Abstract
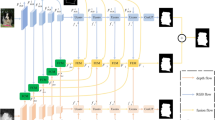
RGB and depth modalities can be exploited to effectively recognize the most eye-catching objects in different scenes. Therefore, RGB-D salient object detection (RGB-D SOD) has been a popular direction focused by researchers. Particularly in recent years, various newfangled RGB-D SOD algorithms have been proposed endlessly and achieved outstanding performance. However, most approaches adopt the common pyramid structure to integrate multi-scale cues but ignore the complementarity of features in cross-layers. Besides, it is still challenging to fully utilize RGB and Depth information for cross-modal interaction. To compensate for these shortcomings, we propose a CRA-Net (Cross-modal Refined Adjacent-guided Network), which takes advantage of the high-level semantic information contained in the high layers to guide the details of the local characteristics in the low layers for improving detection accuracy. Specifically, a multiplier refinement module (MRM) is proposed to adequately carry out the information interaction between two modalities, in which a five-layer refinement mechanism is adopted to enhance cross-modal fusion representations. Moreover, for the purpose of obliterating the interference of non-significant factors in the low-level backgrounds, we design an adjacent-guided aggregation module (AAM). The multi-level features are fed in groups into two AAMs with identical structures. By utilizing an adjacent-layer guidance strategy to effectively guide multi-scale features assemblage from deep to shallow. Numerous experiments show that our CRA-Net is competitive for four common evaluation metrics on four popular datasets.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The NJU2K dataset, NLPR dataset, SSD dataset, and SIP dataset used in the study are publicly available. The NJU2K dataset can be downloaded from the website: http://mcg.nju.edu.cn/resource.html. The NLPR dataset can be downloaded from the website: https://sites.google.com/site/rgbdsaliency/dataset. The SSD dataset can be downloaded from the website: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1zNL9-KSQwGILdAAfStMXWQ. The SIP dataset can be downloaded from the website: https://pan.baidu.com/s/14VjtMBn0_bQDRB0gMPznoA. All data, models, or code generated or used during the current study are available from the corresponding author by reasonable request.
References
Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, Susstrunk S (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 1597–1604
Arbelaez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, Malik J (2010) Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(5):898–916
Chen S, Tian Y (2013) Margin-constrained multiple kernel learning based multi-modal fusion for affect recognition. In: 2013 10th IEEE international conference and workshops on automatic face and gesture recognition (FG). IEEE, pp 1–7
Cheng Y, Fu H, Wei X, Xiao J, Cao X (2014) Depth enhanced saliency detection method. In: Proceedings of international conference on internet multimedia computing and service, pp 23–27
Chen H, Li Y (2018) Progressively complementarity-aware fusion network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3051–3060
Chen H, Li Y, Su D (2019) Multi-modal fusion network with multi-scale multi-path and cross-modal interactions for RGB-D salient object detection. Pattern Recogn 86:376–385
Chen H, Deng Y, Li Y, Hung T-Y, Lin G (2020) RGBD salient object detection via disentangled cross-modal fusion. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:8407–8416
Chen Q, Fu K, Liu Z, Chen G, Du H, Qiu B, Shao L (2021) EF-Net: a novel enhancement and fusion network for RGB-D saliency detection. Pattern Recogn 112:107740
Chen Q, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Fu K, Zhao Q, Du H (2021) RGB-D salient object detection via 3d convolutional neural networks. arXiv:2101.10241
Chen Y, Ma T, Yang X, Wang J, Song B, Zeng X (2021) MUFFIN: multi-scale feature fusion for drug–drug interaction prediction. Bioinformatics 37(17):2651–2658
Cheng B, Schwing A, Kirillov A (2021) Per-pixel classification is not all you need for semantic segmentation. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst :34
Ciptadi A, Hermans T, Rehg JM (2013) An in depth view of saliency. Georgia Institute of Technology
Desingh K, Krishna KM, Rajan D, Jawahar C (2013) Depth really matters: improving visual salient region detection with depth. In: BMVC, pp 1–11
Ding Y, Liu Z, Huang M, Shi R, Wang X (2019) Depth-aware saliency detection using convolutional neural networks. J Vis Commun Image Represent 61:1–9
Fan X, Liu Z, Sun G (2014) Salient region detection for stereoscopic images. In: 2014 19th international conference on digital signal processing. IEEE, pp 454–458
Fan D-P, Cheng M-M, Liu Y, Li T, Borji A (2017) Structure-measure: a new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 4548–4557
Fan D-P, Gong C, Cao Y, Ren B, Cheng M-M, Borji A (2018) Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. arXiv:1805.10421
Fan D-P, Zhai Y, Borji A, Yang J, Shao L (2020) BBS-Net: RGB-D salient object detection with a bifurcated backbone strategy network. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 275–292
Fan D-P, Lin Z, Zhang Z, Zhu M, Cheng M-M (2020) Rethinking RGB-D salient object detection: models, data sets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32(5):2075–2089
Feng D, Barnes N, You S, McCarthy C (2016) Local background enclosure for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2343–2350
Fidler S, Sharma A, Urtasun R (2013) A sentence is worth a thousand pixels. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1995–2002
Fu K, Fan D-P, Ji G-P, Zhao Q (2020) JL-DCF: joint learning and densely-cooperative fusion framework for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3052–3062
Fu K, Fan D-P, Ji G-P, Zhao Q, Shen J, Zhu C (2021) Siamese network for RGB-D salient object detection and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Gao S-H, Cheng M-M, Zhao K, Zhang X-Y, Yang M-H, Torr P (2019) Res2Net: a new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(2):652–662
Guo J, Ren T, Bei J (2016) Salient object detection for RGB-D image via saliency evolution. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME). IEEE, pp 1–6
Han J, Chen H, Liu N, Yan C, Li X (2017) CNNs-based RGB-D saliency detection via cross-view transfer and multiview fusion. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(11):3171–3183
Hu R, Deng Z, Zhu X (2021) Multi-scale graph fusion for co-saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 35, pp 7789–7796
Hou Q, Cheng M-M, Hu X, Borji A, Tu Z, Torr PH (2017) Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3203–3212
Ji W, Li J, Zhang M, Piao Y, Lu H (2020) Accurate RGB-D salient object detection via collaborative learning. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 52–69
Ji W, Li J, Yu S, Zhang M, Piao Y, Yao S, Bi Q, Ma K, Zheng Y, Lu H et al (2021) Calibrated RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 9471–9481
Ju R, Ge L, Geng W, Ren T, Wu G (2014) Depth saliency based on anisotropic center-surround difference. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE, pp 1115–1119
Jin W-D, Xu J, Han Q, Zhang Y, Cheng M-M (2021) CDNet: complementary depth network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:3376–3390
Jiang K, Wang Z, Yi P, Chen C, Huang B, Luo Y, Ma J, Jiang J (2020) Multi-scale progressive fusion network for single image deraining. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 8346–8355
Jiang B, Zhou Z, Wang X, Tang J, Luo B (2020) CmSalGAN: RGB-D salient object detection with cross-view generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans Multimed 23:1343–1353
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980
Li P, Wang D, Wang L, Lu H (2018) Deep visual tracking: review and experimental comparison. Pattern Recogn 76:323–338
Li G, Liu Z, Ling H (2020) ICNet: information conversion network for RGB-D based salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:4873–4884
Li G, Liu Z, Ye L, Wang Y, Ling H (2020) Cross-modal weighting network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 665–681
Li G, Liu Z, Chen M, Bai Z, Lin W, Ling H (2021) Hierarchical alternate interaction network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:3528–3542
Liu S, Huang D et al (2018) Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In: Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 385–400
Liu Z, Shi S, Duan Q, Zhang W, Zhao P (2019) Salient object detection for RGB-D image by single stream recurrent convolution neural network. Neurocomputing 363:46–57
Pang Y, Zhang L, Zhao X, Lu H (2020) Hierarchical dynamic filtering network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 235–252
Perazzi F, Krähenbühl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A (2012) Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 733–740
Peng H, Li B, Xiong W, Hu W, Ji R (2014) RGBD salient object detection: a benchmark and algorithms. In: European Conference On Computer Vision. Springer, pp 92–109
Piao Y, Ji W, Li J, Zhang M, Lu H (2019) Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 7254–7263
Piao Y, Rong Z, Zhang M, Ren W, Lu H (2020) A2dele: adaptive and attentive depth distiller for efficient RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 9060–9069
Ren G, Xie Y, Dai T, Stathaki T (2021) Progressive multi-scale fusion network for RGB-D salient object detection. arXiv:2106.03941
Ren J, Gong X, Yu L, Zhou W, Ying Yang M (2015) Exploiting global priors for RGB-D saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 25–32
Richardson E, Alaluf Y, Patashnik O, Nitzan Y, Azar Y, Shapiro S, Cohen-Or D (2021) Encoding in style: a stylegan encoder for image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2287–2296
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M et al (2015) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Song H, Liu Z, Du H, Sun G, Le Meur O, Ren T (2017) Depth-aware salient object detection and segmentation via multiscale discriminative saliency fusion and bootstrap learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(9):4204–4216
Wang N, Zhou W, Wang J, Li H (2021) Transformer meets tracker: exploiting temporal context for robust visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1571–1580
Wang N, Gong X (2019) Adaptive fusion for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Access 7:55277–55284
Wang R, Fan J, Li Y (2020) Deep multi-scale fusion neural network for multi-class arrhythmia detection. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 24 (9):2461–2472
Wang F, Pan J, Xu S, Tang J (2022) Learning discriminative cross-modality features for RGB-D saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing
Wu J, Zhou W, Luo T, Yu L, Lei J (2021) Multiscale multilevel context and multimodal fusion for RGB-D salient object detection. Sig Process 178:107766
Wu Y-H, Liu Y, Xu J, Bian J-W, Gu Y-C, Cheng M-M (2021) MobileSal: extremely efficient RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Yan B, Peng H, Fu J, Wang D, Lu H (2021) Learning spatio-temporal transformer for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 10448–10457
Yang R, Yu Y (2021) Artificial convolutional neural network in object detection and semantic segmentation for medical imaging analysis. Front Oncol 11:573
Yeh Y-R, Lin T-C, Chung Y-Y, Wang Y-CF (2012) A novel multiple kernel learning framework for heterogeneous feature fusion and variable selection. IEEE Trans Multimed 14(3):563–574
Yuan X, Shi J, Gu L (2021) A review of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery. Expert Syst Appl 169:114417
Zou Z, Shi Z, Guo Y, Ye J (2019) Object detection in 20 years: a survey. arXiv:1905.05055
Zhan F, Yu Y, Cui K, Zhang G, Lu S, Pan J, Zhang C, Ma F, Xie X, Miao C (2021) Unbalanced feature transport for exemplar-based image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 15028–15038
Zhang M, Ren W, Piao Y, Rong Z, Lu H (2020) Select, supplement and focus for RGB-D saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3472–3481
Zhang W, Jiang Y, Fu K, Zhao Q (2021) BTS-Net: bi-directional transfer-and-selection network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: 2021 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME). IEEE, pp 1–6
Zhang J, Fan D-P, Dai Y, Anwar S, Saleh F, Aliakbarian S, Barnes N (2021) Uncertainty inspired RGB-D saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Zhang Z, Lin Z, Xu J, Jin W-D, Lu S-P, Fan D-P (2021) Bilateral attention network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1949–1961
Zhao J-X, Cao Y, Fan D-P, Cheng M-M, Li X-Y, Zhang L (2019) Contrast prior and fluid pyramid integration for RGBD salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3927–3936
Zhao X, Pang Y, Zhang L, Lu H, Zhang L (2020) Suppress and balance: a simple gated network for salient object detection. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 35–51
Zhao X, Pang Y, Zhang L, Lu H, Ruan X (2021) Self-supervised representation learning for RGB-D salient object detection. arXiv:2101.12482
Zhou L, Yang Z, Yuan Q, Zhou Z, Hu D (2015) Salient region detection via integrating diffusion-based compactness and local contrast. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(11):3308–3320
Zhou T, Fu H, Chen G, Zhou Y, Fan D-P, Shao L (2021) Specificity-preserving RGB-D saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 4681–4691
Zhou W, Liu C, Lei J, Yu L, Luo T (2022) HFNet: hierarchical feedback network with multilevel atrous spatial pyramid pooling for RGB-D saliency detection. Neurocomputing 490:347–357
Zhu Y, Liu D, Li Y, Wang X (2015) Selective and incremental fusion for fuzzy and uncertain data based on probabilistic graphical model. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 29(6):2397–2403
Zhu C, Li G, Wang W, Wang R (2017) An innovative salient object detection using center-dark channel prior. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops, pp 1509–1515
Zhu C, Li G (2017) A three-pathway psychobiological framework of salient object detection using stereoscopic technology. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops, pp 3008–3014
Zhu D, Dai L, Luo Y, Zhang G, Shao X, Itti L, Lu J (2018) Multi-scale adversarial feature learning for saliency detection. Symmetry 10(10):457
Zhu C, Cai X, Huang K, Li TH, Li G (2019) PDNet: prior-model guided depth-enhanced network for salient object detection. In: IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME). IEEE, pp 199–204
Acknowledgements
The paper is supported by AnHui Province Key Laboratory of Infrared and Low-Temperature Plasma under No.IRKL2022KF07.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, H., Zhang, J., Wu, R. et al. Cross-modal refined adjacent-guided network for RGB-D salient object detection. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 37453–37478 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14421-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14421-1