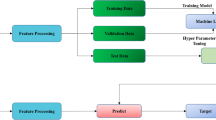
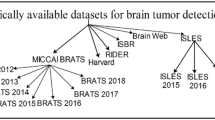
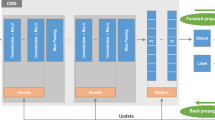
Abstract
Lung cancer has been one of the most prevalent disease in recent years. According to the research of this field, more than 200,000 cases are identified each year in the US. Uncontrolled multiplication and growth of the lung cells result in malignant tumour formation. Recently, deep learning algorithms, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), have become a superior way to automatically diagnose disease. The purpose of this article is to review different models that lead to different accuracy and sensitivity in the diagnosis of early-stage lung cancer and to help physicians and researchers in this field. The main purpose of this work is to identify the challenges that exist in lung cancer based on deep learning. The survey is systematically written that combines regular mapping and literature review to review 32 conference and journal articles in the field from 2016 to 2021. In this work, after a complete analysis and review of the articles, the questions raised in the articles have been answered. This research work provides a more comprehensive review compared to previous published review articles in this research area. Furthermore, it includes recent studies and state of the art research works systematically.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
American Cancer Society, Key Statistics for Lung Cancer (2020) Available from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html. Accessed Jan 2020
(2020) Diagnostic Image Analysis Group. [online]. Available: http://diagnijmegen.nl/index.php/Lung_Cancer. Accessed 02 Oct 2020
(2020) Multi-Task Deep Learning with Margin Ranking Loss for Lung Nodule Analysis. [online]. Available: https://github.com/CaptainWilliam/MTMR-NET.git. Accessed Mar 2020
(2020) Vision and Image Analysis Lab. http://www.via.cornell.edu. Accessed 04 Oct 2020
Abu-Naser S, Zaqout I, Abu Ghosh M, Atallah R, Alajrami E (2015) Predicting student performance using artificial neural network: in the Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology. Int J Hybrid Inform Technol 8(2):221–228. https://doi.org/10.14257/ijhit.2015.8.2.20
Amin SU et al (2019) Deep learning for eeg motor imagery classification based on multi-layer cnns feature fusion. Future Gener Comput Syst 101:542–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.06.027
Aonpong P, Iwamoto Y, Han X-H, Lin L, Chen Y-W (2021) Genotype-Guided Radiomics Signatures for Recurrence Prediction of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. IEEE Access 9:90244–90254. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3088234
Armato SG, McLennan G, Bidaut L, McNitt‐Gray MF, Meyer CR, Reeves AP (2015) Data from LIDC-IDRI. Cancer Imag Arch, [online]. Available: https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/Public/LIDC-IDRI
Bakr S, Gevaert O, Echegaray S, Ayers K, Zhou M, Shafiq M et al (2018) Data descriptor: A radiogenomic dataset of non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Data 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2018.202
Breivold HP, Crnkovic I, Larsson M (2012) A systematic review of software architecture evolution research. Inform Softw Technol 54(1):16–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2011.06.002
Cai L, Long T, Dai Y, Huang Y (2020) Mask R-CNN-Based Detection and Segmentation for Pulmonary Nodule 3D Visualization Diagnosis. IEEE Access 8:44400–44409. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2976432
Chen W, Wei H, Peng S, Sun J, Qiao X, Liu B (2019) HSN: Hybrid Segmentation Network for Small Cell Lung Cancer Segmentation. IEEE Access 7:75591–75603. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2921434
Chiles C, Duan F, Gladish GW, Ravenel JG, Baginski SG, Snyder BS, DeMello S, Desjardins SS, Munden RF, NLST Study Team (2015) Association of coronary artery calcification and mortality in the national lung screening trial: A comparison of three scoring methods. Radiology 276(1):82–90. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.15142062
Ciompi F, Chung K, Riel SJ, Setio AA, Gerke PK, Jacobs C, Scholten ET, Schaefer-Prokop C, Wille MM, Marchianò AV, Pastorino U, Prokop M, Ginneken BV (2017) Towards automatic pulmonary nodule management in lung cancer screening with deep learning. Sci Rep 7:. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46479
Cruz-Benito J (2016) Systematic literature review & mapping. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.165773. Accessed 8 Nov 2016
Buckeye AJ, Kriss J, BoozAllen J, Sullivan J, O’Connell M, Nilofer, Cukierski W (2017) Data Science Bowl 2017. Kaggle. https://kaggle.com/competitions/data-science-bowl-2017
Dou Q, Chen H, Yu L, Qin J, Heng P-A (2017) Multilevel Contextual 3-D CNNs for False Positive Reduction in Pulmonary Nodule Detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(7):1558–1567. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2016.2613502
Goran J, Davcev D (2019) Using double convolution neural network for lung cancer stage detection. Appl Sci 9(3):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030427
Guo H, Kruger U, Wang G, Kalra MK, Yan P (2020) Knowledge-Based Analysis for Mortality Prediction From CT Images. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 24(2):457–464. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2019.2946066
Hossain MS, Muhammad G (2014) Cloud-Based Collaborative Media Service Framework for HealthCare. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 10(3):858712. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/858712
Jiang H, Ma H, Qian W, Gao M, Li Y (2018) An Automatic Detection System of Lung Nodule Based on Multigroup Patch-Based Deep Learning Network. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 22(4):1227–1237. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2017.2725903
Jin H, Li Z, Tong R, Lin L (2018) A deep 3D residual CNN for false-positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection. Med Phys 45(5):2097–2107. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.12846
Krishnaiah V, Jayarama V et al (2013) Diagnosis of lung cancer prediction system using data mining classification techniques. Int J Comput Sci Inf Technol (IJCSIT) 4(1):39–45. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:18745929?utm_source=wikipedia
Kuan K, Ravaut M, Manek G, Chen H, Lin J, Nazir B, Chen C, Howe TC, Zeng Z, Chandrasekhar V (2017) Deep learning for lung cancer detection: Tackling the kaggle data science bowl 2017 challenge, arXiv:1705.09435. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1705.09435. Accessed 26 May 2017
Lakshmanaprabu S (2019) K, Sachi Nandan mohanty, Shankar K, Arunkumar N, Gustavo Ramirez, “Optimal Deep Learning Model for Classification of Lung Cancer on CT Images.” Future Gener Comput Syst 92:274–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.10.009
Li L, Liu Z, Huang H, Lin M, Luo D (2019) Evaluating the performance of a deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis (DL-CAD) system for detecting and characterizing lung nodules: Comparison with the performance of double reading by radiologists. Thorac Cancer 10(2):183–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.12931
Li Y, Zhang L, Chen H, Yang N (2019) Lung Nodule Detection With Deep Learning in 3D Thoracic MR Images. IEEE Access 7:37822–37832. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2905574
Liu Y, Hao P, Zhang P, Xu X, Wu J, Chen W (2018) Dense Convolutional Binary-Tree Networks for Lung Nodule Classification. IEEE Access 6:49080–49088. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2865544
Liu Z, Yao C, Yu H, Wu T (2019) Deep reinforcement learning with its application for lung cancer detection in medical Internet of Things. Internet Things Future Gener Comput Syst 97:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.02.068
Liu L, Dou Q, Chen H, Qin J, Heng P-A (2020) Multi-Task Deep Model With Margin Ranking Loss for Lung Nodule Analysis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(3):718–728. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2934577
Masood A et al (2020) Cloud-Based Automated Clinical Decision Support System for Detection and Diagnosis of Lung Cancer in Chest CT. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/JTEHM.2019.2955458. Art no. 4300113
Mastouri R, Khlifa N, Neji H, Hantous-Zannad S (2020) Deep learning-based CAD schemes for the detection and classification of lung nodules from CT images: A survey. J Xray Sci Technol 28(4):591–617. https://doi.org/10.3233/XST-200660
Mohamed Shakeel P, Burhanuddin MA, Desa MI (2019) Lung cancer detection from CT image using improved profuse clustering and deep learning instantaneously trained neural networks. Measurement 145:702–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.05.027
Monkam P, Qi S, Ma H, Gao W, Yao Y, Qian W (2019) Detection and Classification of Pulmonary Nodules Using Convolutional Neural Networks: A Survey. IEEE Access 7:78075–78091. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2920980
Nasser IM, Naser A (2019) Lung cancer detection using artificial neural network. https://philarchive.org/archive/NASLCD-5. Accessed Mar 2019
Ozdemir O, Russell RL, Berlin AA (2020) A 3D probabilistic deep learning system for detection and diagnosis of lung cancer using low-dose ct scans. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(5):1419–1429. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2947595
Pang S, Zhang Y, Ding M, Wang X, Xie X (2020) A Deep Model for Lung Cancer Type Identification by Densely Connected Convolutional Networks and Adaptive Boosting. IEEE Access 8:4799–4805. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2962862
Paszke A, Gross S, Chintala S, Chanan G, Yang E, De Vito Z, Lin Z, Desmaison A, Antiga L, Lerer A (2017) Automatic differentiation in pytorch, In NIPS 2017 Workshop Autodiff. https://openreview.net/forum?id=BJJsrmfCZ
Petersen K, Vakkalanka S, Kuzniarz L (2015) Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Inform Softw Technol 64:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2015.03.007
Rendon-Gonzalez E, Volodymyr I, Ponomaryov. “Automatic Lung nodule segmentation and classification in CT images based on SVM”. (2016) 9th International Kharkiv Symposium on Physics and Engineering of Microwaves. Millimeter Submillimeter Waves (MSMW) 2016:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSMW.2016.7537995
Sahu P, Yu D, Dasari M, Hou F, Qin H (2019) A Lightweight Multi-Section CNN for Lung Nodule Classification and Malignancy Estimation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23(3):960–968. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2018.2879834
Setio AA et al (2017) Validation, comparison, and combination of al- gorithms for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography images: The LUNA16 challenge. Med Image Anal 42:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.06.015
Shadroo S, Rahmani AM (2018) Systematic survey of big and data mining in internet of things. Comput Netw 139:19–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2018.04.001
Shakeel PM, Manogaran G (2020) Prostate cancer classification from prostate biomedical data using ant rough set algorithm with radial trained extreme learning neural network. Health Technol 10:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12553-018-0279-6
Shiraishi J, Katsuragawa S, Ikezoe J (2000) Development of a digital image database for chest radiographs with and without a lung nodule. Am J Roentgenol 174(1):71–74. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.174.1.1740071
Silva F et al (2021) EGFR Assessment in Lung Cancer CT Images: Analysis of Local and Holistic Regions of Interest Using Deep Unsupervised Transfer Learning. IEEE Access 9:58667–58676. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3070701
Skourt BA et al (2018) Lung CT Image Segmentation Using Deep Neural Networks. Proc Comput Sci 127:109–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.01.104
Sun W, Tseng T-LB, Qian W, Zhang J, Saltzstein EC, Zheng B et al (2015) Using multiscale texture and density features for near-term breast cancer risk analysis. Med Phys 42(6 Par1):2853–2862. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4919772
Teramoto A, Tsukamoto T, Kiriyama Y, Fujita H (2017) Automated Classification of Lung Cancer Types from Cytological Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Biomed Res Int 2017:4067832. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4067832
Wang W et al (2019) Nodule-Plus R-CNN and Deep Self-Paced Active Learning for 3D Instance Segmentation of Pulmonary Nodules. IEEE Access 7:128796–128805. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2939850
Wang J et al (2019) Pulmonary Nodule Detection in Volumetric Chest CT Scans Using CNNs-Based Nodule-Size-Adaptive Detection and Classification. IEEE Access 7:46033–46044. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2908195
Wang C et al (2019) Pulmonary Image Classification Based on Inception-v3 Transfer Learning Model. IEEE Access 7:146533–146541. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2946000
Xie Y et al (2019) Knowledge-based Collaborative Deep Learning for Benign-Malignant Lung Nodule Classification on Chest CT. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(4):991–1004. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2876510
Yu H, Zhou Z, Wang Q (2020) Deep Learning Assisted Predict of Lung Cancer on Computed Tomography Images Using the Adaptive Hierarchical Heuristic Mathematical Model. IEEE Access 8:86400–86410. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2992645
Zhang Q, Kong X (2020) Design of Automatic Lung Nodule Detection System Based on Multi-Scene Deep Learning Framework. IEEE Access 8:90380–90389. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2993872
Zhang C, Sun X, Dang K, Li K, Guo XW, Chang J, Yu ZQ, Huang FY, Wu YS, Liang Z, Liu ZY, Zhang XG, Gao XL, Huang SH, Qin J, Feng WN, Zhou T, Zhang YB, Fang WJ, Zhao MF, Yang XN, Zhou Q, Wu YL, Zhong WZ (2019) Toward an Expert Level of Lung Cancer Detection and Classification Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Oncologist 24(9):1159–1165. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0908
Zheng J, Yang D, Zhu Y, Gu W, Zheng B, Bai C, Zhao L, Shi H, Hu J, Lu S, Shi W, Wang N (2020) Pulmonary nodule risk classification in adenocarcinoma from CT images using deep CNN with scale transfer module. IET Image Process 14:1481–1489. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-ipr.2019.0248
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank you Dr. Armin Chitizade for reviewing the manuscript and Dr. Ghasem Naghib for general guidance through this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Hereby I certify that the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, S.H., Monsefi, R. & Shadroo, S. Deep learning applications for lung cancer diagnosis: A systematic review. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 14305–14335 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16046-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16046-w