Abstract
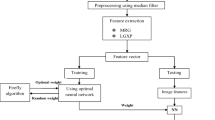
Biometric recognition is very important for automatically recognizing individuals based on feature vectors from behavioral or physiological characteristics. The biometric recognition systems provide suitable personal recognition approaches for determining individuals. Biometrics are broadly employed in several commercial as well as official identification systems for automatic access control. This paper introduces the model for multi-modal biometric recognition based on the feature level fusion method. The overall procedure of the proposed method involves four steps: pre-processing, feature extraction, recognition feature-level fusion, and Bio-metric recognition. The first step is to input the images into pre-processing steps. Thus, pre-processing three traits, like face, finger knuckle, and the hand vein, is done. Then, the feature extraction is done for each modality to extract the features. After that, the feature level fusion is carried out using Elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC) and the proposed Taylor-Grey Wolf optimization (Tay-GWO). After feature fusion, the Bio-metric recognition is done based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), which Tay-GWO trains. The proposed Tay-GWO is designed by integrating the Taylor series and Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO). The analysis shows that the developed model achieves the maximal accuracy of 94.86%, maximal sensitivity of 96.80%, and specificity of 93.74%, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abozaid A, Haggag A, Kasban H, Eltokhy M (2018) Multi-modal biometric scheme for human authentication technique based on voice and face recognition fusion. Multimed Tools Appl pp 1–17
AlameluMangai S, Ravi Sankar B, Alagarsamy K (2014) Taylor series prediction of time series data with error propagated by artificial neural network. Int J Comput Appl 89(1):0975–8887
Alay N, Al-Baity HH (2020) Deep learning approach for multimodal biometric recognition system based on fusion of iris, face, and finger vein traits. Sensors 20
Alpar O (2017) Frequency spectrograms for biometric keystroke authentication using neural network-based classifier. Knowledge-Based Systems 116:163–171
Alsultan A, Warwick K, Wei H (2017) Non-conventional keystroke dynamics for user authentication. Pattern Recogn Lett 89:53–59
Arora A, Miri R (2020) Taylor-Grey rider based deep recurrent neural network using feature level fusion for cryptography enabled biometric system. In: Proceedings of 3rd international conference on intelligent sustainable systems (ICISS). Thoothukudi, India
Bogazici University- Hand Database. http://bosphorus.ee.boun.edu.tr/hand/home.aspx. Accessed on February 2019
Bojja GR, Ofori M, Liu J, Ambati LS (2020) Early public outlook on the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a social media study. AMCIS 2020 Proceedings
Bui TTH, Jambulingam M, Amin M, Hung NT (2021) Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on franchise performance from franchisee perspectives: the role of entrepreneurial orientation, market orientation and franchisor support. J Sustain Finance Invest
Camara C, Peris-Lopez P, Gonzalez-Manzano L, Tapiador J (2017) Real-time electrocardiogram streams for continuous authentication. Appl Soft Comput pp 1–22
Chakraborti T, McCane B, Mills S, Pal U (2017) LOOP descriptor: encoding repeated local patterns for fine-grained visual identification of lepidoptera
Chen Y, Yang J, Wang C, Liu N (2016) Multi-modal biometrics recognition based on local fusion visual features and variational bayesian extreme learning machine. Exp Syst Appl 64:93–103
Chlaoua R, Meraoumia A, Eddine K, Korichi AM (2018) Deep learning for finger-knuckle-print identification system based on PCANet and SVM classifier. Evolving Systems pp 1–12
CVL face imagedataset, "http://www.lrv.fri.uni-lj.si/facedb.html", Accessed on February 2019
Dhana Lakshmi N, MadhaveeLatha Y, Damodaram A (2013) Silhouette extraction of a human body based on fusion of HOG and graph-cut segmentation in dynamic backgrounds
Dwivedi R, Dey S, Sharma MA, Goel A (2018) A fingerprint based crypto-biometric system for secure communication. Cryptography Secur 22
El-Bendary MA (2017) FEC merged with double security approach based on encrypted image steganography for different purpose in the presence of noise and different attack. Multimed Tools Appl 76(24):26463–26501
Goswami G, Mittal P, Majumdar A, Vatsa M, Singh R (2016) Group Sparse Representation Based Classification for Multi-feature Multimodal Biometrics. Information Fusion 32(Part B):3–12
Hung NT (2020) Deciphering the increased popularity of Vietnamese students’ choice of Asian countries for overseas studies: the influence of motivation for studying abroad on career planning and decision-making process of Vietnamese students in Taiwan. In Proceeding of: the international conference on higher education in Vietnam and Asia: similarities and possibilities of cooperation (IHESP)
IIT Delhi Finger Knuckle Database (Version 1.0), "http://www4.comp.polyu.edu.hk/~csajaykr/IITD/iitd_knuckle.htm", Accessed on February 2019
iMirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61
Kuzu RS, Piciucco E, Maiorana E, Campisi P (2020) On-the-fly finger-vein-based biometric recognition using deep neural networks. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 15
Lee JC, Lo TM, Chang CP (2016) Dorsal hand vein recognition based on directional filter bank. J Signal Image Video Process 10(1):145–152
Lumini A, Nanni L (2017) Overview of the combination of biometric matchers. Inf Fusion 33:71–85
Mezai L, Hachouf F (2015) Score-level fusion of face and voice using particle swarm optimization and belief functions. IEEE Trans Human Mach Syst 45(6):761–772
Miura N, Nagasaka A, Miyatake T (2004) Feature extraction of finger-vein patterns based on repeated line tracking and its application to personal identification. Mach Vis Appl 15:194–203
Peng J, AbdEl-Latif AA, Li Q, Niu X (2014) Multi-modal biometric authentication based on score level fusion offinger biometrics. Optik 125(23):6891–6897
Prakash A (2018) Continuous user authentication based score level fusion with hybrid optimization. Cluster Computing pp 1–11
Sabri M, Moin M-S, Razzazi F (2019) A new framework for match on card and match on host quality based multimodal biometric authentication. J Signal Process Syst 91(2):163–177
Shekha S, Patel VM, Nasrabadi NM, Chellappa R (2014) Joint sparse representation for robust multi-modal biometrics recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(1):113–126
Tu F, Yin S, Ouyang P, Tang S, Liu L, Wei S (2017) Deep convolutional neural network architecture with reconfigurable computation patterns. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Syst 25(8):2220–2233
Verma D, Dubey P (2017) Fuzzy least brain storm optimization and entropy-based Euclidean distance for multi-modal vein-based recognition system. J Cent South Univ 24(10):2360–2371
Verma D, Arora A (2020) Fuzzy Rider Optimization Algorithm for vein-based biometric recognition. In: Proceedings of 3rd international conference on intelligent sustainable systems (ICISS). Thoothukudi, India
Verma D, Dubey S (2017) Fuzzy brain storm optimization and adaptive thresholding for multimodel vein-based recognition system. Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 3(5):1756007
Wang YD, Zhang K, Shark LK (2014) Personal identification based on multiple keypoint sets of dorsal hand vein images. IET Biometrics 3(4):234–245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, A., Miri, R. Cryptography and Tay-Grey wolf optimization based multimodal biometrics for effective security. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 44021–44043 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-11993-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-11993-2