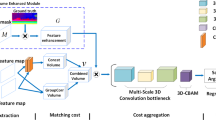
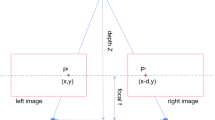
Abstract
Convolutional neural network (CNN) based stereo matching methods using cost volume techniques have gained prominence in stereo matching. State-of-the-art cost volume based methods use two weight-sharing feature extractors to respectively extract left and right unary features and then use them to construct cost volume(s). The quality of those unary features is crucial for the subsequent stereo matching. We propose a Supervised Biadjacency-based (SuperB) module to improve their quality by employing supervised biadjacency matrices to embed stereo information into both unary features. Specifically, disparity supervision is imposed on the biadjacency matrices by transforming them into disparity estimations. The SuperB Module can therefore adaptively enhance matched features and suppress unmatched features. Being aware of the stereo correspondence, the resultant stereo-aware features are more discriminative for subsequent cost aggregation and disparity estimation. Experiments show the SuperB Module can be plugged into cost volume based stereo matching models and lower the disparity estimation error. In addition, a scale-adaptive Voxel-wise Selective Fusion (VSF) module is proposed to adaptively aggregate the multi-scale matching costs. The competitive and efficient experimental results on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the resultant Supervised Biadjacency Stereo matching networks (SuperBStereo).












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used during the current study are available in SceneFlow (https://lmb.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/resources/datasets/SceneFlowDatasets.en.html) and KITTI (https://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_object.php?obj_benchmark=3d), other generated data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y (2015) Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In: International conference on learning representations, San Diego
Chabra R, Straub J, Sweeney C, Newcombe R, Fuchs H (2019) StereoDRNet: dilated residual StereoNet. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Long Beach, pp 11786–11795. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.01206
Chang J -R, Chen Y -S (2018) Pyramid stereo matching network. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Salt Lake City, pp 5410–5418. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00567
Chen L -C, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H (2017) Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv:1706.05587
Cheng X, Zhong Y, Harandi M T, Dai Y, Chang X, Li H, Drummond T, Ge Z (2020) Hierarchical neural architecture search for deep stereo matching. In: Conference on neural information processing systems, vol 33. Online. Curran Associates, Inc., pp 22158–22169
Diederik K, Jimmy B (2015) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: International conference on learning representations, San Diego
Dosovitskiy A, Fischer P, Ilg E, Hausser P, Hazirbas C, Golkov V, van der Smagt P, Cremers D, Brox T (2015) Flownet: learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In: IEEE International conference on computer vision. IEEE, Santiago, pp 2758–2766. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.316
Duggal S, Wang S, Ma W -C, Hu R, Urtasun R (2019) Deeppruner: learning efficient stereo matching via differentiable PatchMatch. In: IEEE International conference on computer vision. IEEE, Seoul, pp 4384–4393. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00448
Geiger A, Lenz P, Urtasun R (2012) Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Providence, pp 3354–3361. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6248074
Girshick R (2015) Fast r-CNN. In: IEEE International conference on computer vision. IEEE, Santiago, pp 1440–1448. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169
Guo X, Yang K, Yang W, Wang X, Li H (2019) Group-wise correlation stereo network. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Long Beach, pp 3268–3277. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00339
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Las Vegas, pp 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
He Y, Yan R, Fragkiadaki K, Yu S -I (2020) Epipolar transformers. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Seattle, pp 7776–7785. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00780
Hirschmuller H (2008) Stereo processing by semiglobal matching and mutual information. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30 (2):328–341. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1166
Ilg E, Mayer N, Saikia T, Keuper M, Dosovitskiy A, Brox T (2017) Flownet 2.0: evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 1647–1655. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.179
Ji C, Liu G, Zhao D (2022) Monocular 3D object detection via estimation of paired keypoints for autonomous driving. Multimed Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11801-3
Kendall A, Martirosyan H, Dasgupta S, Henry P, Kennedy R, Bachrach A, Bry A (2017) End-to-end learning of geometry and context for deep stereo regression. In: IEEE International conference on computer vision. IEEE, Venice, pp 66–75. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.17
Khamis S, Fanello S, Rhemann C, Kowdle A, Valentin J, Izadi S (2018) Stereonet: guided hierarchical refinement for real-time edge-aware depth prediction. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer International Publishing, Munich, pp 596–613. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_35
Kim T, Ryu K, Song K, Yoon K -J (2020) Loop-net: joint unsupervised disparity and optical flow estimation of stereo videos with spatiotemporal loop consistency. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 5(4):5597–5604. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2020.3009065
Liang Z, Feng Y, Guo Y, Liu H, Chen W, Qiao L, Zhou L, Zhang J (2018) Learning for disparity estimation through feature constancy. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Salt Lake City, pp 2811–2820. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00297
Liu S, Qi L, Qin H, Shi J, Jia J (2018) Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Salt Lake City, pp 759–8768. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00913
Liang W, Xu P, Guo L, Bai H, Zhou Y, Chen F (2021) A survey of 3D object detection. Multimed Tools Appl 80(19):29617–29641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11137-y
Lin T -Y, Dollár P, Girshick R B, He K, Hariharan B, Belongie S J (2017) Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 936–944. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.106
Liu Y, Ren J, Zhang J, Liu J, Lin M (2020) Visually imbalanced stereo matching. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Seattle, pp 2026–2035. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00210
Mayer N, Ilg E, Hausser P, Fischer P, Cremers D, Dosovitskiy A, Brox T (2016) A large dataset to train convolutional networks for disparity, optical flow, and scene flow estimation. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Las Vegas, pp 4040–4048. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.438
Menze M, Heipke C, Geiger A (2015) Joint 3D estimation of vehicles and scene flow. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences II-3/W5:427–434. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsannals-II-3-W5-427-2015
Menze M, Heipke C, Geiger A (2018) Object scene flow. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 140:60–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.09.013
Naga Srinivasu P, Balas V E (2021) Self-learning network-based segmentation for real-time brain M.R. images through HARIS. PeerJ Comput Sci 7:654. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.654
Newell A, Yang K, Deng J (2016) Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer International Publishing, Amsterdam, pp 483–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_29
Nie G -Y, Cheng M -M, Liu Y, Liang Z, Fan D -P, Liu Y, Wang Y (2019) Multi-level context ultra-aggregation for stereo matching. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Long Beach, pp 3278–3286. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00340
Pang Y, Nie J, Xie J, Han J, Li X (2020) Bidnet: binocular image dehazing without explicit disparity estimation. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Seattle, pp 5930–5939. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00597
Pang Y, Cao J, Li Y, Xie J, Sun H, Gong J (2021) TJU-DHD: a diverse high-resolution dataset for object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:207–219. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3034487
Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G, Killeen T, Lin Z, Gimelshein N, Antiga L, Desmaison A, Kopf A, Yang E, DeVito Z, Raison M, Tejani A, Chilamkurthy S, Steiner B, Fang L, Bai J, Chintala S (2019) Pytorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Wallach H, Larochelle H, Beygelzimer A, de-Buc F, Fox E, Garnett R (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems 32. Curran Associates, Inc., Vancouver, pp 8024–8035
Rahman M M, Islam M S, Sassi R, Aktaruzzaman Md (2019) Convolutional neural networks performance comparison for handwritten Bengali numerals recognition. SN Appl Sci 1(12):1660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1682-y
Rhemann C, Hosni A, Bleyer M, Rother C, Gelautz M (2011) Fast cost-volume filtering for visual correspondence and beyond. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Colorado Springs, pp 3017–3024. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995372
Su K, Yan W, Wei X, Gu M (2021) Stereo voVNet-CNN for 3D object detection multimedia tools and applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11506-7
Sun H, Cao J, Pang Y (2023) Semantic-aware self-supervised depth estimation for stereo 3D detection. Pattern Recogn Lett 167:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2023.02.006
Tan M, Pang R, Le Q V (2020) Efficientdet: scalable and efficient object detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Seattle, pp 10778–10787. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01079
Tankovich V, Hane C, Zhang Y, Kowdle A, Fanello S, Bouaziz S (2021) HITNEt: hierarchical iterative tile refinement network for real-time stereo matching. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Nashville, pp 14357–14367. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01413
Tonioni A, Tosi F, Poggi M, Mattoccia S, Stefano L D (2019) Real-time self-adaptive deep stereo. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Long Beach, pp 195–204. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00028
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser L, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Conference on neural information processing systems, vol 30. Curran Associates, Inc., Long Beach, pp 6000–6010
Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, He K (2018) Non-local neural networks. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Salt Lake City, pp 7794–7803. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00813
Wang L, Wang Y, Liang Z, Lin Z, Yang J, An W, Guo Y (2019) Learning parallax attention for stereo image super-resolution. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Long Beach, pp 12242–12251. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.01253
Wang X, Zhang S, Yu Z, Feng L, Zhang W (2020) Scale-equalizing pyramid convolution for object detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Seattle, pp 13356–13365. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01337
Wu Z, Wu X, Zhang X, Wang S, Ju L (2019) Semantic stereo matching with pyramid cost volumes. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision. IEEE, Seoul, pp 7483–7492. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00758
Wu J, Cong R, Fang L, Guo C, Zhang B, Ghamisi P (2023) Unpaired remote sensing image super-resolution with content-preserving weak supervision neural network. Sci China Inf Sci 66(1):119105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-021-3575-1
Xu H, Zhang J (2020) AANEt: adaptive aggregation network for efficient stereo matching. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Seattle, pp 1959–1968. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00203
Yang M, Wu F, Li W (2020) Waveletstereo: learning wavelet coefficients of disparity map in stereo matching. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Seattle, pp 12885–12894. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01290
Yi H, Wei Z, Ding M, Zhang R, Chen Y, Wang G, Tai Y -W (2020) Pyramid multi-view stereo net with self-adaptive view aggregation. In: European conference on computer vision. Online. Springer International Publishing, pp 766–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58545-7_44
Yin Z, Darrell T, Yu F (2019) Hierarchical discrete distribution decomposition for match density estimation. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Long Beach, pp 6037–6046. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00620
žbontar J, LeCun Y (2016) Stereo matching by training a convolutional neural network to compare image patches. J Mach Learn Res 17(1):2287–2318
Zhang F, Prisacariu V, Yang R, Torr P H S (2019) GA-Net: guided aggregation net for end-to-end stereo matching. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Long Beach, pp 185–194. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00027
Zhang F, Qi X, Yang R, Prisacariu V, Wah B, Torr P (2020) Domain-invariant stereo matching networks. In: European conference on computer vision, vol 12347. Online. Springer International Publishing, pp 420–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_25
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China [2022ZD0160400], the National Key R&D Program of China [2018AAA0102800], and Tianjin Science and Technology Program [19ZXZNGX00050].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Han, J., Pang, Y. et al. Supervised biadjacency networks for stereo matching. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 10247–10272 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15362-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15362-5