Abstract
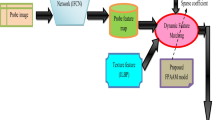
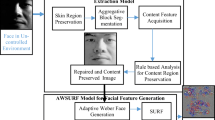
This paper introduces a Partial Face Recognition (PFR) method with the benefits of optimization logic using an optimized feature matching aspect. Besides, for better recognition, the Sparse Representation Classification (SRC) and Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) have been combined. As a novelty, this work aims to tune the sparse coefficient of Dynamic Feature Matching (DFM) optimally, in which the reconstruction error should be minimal. Also, this work presents the structural similarity index measure to calculate the similarity scores between the gallery sub-feature map and probe feature map. For optimization purposes, this work deploys a proposed Sealion Updated Grey Wolf Optimization (SUGWO) algorithm. Finally, the proposed method is executed over the traditional methods concerning certain measures.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNNs:
-
Convolutional Neural Network
- DFM:
-
Dynamic Feature Matching
- DL:
-
Deep Learning
- dPFC:
-
dorsal Prefrontal Cortex
- DRUID:
-
Deep Regression-based User Image Detector
- FCNs:
-
Fully Convolutional Networks
- FMRI:
-
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- FNR:
-
False Negative Rate
- FPR:
-
False Positive Rate
- FR:
-
Face Recognition
- HCI:
-
Human Computer Interface
- HSA:
-
Harmony Search Algorithm
- i-LIDS:
-
imagery Library for Intelligent Detection Systems
- K-NN:
-
K-nearest Neighbours
- LBP:
-
Local Binary Pattern
- LPPLSDA:
-
Locality Preserving Partial Least Square Discriminant Analysis
- MCC:
-
Mathews Correlation Co-efficient
- MFO:
-
Moth Flame Optimization
- MKD-GTP:
-
Multi-Key point Descriptor with Gabor Ternary Pattern
- ML:
-
Machine Learning
- MTLSC:
-
Model-based Transfer Learning and Sparse Coding
- NPV:
-
Negative Predictive Value
- OSPF:
-
Optimized Symmetric Partial Facegraphs
- PCA:
-
Principal Component Analysis
- PFR:
-
Partial Facial Recognition
- PLS-DA:
-
Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis
- RE-ID:
-
Re-identification
- RPSM:
-
Robust Point Set Matching
- SGD:
-
Stochastic Gradient Descent
- SIFT:
-
Scale-Invariant Feature Transform
- SRC:
-
Sparse Representation Classification
- SVM:
-
Support Vector Machine
- STS:
-
Superior Temporal Sulcus
- SUGWO:
-
Sea lion Updated Grey Wolf Optimization
- SURF:
-
Speeded Up Robust Features
- TPGM:
-
Topology Preserving Graph Matching
- TPWCRC:
-
Two-Phase Weighted collaborative Representation Classification
- WOA:
-
Whale Optimization Algorithm
- 3D:
-
Three Dimension
References
Alexandridis, G, Tagaris T, Siolas G, Stafylopatis A (2019) "From free-text user reviews to product recommendation using paragraph vectors and matrix factorization." In Companion Proceedings of The 2019 World Wide Web Conference, pp. 335–343
Alhabib, Mohammed MH, Al-Dabagh MZN, AL-Mukhtar FH, Hussein HI (2019) Exploiting wavelet transform, principal component analysis, support vector machine, and K-nearest neighbors for partial face recognition. Cihan Univ-Erbil Sci J 3(2):80–84
Aminu M, Ahmad NA (2019) locality preserving partial least squares discriminant analysis for face recognition. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci in press, corrected proofAvailable online, 30
Brammya, Suki Antely A (2019) Face recognition using active appearance and Type-2 fuzzy classifier. Multim Res 2(1):1–8
Daniya T (2020) Hybrid crow search and grey wolf optimization algorithm for congestion control in WSN. J Netw Commun Syst 3(3):30
Duan Y, Lu J, Feng J, Zhou J (2018) Topology preserving structural matching for automatic partial face recognition. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 13(7):1823–1837
Elmahmudi A, Ugail H (2019) Deep face recognition using imperfect facial data. Future Gen Comput Syst 99:213–225
Fang C, Zhao Z, Pan Z, Lin Z (2017) Feature learning via partial differential equation with applications to face recognition. Pattern Recog 69:14–25
García E, Escamilla E, Nakano M, Pérez H (Oct. 2017) Face recognition with occlusion using a wireframe model and support vector machine. IEEE Lat Am Trans 15(10):1960–1966
Grati N, Ben-Hamadou A, Hammami M (2020) Learning local representations for scalable RGB-D face recognition. Exp Syst Appl 150:113319
Greening SG, Mitchell DGV, Smith FW (2018) Spatially generalizable representations of facial expressions: decoding across partial face samples. Cortex 101:31–43
Gruber I, Hlaváč M, Železný M, Karpov A (2017) Facing face recognition with ResNet: Round one. In: In International Conference on Interactive Collaborative Robotics, pp. 67–74. Springer, Cham
Gunawan TS, Gani MHH, Rahman FDA, Kartiwi M (2017) Development of face recognition on raspberry pi for security enhancement of smart home system. Indones J Electric Eng Inf (IJEEI) 5(4):317–325
He L, Li H, Zhang Q, Sun Z (2019) Dynamic feature matching for partial face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(2):791–802
He M, Zhang J, Shan S, Kan M, Chen X, “Deformable face net for pose invariant face recognition” Pattern Recognit, vol. 100, Art. no. 107113, 2020
Iranmanesh SM, Riggan B, Hu S, Nasrabadi NM (2020) Coupled generative adversarial network for heterogeneous face recognition. Image Vis Comput 94:103861
Kim H, Kim G, Lee S-H (2019) Effects of individuation and categorization on face representations in the visual cortex. Neurosci Lett 708:134344
Kryza-Lacombe M, Iturri N, Monk CS, Wiggins JL (2020) Face emotion processing in pediatric irritability: neural mechanisms in a sample enriched for irritability with autism Spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adol Psych 59(12):1380–1391
Kumar A, Kaur A, Kumar M (2019) Face detection techniques: a review. Artif Intell Rev 52(2):927–948
Lahasan B, Lutfi SL, Venkat I, Al-Betar MA, San-Segundo R (2018) Optimized symmetric partial facegraphs for face recognition in adverse conditions. Inf Sci 429:194–214
Lei Y, Guo Y, Hayat M, Bennamoun M, Zhou X (2016) A Two-Phase Weighted Collaborative Representation for 3D partial face recognition with single sample. Pattern Recognit 52:218–237
Li P, Chen K, Wang F, Zheng L “An upper-bound analytical model of blow-out for a shallow tunnel in sand considering the partial failure within the face” Tunn Undergr Space Technol, vol. 91, Art. no. 102989, 2019
Lokku, G, Reddy GH, Prasad MNG (2021) "A Robust Face Recognition model using Deep Transfer Metric Learning built on AlexNet Convolutional Neural Network." In 2021 International Conference on Communication, Control and Information Sciences (ICCISc), vol. 1, pp. 1–6. IEEE
Mahbub U, Sarkar S, Chellappa R (February 2019) Partial face detection in the mobile domain. Image Vis Comput 82:1–17
Mahendran MV, Vijayan V (2020) Optimal sizing and siting of distributed generators by hybrid particle swarm optimization-Grey wolf optimization algorithm. J Comput Mech Power Syst Control 3(1):42–47
Marsaline Beno M, Valarmathi IR, Swamy SM, Rajakumar BR (2014) Threshold prediction for segmenting tumour from brain MRI scans. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 24(2):129–137. https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22087
Masadeh R, Mahafzah B, Sharieh A (2019) Sea Lion Optimization Algorithm. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 10:388–395
Meinhardt-Injac B, Kurbel D, Meinhardt G “The coupling between face and emotion recognition from early adolescence to young adulthood” Cognit Dev, vol. 53, Art. no. 100851, 2020
Mirjalili S (2015) Moth-flame optimization algorithm: A novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl Based Syst 89:228–249
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The Whale Optimization Algorithm. Adv Eng Software 95:51–67
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv Eng Software 69:46–61
Mukhedkar MM, Kolekar U (2019) Hybrid PSGWO algorithm for trust-based secure routing in MANET. J Netw Commun Syst 2(3):1–10
Pawar S, Kithani V, Ahuja S, Sahu S (2018) "Smart home security using IoT and face recognition", In 2018 Fourth International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), pp. 1–6. IEEE
Porpiglia F, Amparore D, Checcucci E, Fiori C (2019) Parenchymal mass preserved after partial nephrectomy and “global renal damage”: two faces of the same coin. European Urol Oncol 2(1):104–105
Prasanalakshmi B, Kannammal A, Sridevi R (2011) Multimodal biometric cryptosystem involving face, fingerprint and palm vein. Int J Comput Sci Issues (IJCSI) 8(4):604
Roy RG (2019) Rescheduling based congestion management method using hybrid Grey wolf optimization - grasshopper optimization algorithm in power system. J Comput Mech Power Syst Control 2(1):9–18
Roy RG, Ghoshal D (2020) Grey wolf optimization-based second order sliding mode control for inchworm robot. Robotica 38(9):1539–1557
Savio MMD, Deepa T, Bonasu A, Anurag TS (2021) Image Processing For Face Recognition Using HAAR, HOG, and SVM Algorithms. J Phys Conf Ser 1964(6):062023. IOP Publishing
Shan X, Lu Y, Li Q, Wen Y (2020) Model-based transfer learning and sparse coding for partial face recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Vid Technol 31(11):4347–4356
Srikrishnaswetha K, Kumar S, Mahmood MR (2019) A study on smart electronics voting machine using face recognition and aadhar verification with iot. In: In Innovations in electronics and communication engineering, pp. 87–95. Springer, Singapore
Subramanyam TC, Tulasi Ram SS, Subrahmanyam JBV (2018) HGAGWO: a multi-objective optimal positioning and sizing of fuel cells in DG systems. J Comput Mech Power Syst Control 1(1):34–44
Thomas R, Rangachar MJS (2018) Hybrid optimization based DBN for face recognition using low-resolution images. Multim Res 1(1):33–43
Trigueros DS, Meng L, Hartnett M (2018) Enhancing convolutional neural networks for face recognition with occlusion maps and batch triplet loss. Image Vis Comput 79:99–108
Trofimov A, Drach B, Kachanov M, Sevostianov I (2017) Effect of a partial contact between the crack faces on its contribution to overall material compliance and resistivity. Int J Solids Struct 1081:289–297
Vinolin V (2019) Breast Cancer detection by optimal classification using GWO algorithm. Multim Res 2(2):10–18
Wagh MB, Gomathi N (2019) Improved GWO-CS algorithm-based optimal routing strategy in VANET. J Netw Commun Syst 2(1):34–42
Weng R, Lu J, Tan Y (2016) Robust point set matching for partial face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(3):1163–1176
Werghi N, Tortorici C, Berretti S, Del Bimbo A (2016) Boosting 3D LBP-based face recognition by fusing shape and texture descriptors on the mesh. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 11(5):964–979
Xu Y (2020) Hybrid Grey Wolf Optimization and Cuckoo Search algorithm for UPQC positioning in power distribution network. J Comput Mech Power Syst Control 3(3). https://doi.org/10.46253/jcmps.v3i3.a1
Young SG, Tracy RE, Wilson JP, Rydell RJ, Hugenberg K “The temporal dynamics of the link between configural face processing and dehumanization” J Experiment Soc Psych, vol. 85, Art. no. 103883, 2019
Yu N, Bai D (2020) Facial expression recognition by jointly partial image and deep metric learning. IEEE Access 8:4700–4707
Zheng W, Gou C, Wang F-Y (2020) A novel approach inspired by optic nerve characteristics for few-shot occluded face recognition. Neuro Comput 3761:25–41
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This paper does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, G.G., Banyal, R.K. A hybrid SUGWO optimization for partial face recognition with new similarity index. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 18097–18116 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14205-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14205-z