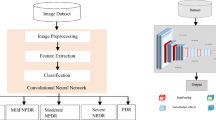
Abstract
This paper proposes a new hybrid method of classification of fundus images provided by the Asia–Pacific Tele-Ophthalmology Society via combining the discrete moment quaternion approach, the artificial intelligence approach, and machine learning in order to automatically distinguish the stage of diabetic retinopathy using reduced databases divided into five classes. The proposed method is based on two main phases: the preprocessing phase, in which using the new radial invariant moments of Hahn in a quaternion optimized by the ant colony algorithm, in order to calculate the original n × n image moments. The second phase is devoted to introducing the calculated moments into the proposed convolutional neural network model. The present work will contribute to creating new neural network architectures that take advantage of Hahn's new 2D radial moment descriptive capability in quaternions. The K-fold cross-validation method is used to measure the proposed model's performance. Finally, graphical measures such as receiver operating characteristic and precision-rapple curves plus a confusion matrix are presented. Furthermore, numerical measures are adopted for f1-score, loss and precision. In 1795 images, the AUC yielded 94.58%, 97.02%, 94.87%, 97.83%, and 96.54% for the five classes of healthy, mild, moderate, severe, and proliferative respectively. These results prove that the proposed method can be used to detect and classify diabetic retinopathy at an early stage.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Antary MT and Arafa Y (2021)“Multi-scale Attention Network for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification,” IEEE Access 9:. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3070685.
Abbas Q, Fondon I, Sarmiento A, Jiménez S, Alemany P (2017) Automatic recognition of severity level for diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy using deep visual features. Med Biol Eng Comput 55(11):1959–1974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1638-6
Abdulhussain SH, Ramli AR, Al-Haddad SAR, Mahmmod BM, Jassim WA (2017) On Computational Aspects of Tchebichef Polynomials for Higher Polynomial Order. IEEE Access 5:2470–2478. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2669218
Adem K, Kiliçarslan S, Cömert O (2019) Classification and diagnosis of cervical cancer with softmax classification with stacked autoencoder. Expert Syst Appl 115:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.08.050
Ahmed KT, Jaffar S, Hussain MG, Fareed S, Mehmood A, Choi GS (2021) Maximum Response Deep Learning Using Markov, Retinal Primitive Patch Binding with GoogLeNet VGG-19 for Large Image Retrieval. IEEE Access 9:41934–41957. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3063545
Almobarak AO et al (2020) The prevalence and risk factors for systemic hypertension among Sudanese patients with diabetes mellitus: A survey in diabetes healthcare facility. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev 14(6):1607–1611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.08.010
Amakdouf H, Zouhri A, EL Mallahi M, and Qjidaa H, (2020) “Color image analysis of quaternion discrete radial Krawtchouk moments,” Multimed. Tools Appl.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09120-0
Amakdouf H, Zouhri A, El Mallahi M, Tahiri A, Chenouni D, Qjidaa H (2021) Artificial intelligent classification of biomedical color image using quaternion discrete radial Tchebichef moments. Multimed Tools Appl 80(2):3173–3192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09781-x
Bacanin N, Stoean R, Zivkovic M, Petrovic A, Rashid TA and Bezdan T, (2021)“Performance of a novel chaotic firefly algorithm with enhanced exploration for tackling global optimization problems: Application for dropout regularization,” Mathematics 9(21):. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9212705.
Batta M (2020) Machine learning algorithms a review. Int J Sci Res (IJ) 9(1):381. https://doi.org/10.21275/ART20203995
Bencherqui A, Daoui A, Karmouni H and Qjidaa H (2022) Optimal reconstruction and compression of signals and images by Hahn moments and artificial bee Colony (ABC ) algorithm, Multimedia Tools and Applications
Beni G, Wang J (1993) Swarm intelligence in cellular robotic systems. In: Robots and biological systems: towards new bionics?. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, p 703–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-58069-7_38
Bewick V, Cheek L, Ball J (2004) Statistics review 13: Receiver operating characteristics curves. Crit Care 8(6):508–512. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc3000
Chen Z, Ho P-H (2019) Global-connected network with generalized ReLU activation. Pattern Recogn 96:106961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.07.006
Chen Y et al (2019) Single-pixel compressive imaging based on the transformation of discrete orthogonal Krawtchouk moments. Opt Express 27(21):29838. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.27.029838
Chen W, Yang B, Li J, Wang J (2020) An approach to detecting diabetic retinopathy based on integrated shallow convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 8:178552–178562. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3027794
Choi KS, Shin JS, Lee JJ, Kim YS, Kim SB, Kim CW (2005) In vitro trans-differentiation of rat mesenchymal cells into insulin-producing cells by rat pancreatic extract. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330(4):1299–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.111
Chong CW, Raveendran P, Mukundan R (2003) Translation invariants of Zernike moments. Pattern Recognit 36(8):1765–1773. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(02)00353-9
Daoui A, Yamni M, El Ogri O, Karmouni H, Sayyouri M, Qjidaa H (2020) “New Algorithm for Large-Sized 2D and 3D Image Reconstruction using Higher-Order Hahn Moments.” Circuits Syst Signal Process 39(9):4552–4577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01384-z
Deeba K, Amutha B (2020) ResNet-deep neural network architecture for leaf disease classification. Microprocess Microsyst :103364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2020.103364
Dorigo M, Maniezzo V, Colorni A (1996) Ant system: Optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 261:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1109/3477.484436
Dubey V (2014) “Quaternion Fourier Transform for Colour Images. Ijcsit 5(3):4411–4416 https://www.ijcsit.com
El Mallahi M, Zouhri A, Qjidaa H (2018) Radial Meixner Moment Invariants for 2D and 3D Image Recognition. Pattern Recognit Image Anal 28(2):207–216. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054661818020128
Gavrilov AD, Jordache A, Vasdani M, Deng J (2018) Preventing model overfitting and underfitting in convolutional neural networks. Int J Softw Sci Comput Intell (IJSSCI) 10(4):19–28. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijssci.2018100102
Gayathri S, Gopi VP, Palanisamy P (2020) A lightweight CNN for Diabetic Retinopathy classification from fundus images. Biomed Signal Process Control 62(August):102115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102115
Giancardo L et al (2012) Exudate-based diabetic macular edema detection in fundus images using publicly available datasets. Med Image Anal 16(1):216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2011.07.004
Gonzalez TF (2007) “Handbook of approximation algorithms and metaheuristics,” pp. 1–1432. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420010749.
Gupta S, Thakur S and Gupta A (2022) Optimized hybrid machine learning approach for smartphone based diabetic retinopathy detection
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) 2016 “Deep residual learning for image recognition”, Proc IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis. Pattern Recognit 2016:770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Idan ZN, Abdulhussain SH, Al-Haddad SAR (2020) A New Separable Moments Based on Tchebichef-Krawtchouk Polynomials. IEEE Access 8:41013–41025. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2977305
Jahid T, Karmouni H, Hmimid A, Sayyouri M, Qjidaa H (2019) Fast computation of Charlier moments and its inverses using Clenshaw’s recurrence formula for image analysis. Multimed Tools Appl 78:12183–12201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6757-z
Kandhasamy JP, Balamurali S, Kadry S, Ramasamy LK (2020) Diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy using multi level set segmentation algorithm with feature extraction using SVM with selective features. Multimed Tools Appl 79(15–16):10581–10596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7485-8
Khoshgoftaar TM, Allen EB (2001) Controlling overfitting in classification-tree models of software quality. Empir Softw Eng 6(1):59–79. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009803004576
Kusrini K et al (2020) Data augmentation for automated pest classification in Mango farms. Comput Electron Agric 179:105842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105842
Lal S et al (2021) Adversarial attack and defence through adversarial training and feature fusion for diabetic retinopathy recognition. Sensors 21(11):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113922
Lin G, Shen W (2018) Research on convolutional neural network based on improved Relu piecewise activation function. Procedia Comput Sci 131:977–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.04.239
Malakar S, Ghosh M, Bhowmik S, Sarkar R, Nasipuri M (2020) A GA based hierarchical feature selection approach for handwritten word recognition. Neural Comput Appl 32(7):2533–2552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3937-8
Maqsood S, Damaševičius R, and Maskeliūnas R (2021) “Hemorrhage detection based on 3d cnn deep learning framework and feature fusion for evaluating retinal abnormality in diabetic patients,” Sensors 21(11):. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113865.
Markoulidakis I, Rallis I, Georgoulas I, Kopsiaftis G, Doulamis A, Doulamis N (2021) Multiclass confusion matrix reduction method and its application on net promoter score classification problem. Technologies 9(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9040081
Ohira M, Ito D, Shimizu T, Shibata M, Ohde H, Suzuki N (2009) Retinopathy: An overlooked adverse effect of interferon-beta treatment of multiple sclerosis. Keio J Med 58(1):54–56. https://doi.org/10.2302/kjm.58.54
Oke SA (2008) A literature review on artificial intelligence. Int J Inf Manag Sci 19(4):535–570
Orlando JI, Prokofyeva E, del Fresno M, Blaschko MB (2018) An ensemble deep learning based approach for red lesion detection in fundus images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 153:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.10.017
Park S, Baek Lee S, Park J (2020) Data augmentation method for improving the accuracy of human pose estimation with cropped images. Pattern Recognit Lett 136:244–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2020.06.015
Pei SC, Cheng CM (1997) Novel block truncation coding of image sequences for limitedcolor display. Lect Notes Comput Sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 1311:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-63508-4_119
Perl YS et al (2020) Data augmentation based on dynamical systems for the classification of brain states. Chaos Solitons Fractals 139:110069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110069
Pires R, Jelinek HF, Wainer J, Valle E and Rocha A (2014) “Advancing bag-of-visual-words representations for lesion classification in retinal images,” PLoS One, 9(6):. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096814.
Poh S, Mohamed Abdul RBB, Lamoureux EL, Wong TY, Sabanayagam C (2016) Metabolic syndrome and eye diseases. Diab Res Clin Pract 113:86–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2016.01.016
Rahman MM, Davis DN (2013) Addressing the Class Imbalance Problem in Medical Datasets. Int J Mach Learn Comput 2013:224–228. https://doi.org/10.7763/ijmlc.2013.v3.307
Ramasamy LK, Padinjappurathu SG, Kadry S, Damaševičius R (2021) Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy Using a Fusion of Textural and Ridgelet Features of Retinal Images and Sequential Minimal Optimization Classifier. PeerJ Comput Sci 7:1–21. https://doi.org/10.7717/PEERJ-CS.456
Reddy SSK (2020) Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus in Older Adults. Clin Geriatr Med 36(3):379–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2020.04.011
Saman G et al (2020) Automatic detection and severity classification of diabetic retinopathy. Multimed Tools Appl 79(43–44):31803–31817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09118-8
Saxena G, Verma DK, Paraye A, Rajan A, Rawat A (2020) Improved and robust deep learning agent for preliminary detection of diabetic retinopathy using public datasets. Intell-Based Med 3:100022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmed.2020.100022
Sayyouri M, Hmimid A, Qjidaa H (2013) Improving the performance of image classification by Hahn moment invariants. J Opt Soc Am A 30(11):2381. https://doi.org/10.1364/josaa.30.002381
Shaban K et al (2020) A convolutional neural network for the screening and staging of diabetic retinopathy. PLoS One 15(6 June):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0233514
Shiferaw WS et al (2020) Glycated hemoglobin A1C level and the risk of diabetic retinopathy in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev 14(6):1941–1949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.10.003
Taheri M, Lim N, and Lederer J (2016) “Balancing Statistical and Computational Precision and Applications to Penalized Linear Regression with Group Sparsity,” pp. 233–240, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1609.07195.
Tahiri MA, Karmouni H, Sayyouri M and Qjidaa H (2022)“2D and 3D image localization, compression and reconstruction using new hybrid moments,” Multidimens Syst Signal Processhttps://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-021-00810-y
Tahiri MA, Karmouni H, Sayyouri M and Qjidaa H (2020) “Stable Computation of Hahn Polynomials for Higher Polynomial Order,” In 2020 International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Computer Vision (ISCV), pp. 0–6 https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCV49265.2020.9204118
Wan S, Liang Y, Zhang Y (2018) Deep convolutional neural networks for diabetic retinopathy detection by image classification. Comput Electr Eng 72:274–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2018.07.042
WanG J, Perez L et al (2017) The effectiveness of data augmentation in image classification using deep learning. Convolutional Neural Networks Vis. Recognit 11(2017):1–8. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1712.04621
Wang Z, Yin Y, Shi J, Fang W, Li H, Wang X (2017) Zoom-in-net: Deep mining lesions for diabetic retinopathy detection. Lect Notes Comput Sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 10435(LNCS):267–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66179-7_31
Wen X (2020) Modeling and performance evaluation of wind turbine based on ant colony optimization-extreme learning machine. Appl Soft Comput J 94:106476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106476
Wu B, Zhu W, Shi F, Zhu S, Chen X (2017) Automatic detection of microaneurysms in retinal fundus images. Comput Med Imaging Graph 55:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2016.08.001
Yamni M et al (2020) Fractional Charlier moments for image reconstruction and image watermarking. Signal Processing 171:107509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107509
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tahiri, M.A., Amakdouf, H., El mallahi, M. et al. Optimized quaternion radial Hahn Moments application to deep learning for the classification of diabetic retinopathy. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 46217–46240 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15582-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15582-9