Abstract
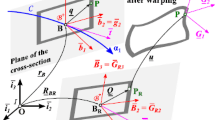
An efficient finite element (FE) formulation for the simulation of multibody systems is derived from Hamilton's principle. According to the classical assumptions of multibody systems, a large rotation formulation has been chosen, where large rotations and large displacements, but only small deformations of the single bodies are taken into account. The strain tensor is linearized with respect to a co-rotated frame. The present approach uses absolute coordinates for the degrees of freedom and forms an alternative to the floating frame of reference formulation that is based on relative coordinates and describes deformation with respect to a co-rotated frame. Due to the modified strain tensor, the present formulation distinguishes significantly from standard nodal based nonlinear FE methods. Constraints are defined in integral form for every pair of surfaces of two bodies. This leads to a small number of constraint equations and avoids artificial stress singularities. The resulting mass and stiffness matrices are constant apart from a transformation based on a single rotation matrix for each body. The particular structure of this transformation allows to prevent from the usually expensive factorization of the system Jacobian within implicit time--integration methods. The present method has been implemented and tested with the FE-package NGSolve and specific 3D examples are verified with a standard beam formulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambróosio, J.A.C.: Geometric and material nonlinear deformations in flexible multibody systems. Computational aspects of nonlinear structural systems with large rigid body motion (J.A.C. Ambrósio and M. Kleiber, Ed.). Nato Science Series, IOS Press (2001)
Argyris, J.: An excursion into large rotations. Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 32, 85–155 (1982)
Belytschko, T., Hsieh, B.J.: Non-linear transient finite element analysis with convected co-ordinates. Int. J. Num. Meth. in Engrg.7, 255–271 (1973)
Bonet, J., Wood, R.D.: Nonlinear continuum mechanics for finite element analysis. Cambridge University Press, U.K. (1997)
Bremer, H., Pfeiffer, F.: Elastische Mehrkörpersysteme. B. G. Teubner, Stuttgart, Germany, (1992)
Brenan, K.E., Campbell, S.L., Petzold, L.R.: Numerical solution of initial-value problems in differential-algebraic equations. SIAM, Philadelphia (1996)
Dibold, M.: Eine Studie zur Computerunterstützten berechnung räumlicher bewegungen inelastischer Maschinenteile, master's thesis. University of Linz, Austria (2002)
Fung, R.F.: Dynamic analysis of the flexible connecting rod of a slider–crank mechanism. J. Vib. and Acoust. 118, 687–689 (1996)
Géradin, M., Cardona, A.: Flexible multibody dynamics – A finite element approach. Wiley, New York, (2001)
Gerstmayr, J.: A solution strategy for elasto – plastic multibody systems and related problems. University of Linz, Austria, (2001)
Gerstmayr, J., Irschik, H.: Vibrations of the elasto–plastic pendulum. Int. J. Nonlin. Mech. 38, 111–122 (2003)
Gerstmayr, J.: The absolute coordinate formulation with elasto – plastic deformations. Journal of Multibody System Dynamics 12, 363–383 (2004)
Gerstmayr, J.: Strain tensors in the absolute nodal coordinate and the floating frame of reference formulation. Nonlinear Dynamics 34, 133–145 (2003)
Gerstmayr, J., Schöberl, J.: A 3D finite element approach to flexible multibody systems, proceedings of the fifth world congress on computational mechanics (WCCM V). (eds.): Mang, H.A.; Rammerstorfer, F.G.; Eberhardsteiner, J. Vienna University of Technology, Vienna, Austria (2002). http://wccm.tuwien.ac.at
Gerstmayr, J., Schöberl, J.: An implicit Runge-Kutta based solver for 3-dimensional multibody systems. PAMM, 3(1), 154–155 (2003)
Hairer, E., Nørsett, S.P., Wanner, G.: Solving ordinary differential equations I, nonstiff problems. Springer–Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, (1987)
Hairer, E., Wanner, G.: Solving ordinary differential equations 2, stiff and differential-algebraic problems. Springer–Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, (1991)
Hairer, E., Lubich, Ch., Roche, M.: The numerical solution of differential-algebraic systems by runge-kutta methods. Lecture Notes in Math. 1409, Springer–Verlag, (1989)
Haug, E.J.: Computer-aided kinematics and dynamics of mechanical systems. Allyn and Bacon, Boston, 1989.
de Jalón, J.G., Bayo, E.: Kinematic and dynamic simulation of multibody systems: The real time challenge. Springer, New York, (1994)
Kübler, L., Eberhard, P., Geisler, J.: Flexible multibody systems with large deformations and nonlinear structural damping using absolute nodal coordinates. Nonlinear Dynamics 34, 31–52 (2003)
Magnus, K.: Dynamics of multibody systems. Springer Verlag, Berlin, (1978)
Nikravesh, P.E.: Computer-aided analysis of mechanical systems. Prentice-Hall, (1988)
Orden, J.C.G., Goicolea, J.M.: Conserving properties in constrained dynamics of flexible multibody systems. Multibody Sys. Dyn., 4, 225–244 (2000)
Pan, W., Haug, E.J.: Dynamic simulation of general flexible multibody systems. Mech. Struct. Mach. 27, 217–251 (1999)
Pfister, J., Eberhard, P.: Frictional contact of flexible and rigid bodies. Granular Matter 4, Springer-Verlag, 25–36 (2002)
Shabana, A.A.: Dynamics of multibody systems. Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons, (1998)
Schiehlen, W. (ed.): Multibody system dynamics. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, (1997)
Von Schwerin, R.: Multibody system simulation; numerical methods. algorithms, and software. Springer Verlag Berlin (1999)
Schwertassek, R., Wallrapp. O., Shabana, A.A.: Flexible multibody simulation and choice of shape functions. Nonl. Dyn. 20, 361–380 (1999)
Simeon, B.: Numerische Integration mechanischer mehrkörpersysteme: Projizierende Deskriptorformen, algorithmen und rechenprogramme. Tech. report, Fortschritt-Berichte VDI, Reihe 20, Nr. 130, VDI Verlag, Düsseldorf, Germany, (1994)
Simo, J.C., Vu-Quoc, L.: On the dynamics of flexible beams under large overall motions – the plane case: Part I. J. Appl. Mech. 53, 849–863 (1986)
Wittenburg, J.: Dynamics of systems of rigid bodies. Teubner, Stuttgart, (1977)
Zienkiewicz, O.C., Taylor, R.L.: The finite element method. Volume 2 – solid mechanics. Butterworth Heinemann, London (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerstmayr, J., Schöberl, J. A 3D Finite Element Method for Flexible Multibody Systems. Multibody Syst Dyn 15, 305–320 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-006-9009-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-006-9009-3