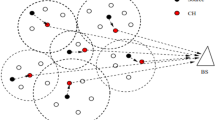
Abstract
Whether it is Internet of Things for smart homes & industrial units or surveillance of inaccessible terrain, Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) are penetrating at a very fast pace in variety of applications. This increase in span of WSN implementation has accelerated research in the field. Energy efficiency, life time improvement, reducing production costs, data security and node mobility are some of the key areas of interest. This paper evaluates clustering-based methodologies already proposed for improving energy efficiency of sensor networks. The gaps in the methodologies have been identified and have been addressed through the new methodology Hibernated Clustering Wireless Sensor Networks (HC-WSN) proposed in this research work. The proposed methodology improves period of operation of individual sensor node followed by improvement in overall network lifetime. The simulation results show that our proposed scheme surpasses the existing schemes in terms of lifespan of individual nodes, average energy and throughput. Moreover, the proposed methodology prolongs the lifespan of WSNs and as well as of individual nodes.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adil M et al (2020) An efficient load balancing scheme of energy gauge nodes to maximize the lifespan of constraint oriented networks. IEEE Access 8:148510–148527. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3015941
Adil M et al (2020) An energy proficient load balancing routing scheme for wireless sensor networks to maximize their lifespan in an operational environment. IEEE Access 8:163209–163224
Akan OB. Spatiotemporal correlation theory for wireless sensor networks. Chapter in book - Algorithms and Protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks, pp 105–127 edited by Azzedine Boukerche by John Wiley & Sons Inc
Amini N, Miremadi SG, Fazeli M (2007) A hierarchical routing protocol for energy load balancing in wireless sensor networks. 2007 Canadian Conference onElectrical and Computer Engineering, pp 1086–1089. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCECE.2007.277
Gast MS, Loukides M (2002) 802.11 wireless networks: the definitive guide
Heinzelman WR, Chandrakasan A, Balakrishnan H (2000)Energy-Efficient Communication Protocol for Wireless Microsensor Networks. IEEE, Hawaii Int. Conf. Syst. Sci., pp 1–10
Heinzelman WB, Chandrakasan AP, Balakrishnan H (2002) An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 1(4):660–670
Hu H, Hu X, Xiao J, Liu X (2017)CDMA-based MAC protocol for multi-hop wireless sensor networks. 2nd IEEE Int. Conf. Intell. Transp. Eng. ICITE 2017, pp 266–271
Khera S, Turk N, Kaur N (2020) A practical approach to energy consumption in wireless sensor networks. Int J Adv Intell Paradig 16(2):190–202
Liu X, Shi J (2012) Clustering routing algorithms in wireless sensor networks: An overview. KSII Trans Internet Inf Syst 6(7):1735–1755
Munadi R, Sulistyorini AE, Fauzi FUS, Adiprabowo T (2016) Simulation and analysis of energy consumption for S-MAC and T-MAC protocols on wireless sensor network. APWiMob 2015 - IEEE Asia Pacific Conf. Wirel. Mob., pp 142–146
Nataf E, Festor O (2012) Online estimation of battery lifetime for wireless sensors network. ArXiv, abs/1209.2234
Qing L, Zhu Q, Wang M (2006) Design of a distributed energy-efficient clustering algorithm for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Comput Commun 29(12):2230–2237
Raghatate M, Wajgi DW (2014) An energy saving algorithm to prolong the lifetime of wireless sensor network. Int J Wirel Mob Netw 6(5):33–44
Raghavendra CS, Lindsey S, Lindsey S (2001) PEGASIS: Power-Efficient Gathering in Sensor Information Systems Stephanie Lindsey. Proc. IEEE ICC vol 3
Razaque A, Mudigulam S, Gavini K, Amsaad F, Abdulgader M, Krishna GS (2016) H-LEACH: Hybrid-low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy for wireless sensor networks. 2016 IEEE Long Isl. Syst. Appl. Technol. Conf.
Shih E et al (2001) Physical layer driven protocol and algorithm design for energy-efficient wireless sensor networks. ACM SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev., pp 272–287
Soro S, Heinzelman WB. Prolonging the lifetime of wireless sensor networks via prolonging the lifetime of wireless sensor networks via. 19th IEEE Int. Parallel Distrib. Process. Symp., pp 236b-236b
Tan ND, Viet ND (2015) SSTBC: Sleep scheduled and tree-based clustering routing protocol for energy-efficient in wireless sensor networks. Proc. – 2015 IEEE RIVF Int. Conf. Comput. Commun. Technol. Res. Innov. Vis. Futur., IEEE RIVF, pp 180–185
Wei C (2011)Cluster-based routing protocols in wireless sensor networks: a survey. Int. Conf. Comput. Sci. Netw. Technol., p 146
Younis O, Fahmy S (2004) HEED: a hybrid, energy-efficient, distributed clustering approach for ad hoc sensor networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 3:366–379
Zarko Z, Predrag RT, Miroslav H (2008) Wireless sensor network application programming and simulation system. Comput Sci Inf Syst 5:109–126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest/Competing interests
Authors have no conflicts of interest/Competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Financial interests
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khera, S., Turk, N. & Kaur, N. HC-WSN: a Hibernated Clustering based framework for improving energy efficiency of wireless sensor networks. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 3879–3894 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13446-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13446-2