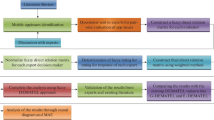
Abstract
An integral part of developing any mobile app is determining how much time and money will be needed to complete the task. Inaccuracy and imprecision will have serious consequences for the project's timeline and cost. Estimating how much work will go into making an app can be done in a number of ways. The accuracy of the COCOMO II app's effort estimation is very sensitive to the input parameters, which include things like the scope of the project, the coefficients used, and the cost predictors. In this research, author apply a multi-criteria decision-making algorithm Interval valued intuinistic fuzzy Decision Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (IVIF-DEMATEL) to determine the relationship between 16 different cost predictors, thereby decreasing the margin of estimating error (MMRE). In this work, author provide the results of an empirical investigation into the relationship between the impact cost predictors in app development methods and the cost predictors, as well as the development in app productivity over time. IVIF-DEMATEL with choquet integral was then used to analyze the mobiles cost predictors and divide them into cause/effect groups. As a first step, a group of experts examine how mobile app cost predictors are linked to each other in terms of direct correlation. Floppy triangle numbers display the findings of the evaluation (TFN). The second step is to translate the linguistic terms into TFN. According to DEMATEL, the cause-effect classifications of cost predictors can be determined. Finally, CMIs in mobile apps are identified as the cost predictors in the cause category. The IVIF-DEMATEL with choquet integral is found to be the most appropriate method for analyzing the interrelationship between DEMATEL variants such as Rough-DEMATEL and Hesitant-DEMATEL.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Al-Subaihin, A., Finkelstein, A., Harman, M., Jia, Y., Martin, W., Sarro, F., & Zhang, Y. (2015, August). App store mining and analysis. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Software Development Lifecycle for Mobile (pp. 1–2).
Martin, W., Harman, M., Jia, Y., Sarro, F., & Zhang, Y. (2015, May). The app sampling problem for app store mining. In 2015 IEEE/ACM 12th Working Conference on Mining Software Repositories (pp. 123–133). IEEE.
Wang M, Li X (2017) Effects of the aesthetic design of icons on app downloads: evidence from an android market. Electron Commer Res 17:83–102
Widnall E, Grant CE, Wang T, Cross L, Velupillai S, Roberts A, Downs J (2020) User perspectives of mood-monitoring apps available to young people: qualitative content analysis. JMIR mHealth and uHealth 8(10):e18140
Williams G, Mahmoud A (2018) Modeling user concerns in the app store: A case study on the rise and fall of yik yak. In 2018 IEEE 26th international requirements engineering conference (rE) (pp. 64–75). IEEE
Khalid M, Asif M, Shehzaib U (2015) Towards improving the quality of mobile app reviews. Int J Inform Technol Comput Sci (IJITCS) 7(10):35
Vu PM, Nguyen TT. Pham HV (2013) Mining User Opinions in Mobile App Reviews: A Keyword-based Approach, https://arxiv.org/pdf/1505.04657.pdf
Zhang L, Huang XY, Hu YK (2017) CSLabel:An Approach for Labelling Mobile App Reviews, 32 (6), 1076–1089
Huebner J, Frey RM, Ammendola C, Fleisch E, Ilic A (2018) What people like in mobile finance apps: An analysis of user reviews. In Proceedings of the 17th international conference on mobile and ubiquitous multimedia (pp. 293–304).l
Muñoz S, Araque O, Llamas AF, Iglesias CA (2018) A cognitive agent for mining bugs reports, feature suggestions and sentiment in a mobile application store. In 2018 4th international conference on Big Data innovations and applications (innovate-data) (pp. 17–24). IEEE.
Huebner J, Girardello A, Sliz O, Fleisch E, Ilic A (2020) What People Focus on When Reviewing Your App-An Analysis Across App Categories. IEEE Softw 38(3):96–105
Kalaichelavan K, Malik H, Husnu N, Shreenath S (2020) What Do People Complain About Drone Apps? A Large-Scale Empirical Study of Google Play Store Reviews. Procedia Comput Sci 170:547–554
Pandey M, Litoriya R, Pandey P (2018) An ISM approach for modeling the issues and factors of mobile app development. Int J Software Eng Knowl Eng 28(07):937–953
Pandey M, Litoriya R, Pandey P (2019) Perception-based classification of mobile apps: A critical review. In: Luhach AK, Hawari KBG, Mihai IC, Hsiung P-A, Mishra RB (eds) Smart computational strategies: Theoretical and Practical Aspects. Springer, Singapore, p 121–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6295-8_11
Pandey M, Litoriya R, Pandey P (2020) Validation of existing software effort estimation techniques in context with mobile software applications. Wireless Pers Commun 110(4):1659–1677
Pandey M, Litoriya R, Pandey P (2019) Novel approach for mobile based app development incorporating MAAF. Wireless Pers Commun 107(4):1687–1708
Pandey M, Litoriya R, Pandey P (2018) Mobile App development based on agility function. Ingénierie des systèmes d’information RSTI série ISI 23(6):19–44
Pandey M, Litoriya R, Pandey P (2016) Mobile applications in context of big data: A survey. In 2016 Symposium on Colossal Data Analysis and Networking (CDAN) (pp 1–5). IEEE.
Bustince H, Burillo P (1996) Vague sets are intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 79(3):403–405
Wei CP, Wang P, Zhang YZ (2011) Entropy, similarity measure of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications. Inf Sci 181(19):4273–4286
Boran FE, Genç S, Kurt M, Akay D (2009) A multi-criteria intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making for supplier selection with TOPSIS method. Expert Syst Appl 36(8):11363–11368
Rodriguez RM, Martinez L, Herrera F (2011) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 20(1):109–119
Jabangwe R, Edison H, Duc AN (2018) Software engineering process models for mobile app development: A systematic literature review. J Syst Softw 145:98–111
Ebrahimi F, Tushev M, Mahmoud A (2021) Mobile app privacy in software engineering research: A systematic mapping study. Inf Softw Technol 133:106466
Shahwaiz SA, Malik AA, Sabahat N (2016) A parametric effort estimation model for mobile apps. In 2016 19th International Multi-Topic Conference (INMIC) (pp 1–6). IEEE
Catolino G, Salza P., Gravino C, Ferrucci F (2017) A set of metrics for the effort estimation of mobile apps. In 2017 IEEE/ACM 4th International Conference on Mobile Software Engineering and Systems (MOBILESoft) (pp 194–198). IEEE
Murad MA, Abdullah NAS, Rosli MM (2021) Software Cost Estimation for Mobile Application Development-A Comparative Study of COCOMO Models. In 2021 IEEE 11th International Conference on System Engineering and Technology (ICSET) (pp 106–111). IEEE
Inukollu VN, Keshamoni DD, Kang T, Inukollu M (2014) Factors influencing quality of mobile apps: Role of mobile app development life cycle. arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.4537
Joorabchi ME, Mesbah A, Kruchten P (2013) Real challenges in mobile app development. In 2013 ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement (pp 15–24). IEEE
Heriyanto A (2013) Procedures and tools for acquisition and analysis of volatile memory on android smartphones
Brans PD, Basole RC (2008) A comparative anatomy of mobile enterprise applications: Towards a framework of software reuse. Inf Knowl Syst Manag 7(1–2):145–158
Batra S, Sachdeva S, Bhalla S (2019) Generic data storage-based dynamic mobile app for standardised electronic health records database. Int J High Perform Comput Networking 15(1–2):91–105
Riegler A, Holzmann C (2018) Measuring visual user interface complexity of mobile applications with metrics. Interact Comput 30(3):207–223
Latif M, Lakhrissi Y, Es-Sbai N (2016) Cross platform approach for mobile application development: A survey. In 2016 International Conference on Information Technology for Organizations Development (IT4OD) (pp 1–5). IEEE
Barack O, Huang L (2020) Assessment and prediction of software reliability in mobile applications. J Softw Eng Appl 13(9):179–190
Flora HK, Chande SV, Wang X (2014) Adopting an agile approach for the development of mobile applications. Int J Comput Appl 94(17):43–50
Zuo C, Lin Z (2017) Smartgen: Exposing server urls of mobile apps with selective symbolic execution. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web (pp 867–876)
Elena GH, Charles B, Klaus F, Remo F, Alexander I (2018) Assessing exposure factors in the smartphone generation: Design and evaluation of a smartphone app that collects use patterns of cosmetics and household chemicals. Food Chem Toxicol 118:532–540
Flora HK, Wang X, Chande SV (2014) An investigation into mobile application development processes: challenges and best practices. Int J Mod Educ Comput Sci 6(6):1–9. https://doi.org/10.5815/ijmecs.2014.06.01
Hoffman L, Benedetto E, Huang H, Grossman E, Kaluma D, Mann Z, Torous J (2019) Augmenting mental health in primary care: a 1-year study of deploying smartphone apps in a multi-site primary care/behavioral health integration program. Front Psychiatry 10:94. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00094
Da Silva LP, e Abreu FB (2014) Model-driven gui generation and navigation for android bis apps. In 2014 2nd International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development (MODELSWARD) (pp 400–407). IEEE
Pandey M, Litoriya R, Pandey P (2019) Application of fuzzy DEMATEL approach in analyzing mobile app issues. Program Comput Softw 45:268–287
Pandey M, Litoriya R, Pandey P (2019) Identifying causal relationships in mobile app issues: An interval type-2 fuzzy DEMATEL approach. Wireless Pers Commun 108(2):683–710
Pandey M, Litoriya R, Pandey P (2023) Scrutinizing student dropout issues in MOOCs using an intuitionistic fuzzy decision support system. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 44(3):4041–4058. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-190357
Kang B, Wei D, Li Ya, Deng Y (2012) A Method of Converting Z-number to Classical Fuzzy Number. J Inf Comput Sci 9(3):703–709
Tarokh M, Cross M, Lee M (2010) Erratum to: Fuzzy logic decision making for multi-robot security systems. Artif Intell Rev 34:289
Si SL, You XY, Liu HC (2018) DEMATEL Technique: A Systematic Review of the State-of-the-Art Literature on Methodologies and Applications. Mathematical problems in Engineering, doi-. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3696457
Chang B, Chang C, W., Wu, C. H. (2011) Fuzzy DEMATEL method for developing supplier selection criteria. Expert Syst Appl 38(3):1850–1858
Yuksel S, Dincer H, Eti S, Adali Z (2022) Strategy improvements to minimize the drawbacks of geothermal investments by using spherical fuzzy modelling. International journal of energy research, doi-. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7880
Gul S (2021) Extending ARAS with Integration of Objective Attribute Weighting under Spherical Fuzzy Environment. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 20(3):1011–1036
Shahzaib A, Saleem A, Muhammad A, Muhammad Q, Marwan K (2019) Spherical fuzzy sets and its representation of spherical fuzzy t-norms and t-conorms. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 36(6):6089–6102
Gundogdu K, Fatma, Cengiz, Kahaman (2019) A novel VIKOR method using spherical fuzzy sets and its application to warehouse site selection, J Intell Fuzzy Syst, 37(1), 1197-1211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, M., Litoriya, R. & Pandey, P. An integrated MCDM approach for mobile app cost predictor based on DEMATEL extended with choquet integral. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 34943–34962 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16856-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16856-y