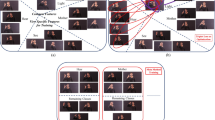
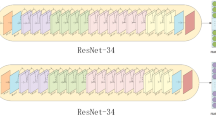
Abstract
Mobile based sign language recognition (SLR) is challenging in real time due to camera shudder and the signer movements for capturing continuous video data for recognition. Even though there are many state-of-the-art methods for SLR, they have ignored view sensitivity and its effects on the accuracy of the system. This work proposes a novel multi view deep metric feature learning (MVslDML) model for building a view sensitive environment into SLR, which is being investigated profoundly in human action recognition. The MVslDMLNet is an end-to-end trainable convolutional neural network where the features extracted from multiple views are learned based on the sharable and unshareable latent features within class multi view data through metric learning. Experiments performed on our multi view sign language and four benchmark action video datasets indicate a higher accuracy for the proposed framework.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achmed I (2014) Independent hand-tracking from a single two-dimensional view and its application to south african sign language recognition. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Western Cape
Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein A (2006) K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 54(11):4311–4322. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsp.2006.881199
Bashir F I, Khokhar A A, Schonfeld D (2006) View-invariant motion trajectory-based activity classification and recognition. Multimedia Systems 12(1):45–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-006-0024-2
Camgoz N C, Koller O, Hadfield S, Bowden R (2020) Sign language transformers: Joint end-to-end sign language recognition and translation. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr42600.2020.01004. IEEE
Cheng G, Yang C, Yao X, Guo L, Han J (2018) When deep learning meets metric learning: Remote sensing image scene classification via learning discriminative CNNs. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 56(5):2811–2821. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2017.2783902
Cui R, Liu H, Zhang C (2017) Recurrent convolutional neural networks for continuous sign language recognition by staged optimization. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2017.175. IEEE
Cui R, Liu H, Zhang C (2019) A deep neural framework for continuous sign language recognition by iterative training. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 21(7):1880–1891. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmm.2018.2889563
De Coster M, Van Herreweghe M, Dambre J (2020) Sign language recognition with transformer networks. In: 12th international conference on language resources and evaluation
Dhiman C, Vishwakarma D K (2020) View-invariant deep architecture for human action recognition using two-stream motion and shape temporal dynamics. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:3835–3844. https://doi.org/10.1109/tip.2020.2965299
Efthymiou N, Koutras P, Filntisis P P, Potamianos G, Maragos P (2018) Multi- view fusion for action recognition in child-robot interaction. In: 2018 25th IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). https://doi.org/10.1109/icip.2018.8451146. IEEE
Elons A S, Abull-ela M, Tolba MF (2013) A proposed PCNN features quality optimization technique for pose-invariant 3d arabic sign language recognition. Appl Soft Comput 13(4):1646–1660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2012.11.036
Gao Z, Zhang H, Xu GP, Xue YB, Hauptmann AG (2015) Multi-view discriminative and structured dictionary learning with group sparsity for human action recognition. Signal Process 112:83–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.08.034
Gao Z, Xuan H-Z, Zhang H, Wan S, Choo K-K R (2019) Adaptive fusion and category-level dictionary learning model for multiview human action recognition. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 6(6):9280–9293. https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2019.2911669
Gao Z, Xuan H-Z, Zhang H, Wan S, Choo K-K R (2019) Adaptive fusion and category-level dictionary learning model for multiview human action recognition. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 6(6):9280–9293. https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2019.2911669
Ge W, Huang W, Dong D, Scott M R (2018) Deep metric learning with hierarchical triplet loss. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01231-1_17. Springer International Publishing, pp 272–288
Ghahabi O, Hernando J (2017) Deep learning backend for single and multisession i-vector speaker recognition. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing 25(4):807–817. https://doi.org/10.1109/taslp.2017.2661705
Gorelick L, Blank M, Shechtman E, Irani M, Basri R (2007) Actions as space-time shapes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(12):2247–2253. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2007.70711
He Z, Jung C, Fu Q, Zhang Z (2018) Deep feature embedding learning for person re-identification based on lifted structured loss. Multimedia Tools and Applications 78(5):5863–5880. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6408-4
Hoffer E, Ailon N (2015) Deep metric learning using triplet network. In: Similarity-based pattern recognition. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24261-3_7. Springer International Publishing, pp 84–92
Hu J, Lu J, Tan Y-P (2014) Discriminative deep metric learning for face verification in the wild. In: 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2014.242. IEEE
Hu J, Lu J, Tan Y-P (2018) Sharable and individual multi-view metric learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(9):2281–2288. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2017.2749576
Huang K-K, Ren C-X, Liu H, Lai Z-R, Yu Y-F, Dai D-Q (2020) Hyperspectral image classification via discriminative convolutional neural network with an improved triplet loss. Pattern Recogn, pp 107744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107744
Iosifidis A, Tefas A, Pitas I (2013) Multi-view action recognition based on action volumes, fuzzy distances and cluster discriminant analysis. Signal Process 93(6):1445–1457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.08.015
Ji X, Ju Z, Wang C, Wang C (2015) Multi-view transition HMMs based view-invariant human action recognition method. Multimedia Tools and Applications 75(19):11847–11864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2661-y
Ji Y, Yang Y, Shen F, Shen H T, Zheng W-S (2020) Arbitrary-view human action recognition: A varying-view RGB-d action dataset. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, pp 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsvt.2020.2975845
Junejo I N, Dexter E, Laptev I, Pérez P (2011) View-independent action recognition from temporal self-similarities. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(1):172–185. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2010.68
Kishore P V V, Kumar D A, Sastry A S C S, Kumar E K (2018) Motionlets matching with adaptive kernels for 3-d indian sign language recognition. IEEE Sensors J 18 (8):3327–3337. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2018.2810449
Kishore P V V, Prasad M V D, Prasad C R, Rahul R (2015) 4-camera model for sign language recognition using elliptical fourier descriptors and ANN. In: 2015 international conference on signal processing and communication engineering systems. https://doi.org/10.1109/spaces.2015.7058288. IEEE
Kishore PVV, Kumar D A, E.N.D G, Manikanta M (2016) Continuous sign language recognition from tracking and shape features using fuzzy inference engine. In: 2016 international conference on wireless communications, signal processing and networking (WiSPNET). https://doi.org/10.1109/wispnet.2016.7566526. IEEE
Kocabas M, Karagoz S, Akbas E (2019) Self-supervised learning of 3d human pose using multi-view geometry. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2019.00117. IEEE
Koller O, Zargaran S, Ney H, Bowden R (2018) Deep sign: Enabling robust statistical continuous sign language recognition via hybrid CNN-HMMs. Int J Comput Vis 126(12):1311–1325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-018-1121-3
Kumar P, Gauba H, Roy P P, Dogra D P (2017) Coupled HMM-based multi-sensor data fusion for sign language recognition. Pattern Recogn Lett 86:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2016.12.004
Li C, Liu C, Duan L, Gao P, Zheng K (2019) Reconstruction regularized deep metric learning for multi-label image classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, pp 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2019.2924023
Li C, Zhong Q, Xie D, Pu S (2019) Collaborative spatiotemporal feature learning for video action recognition. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2019.00806. IEEE
Li D, Opazo C R, Yu X, Li H (2020) Word-level deep sign language recognition from video: A new large-scale dataset and methods comparison. In: 2020 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV). https://doi.org/10.1109/wacv45572.2020.9093512. IEEE
Li Y, Liu K, Jin Y, Wang T, Lin W (2020) VARID: Viewpoint-aware re-IDentification of vehicle based on triplet loss. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, pp 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/tits.2020.3025387
Liao Y, Xiong P, Min W, Min W, Lu J (2019) Dynamic sign language recognition based on video sequence with BLSTM-3d residual networks. IEEE Access 7:38044–38054. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2904749
López-Sánchez D, Arrieta A G, Corchado J M (2019) Visual content-based web page categorization with deep transfer learning and metric learning. Neurocomputing 338:418–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.08.086
Lu J, Wang G, Deng W, Moulin P, Zhou J (2015) Multi-manifold deep metric learning for image set classification. In: 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7298717. IEEE
Mittal A, Kumar P, Roy P P, Balasubramanian R, Chaudhuri B B (2019) A modified LSTM model for continuous sign language recognition using leap motion. IEEE Sensors J 19(16):7056–7063. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2019.2909837
Mustafa M (2020) A study on arabic sign language recognition for differently abled using advanced machine learning classifiers. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01790-w
Nowak E, Jurie F, Triggs B (2006) Sampling strategies for bag-of-features image classification. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2006. https://doi.org/10.1007/11744085_38. Springer, Berlin, pp 490–503
Peng Y, Zhao Y, Zhang J (2019) Two-stream collaborative learning with spatial-temporal attention for video classification. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Vid Technol 29(3):773–786. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsvt.2018.2808685
Pezzuoli F, Corona D, Corradini M L (2019) Improvements in a wearable device for sign language translation Advances in human factors in wearable technologies and game design. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20476-1_9. Springer International Publishing, pp 70–81
Qian Q, Shang L, Sun B, Hu J, Tacoma T, Li H, Jin R (2019) SoftTriple loss: Deep metric learning without triplet sampling. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2019.00655. IEEE
Qu F, Liu J, Liu X, Jiang L (2021) A multi-fault detection method with improved triplet loss based on hard sample mining. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy 12(1):127–137. https://doi.org/10.1109/tste.2020.2985217
Rao G A, Syamala K, Kishore P V V, Sastry A S C S (2018) Deep convolutional neural networks for sign language recognition. In: 2018 conference on signal processing and communication engineering systems (SPACES). https://doi.org/10.1109/spaces.2018.8316344. IEEE
Rastgoo R, Kiani K, Escalera S (2020) Hand sign language recognition using multi-view hand skeleton. Expert Syst Appl 150:113336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113336
Rastgoo R, Kiani K, Escalera S (2021) Sign language recognition: A deep survey. Expert Syst Appl 164:113794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113794
Ravi S, Maloji S, Polurie V V K, Eepuri K K (2018) Sign language recognition with multi feature fusion and ANN classifier. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences 26(6):2872–2886. https://doi.org/10.3906/elk-1711-139
Ravi S, Suman M, Kishore PVV, E K K, M T K K, D A K (2019) Multi modal spatio temporal co-trained CNNs with single modal testing on RGB–d based sign language gesture recognition. Journal of Computer Languages 52:88–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cola.2019.04.002
Shahroudy A, Liu J, Ng T-T, Wang G (2016) NTU RGB+d: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.115. IEEE
Singh S, Velastin SA, Ragheb H (2010) MuHAVi: A multicamera human action video dataset for the evaluation of action recognition methods. In: 2010 7th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance. https://doi.org/10.1109/avss.2010.63. IEEE
Sohn K (2016) Improved deep metric learning with multi-class n-pair loss objective. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1857–1865
Tao W, Leu M C, Yin Z (2018) American sign language alphabet recognition using convolutional neural networks with multiview augmentation and inference fusion. Eng Appl Artif Intell 76:202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2018.09.006
Wang D, Ouyang W, Li W, Xu D (2018) Dividing and aggregating network for multi-view action recognition. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_28. Springer International Publishing, pp 457–473
Wang H, Feng L, Meng X, Chen Z, Yu L, Zhang H (2017) Multi-view metric learning based on KL-divergence for similarity measurement. Neurocomputing 238:269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.062
Wang J, Zhou F, Wen S, Liu X, Lin Y (2017) Deep metric learning with angular loss. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2017.283. IEEE
Wang L, Ding Z, Tao Z, Liu Y, Fu Y (2019) Generative multi-view human action recognition. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2019.00631. IEEE
Wang Q, Chen X, Zhang L-G, Wang C, Gao W (2007) Viewpoint invariant sign language recognition. Comput Vis Image Underst 108(1-2):87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2006.11.009
Wang X, Han X, Huang W, Dong D, Scott M R (2019) Multi-similarity loss with general pair weighting for deep metric learning. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2019.00516. IEEE
Xiao Y, Chen J, Wang Y, Cao Z, Zhou J T, Bai X (2019) Action recognition for depth video using multi-view dynamic images. Inf Sci 480:287–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.12.050
Yan Y, Liu G, Ricci E, Sebe N (2013) Multi-task linear discriminant analysis for multi-view action recognition. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on image processing. https://doi.org/10.1109/icip.2013.6738585. IEEE
Yi D, Lei Z, Liao S, Li S Z (2014) Deep metric learning for person re-identification. In: 2014 22nd international conference on pattern recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/icpr.2014.16. IEEE
Zare A, Moghaddam H A, Sharifi A (2019) Video spatiotemporal mapping for human action recognition by convolutional neural network. Pattern Anal Applic 23(1):265–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-019-00788-1
Zhang P, Lan C, Xing J, Zeng W, Xue J, Zheng N (2019) View adaptive neural networks for high performance skeleton-based human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(8):1963–1978. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2019.2896631
Zheng W, Chen Z, Lu J, Zhou J (2019) Hardness-aware deep metric learning. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE
Zhu F, Shao L, Lin M (2013) Multi-view action recognition using local similarity random forests and sensor fusion. Pattern Recogn Lett 34 (1):20–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2012.04.016
Zhu J, Zou W, Zhu Z, Xu L, Huang G (2019) Action machine: Toward person-centric action recognition in videos. IEEE Signal Process Lett 26 (11):1633–1637. https://doi.org/10.1109/lsp.2019.2942739
Zhu K, Wang R, Zhao Q, Cheng J, Tao D (2020) A cuboid CNN model with an attention mechanism for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 22(11):2977–2989. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmm.2019.2962304
Zhu Y, Liu G (2019) Fine-grained action recognition using multi-view attentions. Vis Comput 36(9):1771–1781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01770-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suneetha, M., Prasad, M.V.D. & Kishore, P.V.V. Sharable and unshareable within class multi view deep metric latent feature learning for video-based sign language recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 27247–27273 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12646-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12646-0