 33 265–282 Occurrence Handle2259368 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M%2FotV2jsw%3D%3D
YL Yang (2003) ArticleTitleVirulence factors of Candida species J Microbiol Immunol Infect 36 223–228 Occurrence Handle14723249 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXht1Snt7k%3D
MA Ghannoum (2000) ArticleTitlePotential role of phospholipases in virulence and fungal pathogenesis Clin Microbiol Rev 13 122–143 Occurrence Handle10627494 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXntFaguw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1128/CMR.13.1.122-143.2000
T Lane JR Garcia (1991) ArticleTitlePhospholipase production in morphological variants of Candida albicans Mycoses 34 217–220 Occurrence Handle1795715 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XisFWrsb8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1439-0507.1991.tb00646.x
AV Newton (1962) ArticleTitleDenture sore mouth. A possible etiology Br Dent J 112 357–360
LP Samaranayake JM Raeside TW MacFarlane (1984) ArticleTitleFactors affecting the phospholipase activity of Candida species in vitro Sabouraudia 22 201–207 Occurrence Handle6379916 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXlsVOgtbk%3D
RP Santarpia JJ Pollock RP Renner E Spiechowicz (1990) ArticleTitleAn in vivo replica method for the site-specific detection of Candida albicans on the denture surface in denture stomatitis patients: correlation with clinical disease J Prosthet Dent 63 437–443 Occurrence Handle2184228 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-3913(90)90234-4
K Barrett-Bee Y Hayes RG Wilson JF Ryley (1985) ArticleTitleA comparison of phospholipase activity, cellular adherence and pathogenicity of yeasts J Gen Microbiol 131 1217–1221 Occurrence Handle3894572 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2M3mtlGhtQ%3D%3D
MF Price ID Wilkinson LO Gentry (1982) ArticleTitlePlate method for detection of phospholipase activity in Candida albicans Sabouraudia 15 179–185
AM Willis WA Coulter CR Fulton JR Hayes PM Bell PJ Lamey (2001) ArticleTitleThe influence of antifungal drugs on virulence properties of Candida albicans in patients with diabetes mellitus Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 91 317–321 Occurrence Handle11250629 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3kslShsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1067/moe.2001.112155
VL Bosco EG Birman AE Cury CR Paula (2003) ArticleTitleYeasts from the oral cavity of children with AIDS: exoenzyme production and antifungal resistance Pesqui Odontol Bras 17 217–222 Occurrence Handle14762498
J Hannula M Saarela B Dogan J Paatsama P Koukila-Kähkölä S Pirinen HL Alakomi J Perheentupa S Asikainen (2000) ArticleTitleComparison of virulence factors of oral Candida dubliniensis and Candida albicans isolates in healthy people and patients with chronic candidosis Oral Microbiol Immunol 15 238–244 Occurrence Handle11154409 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7hvVaitQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1399-302x.2000.150405.x
S Anil LP Samaranayake (2003) ArticleTitleBrief exposure to antimycotics reduces the extracellular phospholipase activity of Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis Chemotherapy 49 243–247 Occurrence Handle14504435 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnsVOqtL4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1159/000072448
Clancy CJ, Ghannoum MA, Nguyen MH. 36th Annual Meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, 1998: 317
Y Fu AS Ibrahim W Fonzi X Zhou CF Ramos MA Ghannoum (1997) ArticleTitleCloning and characterization of a gene (LIP1) which encodes a lipase from the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans Microbiology 143 331–340 Occurrence Handle9043110 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXht1enur8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1099/00221287-143-2-331
Y Banno T Yamada Y Nozawa (1985) ArticleTitleSecreted phospholipases of the dimorphic fungus, Candida albicans; separation of three enzymes and some biological properties Sabouraudia 23 47–54 Occurrence Handle3887602 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXktVehurw%3D
F Mirbod Y Banno MA Ghannoum AS Ibrahim S Nakashima Y Kitajima GT Cole Y Nozawa (1995) ArticleTitlePurification and characterization of lysophospholipase–transacylase (h-LPTA) from a highly virulent strain of Candida albicans Biochim Biophys Acta 1257 181–188 Occurrence Handle7619859
S Shimizu Y Tani H Yamada M Tabata T Murachi (1980) ArticleTitleEnzymatic determination of serum-free fatty acids: a colorimetric method Anal Biochem 107 193–198 Occurrence Handle6776842 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXlvVagsLw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-2697(80)90511-4
CY Koga-Ito JP Lyon V Vidotto MA Resende Particlede (2006) ArticleTitleVirulence factors and susceptibility of Candida albicans isolates from oral candidosis patients and control individuals Mycopathologia 161 219–223 Occurrence Handle16552484 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28Xis1Okt7g%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/s11046-005-0001-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gümrü, B., Kadir, T., Uygun-Can, B. et al. Distribution and phospholipase activity of Candida species in different denture stomatitis types. Mycopathologia 162, 389–394 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-006-0074-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-006-0074-1