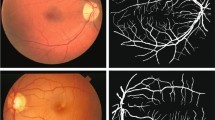
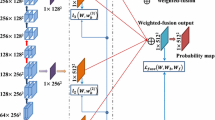
Abstract
The automatic segmentation of blood vessels in fundus images can help analyze the condition of retinal vasculature, which is crucial for identifying various systemic diseases like hypertension, diabetes, etc. Despite the success of Deep Learning-based models in this segmentation task, most of them are heavily parametrized and thus have limited use in practical applications. This paper proposes IterMiUnet, a new lightweight convolution-based segmentation model that requires significantly fewer parameters and yet delivers performance similar to existing models. The model makes use of the excellent segmentation capabilities of Iternet (Li et al (2020)) architecture but overcomes its heavily parametrized nature by incorporating the encoder-decoder structure of MiUnet (Hu et al. (2019) IEEE Access 7:174167-174177) model within it. Thus, the new model reduces parameters without any compromise with the network's depth, which is necessary to learn abstract hierarchical concepts in deep models. This lightweight segmentation model speeds up training and inference time and is potentially helpful in the medical domain where data is scarce and, therefore, heavily parametrized models tend to overfit. The proposed model was evaluated on three publicly available datasets: DRIVE, STARE, and CHASE-DB1. Further cross-training and inter-rater variability evaluations have also been performed. The proposed model has a lot of potential to be utilized as a tool for the early diagnosis of many diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All datasets are publicly available DRIVE- https://drive.grand-challenge.org/ STARE-https://cecas.clemson.edu/~ahoover/stare/probing/index.html CHASE DB1- https://blogs.kingston.ac.uk/retinal/chasedb1/
Code availability
We are intending to build a larger system. Once all components get published, we will share the code.
References
Abadi M, Barham P, Chen J, et al (2016) TensorFlow: A system for large-scale machine learning. In: 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 16). pp 265–283
Abràmoff MD, Garvin MK, Sonka M (2010) Retinal Imaging and Image Analysis. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 3:169–208. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2010.2084567
Alom MZ, Hasan M, Yakopcic C, et al (2018) Recurrent Residual Convolutional Neural Network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv:180206955 [cs]
Azzopardi G, Strisciuglio N, Vento M, Petkov N (2015) Trainable COSFIRE filters for vessel delineation with application to retinal images. Med Image Anal 19:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2014.08.002
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R (2017) SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39:2481–2495. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
Chanwimaluang T, Fan G (2003) An efficient blood vessel detection algorithm for retinal images using local entropy thresholding. In: 2003 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). p V–V
Chatziralli IP, Kanonidou ED, Keryttopoulos P et al (2012) The Value of Fundoscopy in General Practice. Open Ophthalmol J 6:4–5. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874364101206010004
Dai J, He K, Sun J (2015) BoxSup: Exploiting Bounding Boxes to Supervise Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). pp 1635–1643
Fan Z, Lu J, Wei C et al (2019) A Hierarchical Image Matting Model for Blood Vessel Segmentation in Fundus Images. IEEE Trans Image Process 28:2367–2377. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2885495
Fraz MM, Barman SA, Remagnino P et al (2012) An approach to localize the retinal blood vessels using bit planes and centerline detection. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 108:600–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2011.08.009
Fraz MM, Remagnino P, Hoppe A et al (2012) An Ensemble Classification-Based Approach Applied to Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59:2538–2548. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2012.2205687
Hoover AD, Kouznetsova V, Goldbaum M (2000) Locating blood vessels in retinal images by piecewise threshold probing of a matched filter response. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.845178
Hu J, Wang H, Gao S et al (2019) S-UNet: A Bridge-Style U-Net Framework With a Saliency Mechanism for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. IEEE Access 7:174167–174177. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2940476
Jin Q, Meng Z, Pham TD et al (2019) DUNet: A deformable network for retinal vessel segmentation. Knowl-Based Syst 178:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.04.025
Kingma DP, Ba J (2017) Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv:14126980 [cs]
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates, Inc.
Lam BSY, Gao Y, Liew AW-C (2010) General Retinal Vessel Segmentation Using Regularization-Based Multiconcavity Modeling. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29:1369–1381. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2010.2043259
LeCun Y, Boser B, Denker J, et al (1989) Handwritten Digit Recognition with a Back-Propagation Network. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Morgan-Kaufmann
Li L, Verma M, Nakashima Y, et al (2020) IterNet: Retinal Image Segmentation Utilizing Structural Redundancy in Vessel Networks. In: 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). pp 3645–3654
Li Q, Feng B, Xie L et al (2016) A Cross-Modality Learning Approach for Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2015.2457891
Liskowski P, Krawiec K (2016) Segmenting Retinal Blood Vessels With Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35:2369–2380. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2546227
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp 3431–3440
Marín D, Aquino A, Gegundez-Arias ME, Bravo JM (2011) A New Supervised Method for Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Images by Using Gray-Level and Moment Invariants-Based Features. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 30:146–158. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2010.2064333
Martinez-Perez ME, Hughes AD, Thom SA et al (2007) Segmentation of blood vessels from red-free and fluorescein retinal images. Med Image Anal 11:47–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2006.11.004
Mou L, Zhao Y, Fu H, et al (2021) CS2-Net: Deep learning segmentation of curvilinear structures in medical imaging. Medical Image Analysis 67:101874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101874
Nair V, Hinton GE (2010) Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Omnipress, Madison, WI, USA, pp 807–814
Oliveira A, Pereira S, Silva CA (2018) Retinal vessel segmentation based on Fully Convolutional Neural Networks. Expert Syst Appl 112:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.06.034
Owen CG, Rudnicka AR, Mullen R et al (2009) Measuring Retinal Vessel Tortuosity in 10-Year-Old Children: Validation of the Computer-Assisted Image Analysis of the Retina (CAIAR) Program. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:2004–2010. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.08-3018
Patton N, Aslam TM, MacGillivray T et al (2006) Retinal image analysis: Concepts, applications and potential. Prog Retin Eye Res 25:99–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2005.07.001
Pizer SM, Amburn EP, Austin JD et al (1987) Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing 39:355–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-189X(87)80186-X
Ricci E, Perfetti R (2007) Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation Using Line Operators and Support Vector Classification. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26:1357–1365. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2007.898551
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In: Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells WM, Frangi AF (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 234–241
Roychowdhury S, Koozekanani DD, Parhi KK (2015) Blood Vessel Segmentation of Fundus Images by Major Vessel Extraction and Subimage Classification. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 19:1118–1128. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2014.2335617
Roychowdhury S, Koozekanani DD, Parhi KK (2015) Iterative Vessel Segmentation of Fundus Images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 62:1738–1749. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2015.2403295
Sasaki Y (2007) The truth of the F-measure. Teach Tutor Mater
Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A et al (2014) Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J Mach Learn Res 15:1929–1958
Staal J, Abramoff MD, Niemeijer M et al (2004) Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23:501–509. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2004.825627
Tian F, Li Y, Wang J, Chen W (2021) Blood Vessel Segmentation of Fundus Retinal Images Based on Improved Frangi and Mathematical Morphology. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine 2021:e4761517. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4761517
Uysal E, Güraksin GE (2021) Computer-aided retinal vessel segmentation in retinal images: convolutional neural networks. Multimed Tools Appl 80:3505–3528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09372-w
Yan Z, Yang X, Cheng K-T (2018) Joint Segment-Level and Pixel-Wise Losses for Deep Learning Based Retinal Vessel Segmentation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 65:1912–1923. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2018.2828137
Yan Z, Yang X, Cheng K-T (2019) A Three-Stage Deep Learning Model for Accurate Retinal Vessel Segmentation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23:1427–1436. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2018.2872813
Zhang Y, He M, Chen Z, et al (2022) Bridge-Net: Context-involved U-net with patch-based loss weight mapping for retinal blood vessel segmentation. Expert Systems with Applications 195:116526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116526
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
No conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Agrawal, R.K. & Joseph, L. IterMiUnet: A lightweight architecture for automatic blood vessel segmentation. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 43207–43231 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15433-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15433-7