Abstract
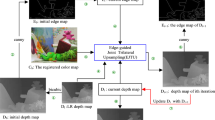
Depth images captured by conventional RGB-D sensors such as ToF cameras have limited resolution. Despite recent advances in depth camera technology, there is still a significant difference between the resolution of depth and color images. Therefore, depth map Super-Resolution (SR) techniques have received attention. Specifically, achieving an algorithm performing well at large scaling factors is of great importance and also challenging. In most existing methods, the up-sampling of low resolution depth images to the desired size is performed by an interpolation operation during the beginning stage and quality improvement filters are applied then. Due to the different nature of depth images and their sparsity, magnifying the images in a single step brings heavy artifacts specially at large up-sampling factors (e.g., 16). To tackle this problem, we propose a progressive multi-step depth map SR method where interpolation and modified enhancement processes are applied iteratively. This extremely improves the quality of the output depth image. Moreover, considering the importance of edges and discontinuities in depth images, instead of using conventional symmetric kernel, an edge directed kernel is applied which effectively avoids blurring. In addition, texture copying and depth bleeding artifacts are reduced employing a depth range filter. Quantitative and qualitative results of comprehensive experiments on Middlebury and real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach over prior depth SR works, especially for large scaling factors of 16, 32 and even 64.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chowdhary CL (2019) 3D object recognition system based on local shape descriptors and depth data analysis. Recent Pat Comput Sci 12(1):18–24. https://doi.org/10.2174/2213275911666180821092033.
Chowdhary CL, Muatjitjeja K, Jat DS (2015) Three-dimensional object recognition based intelligence system for identification. In: International Conference on Emerging Trends in Networks and Computer Communications (ETNCC), Windhoek, Namibia, pp 162-166. https://doi.org/10.1109/ETNCC.2015.7184827
Cui Y, Schuon S, Chan D, Thrun S, Theobalt C (2010) 3D shape scanning with a time-of-flight camera. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, pp 1173-1180. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2010.5540082
da Silva SPP, Almeida JS, Ohata EF, Rodrigues JJPC, de Albuquerque VHC, Rebouças PP (2020) Monocular vision aided depth map from RGB images to estimate of localization and support to navigation of mobile robots. IEEE Sens J 20(20):12040–12048. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.2964735
Diebel J, Thrun S (2005) An application of markov random fields to range sensing. In: Proceedings of Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). MIT Press, Cambridge
DIML RGB-D, Dataset. Available online at https://dimlrgbd.github.io/. Accessed Dec 2020
Ferstl D, Reinbacher C, Ranftl R, Ruether M, Bischof H (2013) Image guided depth upsampling using anisotropic total generalized variation. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, pp 993-1000. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.127
Ferstl D, Rüther M, Bischof H (2015) Variational depth superresolution using example-based edge representations. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 513-521. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.66
Giulio Marin G, Agresti L, Minto P, Zanuttigh (2019) A multi-camera dataset for depth estimation in an indoor scenario. Data in Brief 27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.104619
He K, Sun J, Tang X (2013) Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(6):1397–1409. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.213
Hornácek M, Rhemann C, Gelautz M, Rother C (2013) Depth super resolution by rigid body self-similarity in 3D. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1123-1130. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.149
Horng Y, Tseng Y, Chang T (2010) Stereoscopic images generation with directional Gaussian filter. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Paris, pp 2650-2653. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS.2010.5537052
Hui TW, Loy CC, Tang X (2016) Depth map super-resolution by deep multi-scale guidance. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. ECCV 2016, vol 9907. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9_22
Kaashki NN (2018) RGB-D face recognition under various conditions via 3D constrained local model. J Vis Commun Image Represent 52:66–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.02.003
Kim Y, Ham B, Oh C, Sohn K (2016) Structure selective depth superresolution for RGB-D cameras. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(11):5227–5238. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2601262
Kopf J, Cohen MF, Lischinski D, Uyttendaele M (2007) Joint bilateral upsampling. ACM Trans Graph 26(3):96-es. https://doi.org/10.1145/1276377.1276497
Landau MJ, Choo BY, Beling PA (2016) Simulating Kinect infrared and depth images. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(12):3018–3031
Li Z, Zheng J, Zhu Z, Yao W, Wu S (2015) Weighted guided image filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(1):120–129. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2014.2371234
Li Y, Wang Y, Wang D (2018) Multiple RGB-D sensor-based 3-D reconstruction and localization of indoor environment for mini MAV. Comput Electr Eng 70:509–524
Liao Y-W, Chen M-J, Yeh C-H, Lin J-R, Chen C-W (2019) Efficient inter-prediction depth coding algorithm based on depth map segmentation for 3D-HEVC. Multimed Tools Appl 78:10181–10205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6547-7
Liu X, Kang K, Liu Y (2017) Stereoscopic image quality assessment based on depth and texture information. IEEE Syst J 11(4):2829–2838. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2015.2478119
Lo K, Wang YF, Hua K (2018) Edge-preserving depth map upsampling by joint trilateral filter. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(1):371–384. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2016.2637661
Lu H et al (2017) Depth map reconstruction for underwater kinect camera using inpainting and local image mode filtering. IEEE Access 5:7115–7122. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2690455
Mac Aodha O, Campbell NDF, Nair A, Brostow GJ (2012) Patch based synthesis for single depth image super-resolution. In: Fitzgibbon A, Lazebnik S, Perona P, Sato Y, Schmid C (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2012. ECCV 2012, vol 7574. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33712-3_6
Massimo Camplani A, Paiement M, Mirmehdi D, Damen S, Hannuna, Tilo, Burghardt L, Tao (2017) Multiple human tracking in RGB-depth data, a survey. IET Comput Vision 11(4):265–285. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cvi.2016.0178
Middlebury Stereo Dataset. Available online at https://vision.middlebury.edu/stereo/data/ . Accessed Dec 2020
Paris S, Kornprobst P, Tumblin J, Durand F (2009) Bilateral filtering: theory and applications. Found Trends Comput Graph Vis 4(1):1–73. https://doi.org/10.1561/0600000020
Park J, Kim H, Tai Y-W, Brown MS, Kweon I (2011) High quality depth map upsampling for 3D-TOF cameras. In: International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, pp 1623-1630. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126423
Petschnigg G, Szeliski R, Agrawala M, Cohen M, Hoppe H (2004) Digital photography with flash and no-flash image pairs. ACM Trans Graph 23(3):664–672. https://doi.org/10.1145/1015706.1015777
Riegler G, Rüther M, Bischof H (2016) ATGV-Net: accurate depth super-resolution. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. ECCV 2016, vol 9907. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9_17
Scharstein D, Szeliski R (2002) A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. Int J Comput Vis 47:7–42. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014573219977
Scharstein D, Szeliski R (2003) High-accuracy stereo depth maps using structured light. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2003), vol 1, pp 195-202, Madison, WI
Sun CC, Wang YH, Sheu MH (2017) Fast motion object detection algorithm using complementary depth image on an RGB-D camera. IEEE Sens J 17(17):5728–5734
Tech G, Chen Y, Müller K, Ohm J, Vetro A, Wang Y (2016) Overview of the multiview and 3D Extensions of High Efficiency Video Coding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 26(1):35–49. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2015.2477935
Voo KHB, Bong DBL (2018) Quality assessment of stereoscopic image by 3D structural similarity. Multimed Tools Appl 77:2313–2332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4361-2
Wang Y, Zhang J, Liu Z, Wu Q, Zhang Z, Jia Y (2018) Depth super-resolution on RGB-D video sequences with large displacement 3D motion. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(7):3571–3585
Xie J, Feris RS, Yu S, Sun M (2015) Joint super resolution and denoising from a single depth image. IEEE Trans Multimed 17(9):1525–1537. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2015.2457678
Xie J, Feris RS, Sun MT (2016) Edge-guided single depth image super resolution. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(1):428–438
Zhai G, Min X (2020) Perceptual image quality assessment: a survey. Sci China Inf Sci 63:211301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-019-2757-1
Zhang Y, Ding L, Gaurav Sharma (2019) Local-linear-fitting-based matting for joint hole filling and depth upsampling of RGB-D images. J Electron Imaging 28(3). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JEI.28.3.033019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoddami, A.A., Moallem, P. & Kazemi, M. Large scaling factor depth map super-resolution using progressive joint-multilateral filtering. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 11461–11478 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12253-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12253-z