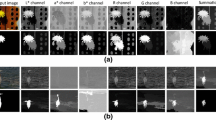
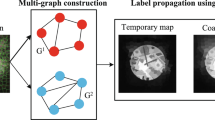
Abstract
Salient object detection based on the diffusion process on the graph has achieved considerable performance. It mainly depends on the affinity matrix construction considering the local structure. This paper aims to depict the local and global structures from image features, intensifying the graph-based diffusion model by simultaneously integrating the sparse graph matrix and affinity graph matrix. The contribution work computes the affinity graph matrix and delivers an affinity matrix by incorporating the sparse representation and diffusion process. It estimates a sparse graph matrix by integrating sparse representation and laplacian smoothness. To this end, a two-stage graph-based diffusion model has been constructed by embedding the manifold smoothness and manifold reconstruction. The first stage follows the boundary-prior to generate a coarse saliency map. After, the second stage combines the saliency map and Harris convex hull to obtain the foreground seeds. Extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets have demonstrated the superiority of the proposed method compared to other state-of-the-art methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achantay R, Hemamiz S, Estraday F, Süsstrunky S (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: 2009 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, CVPR workshops 2009, pp 1597–1604. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2009.5206596
Alpert S, Galun M, Brandt A, Basri R (2012) Image segmentation by probabilistic bottom-up aggregation and cue integration. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(2):315–327. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2011.130
Aytekin Ç, Iosifidis A, Kiranyaz S, Gabbouj M (2017) Learning graph affinities for spectral graph-based salient object detection. Pattern Recognit 64:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.11.005. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031320316303570
Cheng M-M, Zhang G-X, Mitra N, Huang X, Hu S-M (2011) Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995344
Dornaika F, Weng L (2019) Sparse graphs with smoothness constraints: application to dimensionality reduction and semi-supervised classification. Pattern Recognit 95:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.015. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031320319302456
Du H, Liu Z, Wang J, Mei L, He Y (2014) Video retargeting based on spatiotemporal saliency model. Lecture Notes Electr Engin 309:397–402
Duan L, Ke C, Wu C, Zhen Y, Miao J (2012) A natural image compression approach based on independent component analysis and visual saliency detection. J Computat Theoretical Nanosci 6(1):385–388
Fu K, Gu I, Gong C, Yang J (2015) Robust manifold-preserving diffusion-based saliency detection by adaptive weight construction. Neurocomputing 175:336–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.066
Gopalakrishnan V, Hu Y, Rajan D (2010) Random walks on graphs for salient object detection in images. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(12):3232–3242. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2053940
Hadizadeh H, Bajic IV (2014) Saliency-aware video compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(1):19–33
Han S, Vasconcelos N (2010) Biologically plausible saliency mechanisms improve feedforward object recognition. Vis Res 50(22):2295–2307
Hou X, Zhang L (2007) Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach. In: 2007 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–8
Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E (1998) A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(11):1254–1259
Jiang H, Wang J, Yuan Z, Wu Y, Zheng N, Li S (2013) Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2083–2090
Jiang B, Zhang L, Lu H, Yang C, Yang M-H (2013) Saliency detection via absorbing markov chain. In: The IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 1665–1672
Kim J, Han D, Tai Y-W, Kim J (2014) Salient region detection via high-dimensional color transform. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Lee CY, Leou JJ, Hsiao HH (2012) Saliency-directed color image segmentation using modified particle swarm optimization. Signal Process 92(1):1–18
Li Y, Hou X, Koch C, Rehg JM, Yuille AL (2014) The secrets of salient object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 280–287
Li Y, Jia W, Shen C, Van Den Hengel A (2014) Characterness: an indicator of text in the wild. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(4):1666–1677. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2014.2302896
Li X, Li Y, Shen C, Dick A, Van Den Hengel A (2013) Contextual hypergraph modeling for salient object detection. In: The IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 3328–3335
Li H, Lu H, Lin Z, Shen X, Price B (2015) Inner and inter label propagation: salient object detection in the wild. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(10):3176–3186
Li G, Yu Y (2016) Visual saliency detection based on multiscale deep cnn features. IEEE Trans Image Process 25:5012–5024. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2602079
Li C, Yuan Y, Cai W, Xia Y, Dagan Feng D (2015) Robust saliency detection via regularized random walks ranking. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2710–2717
Li X, Zhao L, Wei L, Yang M-H, Wu F, Zhuang Y, Ling H, Wang J (2015) Deepsaliency: multi-task deep neural network model for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process, vol 25. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2579306
Liu N, Han J (2016) Dhsnet: deep hierarchical saliency network for salient object detection. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recog:678–686
Liu Y, Han J, Zhang Q, Wang L (2019) Salient object detection via two-stage graphs. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(4):1023–1037
Liu T, Sun J, Zheng N-N, Tang X, Shum H-Y (2007) Learning to detect a salient object. In: Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2007.383047
Lu S, Mahadevan V, Vasconcelos N (2014) Learning optimal seeds for diffusion-based salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2790–2797
Margolin R, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A (2014) How to evaluate foreground maps?. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 248–255
Moradi M, Bayat F (2021) A salient object segmentation framework using diffusion-based affinity learning. Expert Syst Appl 168:114428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114428. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417420310927
Movahedi V, Elder JH (2010) Design and perceptual validation of performance measures for salient object segmentation. In: 2010 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition - workshops
Otsu N (1979) Threshold selection method from gray-level histograms, ieee transactions on systems man and cybernetics. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern, vol 9
Peng H, Li B, Ling H, Hu W, Xiong W, Maybank SJ (2017) Salient object detection via structured matrix decomposition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(4):818–832
Perazzi F, Krähenbühl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A (2012) Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 733–740
Qin Y, Lu H, Xu Y, Wang H (2015) Saliency detection via cellular automata. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 110–119
Roweis S, Saul L (2000) Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 290(5500):2323–2326
Soni R, Kumar B, Chand S (2019) Text detection and localization in natural scene images based on text awareness score. Appl Intell 49:1376–1405
Souly N, Shah M (2016) Visual saliency detection using group lasso regularization in videos of natural scenes. Int J Comput Vis 117(1):93–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0853-6
Sun J, Lu H, Liu X (2015) Saliency region detection based on markov absorption probabilities. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(5):1639–1649
Wang Q, Chen F, Xu W (2010) Saliency selection for robust visual tracking. In: 2010 IEEE international conference on image processing, pp 2785–2788
Wang Z, Xiang D, Hou S, Wu F (2017) Background-driven salient object detection. IEEE Trans Multimed 19(4):750–762. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2016.2636739
Wei Y, Wen F, Zhu W, Sun J (2012) Geodesic saliency using background priors. In: Fitzgibbon A, Lazebnik S, Perona P, Sato Y, Schmid C (eds) Computer vision – ECCV. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, vol 2012, pp 29–42
Xiao Y, Jiang B, Tu Z, Ma J, Tang J (2018) A prior regularized multi-layer graph ranking model for image saliency computation. Neurocomputing 315:234–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.06.072. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231218308506
Xiao Y, Jiang B, Zheng A, Zhou A, Hussain A, Tang J (2019) Saliency detection via multi-view graph based saliency optimization. Neurocomputing 351:156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.03.066
Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J, Jia J (2013) Hierarchical saliency detection. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1155–1162
Yang X, Qian X, Xue Y (2015) Scalable mobile image retrieval by exploring contextual saliency. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(6):1709–1721
Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang M-H (2013) Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3166–3173
Yuan Y, Li C, Kim J, Cai W, Feng DD (2018) Reversion correction and regularized random walk ranking for saliency detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(3):1311–1322. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2762422
Zhang L, Ai J, Jiang B, Lu H, Li X (2018) Saliency detection via absorbing markov chain with learnt transition probability. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(2):987–998
Zhang M, Pang Y, Wu Y, Du Y, Sun H, Zhang K (2018) Saliency detection via local structure propagation. J Vis Commun Image Represent 52:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.01.004
Zhou L, Yang Z, Zhou Z, Hu D (2017) Salient region detection using diffusion process on a two-layer sparse graph. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(12):5882–5894
Zhu W, Liang S, Wei Y, Sun J (2014) Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2814–2821
Zhu X, Tang C, Wang P, Xu H, Wang M, Tian J (2018) Saliency detection via affinity graph learning and weighted manifold ranking. Neurocomputing 312:239–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.106
Acknowledgements
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Fan Wang. Performed the experiments: Fan Wang. Analyzed the data: Fan Wang. Wrote and reviewed the paper: Fan Wang. Approved the fnal version of the paper: Fan Wang, Guohua Peng.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Peng, G. Intensifying graph diffusion-based salient object detection with sparse graph weighting. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 34113–34127 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14483-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14483-1