Abstract
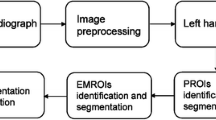
Human hand Bone Age Assessment (BAA) is commonly used by paediatrics for diagnosing the childś health, crime investigation, dead human identification (in case of natural disasters) etc. BAA can be estimated using Epiphysis and Carpal bones of hand X-ray images. These X-ray images may be prone to noise, due to which it might affect the process of background separation and auto-segmentation while performing BAA. Methods existing in the literature of BAA lack in resolving one or more issues (noise reduction, background separation and bone pixel segmentation) individually. This paper proposes a new method to segment Epiphysis bones using the (i) Wavelet packet transformation for noise suppression, (ii) Background suppression using texture features of the image, (iii) Enhancement of bone pixels using histogram equalization and (iv) Finally segmenting the Epiphysis region of interest using clustering method. Performance analysis is performed using two quantitative evaluation methods i.e. supervised and unsupervised evaluation. Unsupervised approach uses Mean Structure Similarity Index (MSSIM) and Homogeneity. Supervised approach uses Precision, Recall, Sensitivity, Accuracy and Error Rate. Proposed method for segmenting the epiphysis bones has shown better accuracy rate of 0.9701.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alshamrani K, Offiah O (2019) Applicability of the Tanner-Whitehouse 3 method to United Kingdom children born in the 21st century. In 9th International Conference on Children, vol. 7. BioScientifica
Al-Taani AT, Ricketts IW, Cairns AY (1996) Classification of hand bones for bone age assessment. Proceedings of the Third IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems. ICECS’96., vol. 2, pp 1088-1091
Bleka Ø, Rolseth V, Dahlberg PS, Saade A, Saade M, Bachs L (2019) BioAlder: a tool for assessing chronological age based on two radiological methods. Int J Legal Med 133(4):1177–1189
Chai HY, Wee LK, Swee TT, Salleh SH (2011) Adaptive crossed reconstructed (acr) k-mean clustering segmentation for computer-aided bone age assessment system. Int J Math Mod Meth Appl Sci 5(3):628–635
Chai HY, Wee LK, Swee TT, Salleh SH, Chia L (2011) An artifacts removal postprocessing for epiphyseal region-of-interest (eroi) localization in automated bone age assessment (baa). Biomed Eng Online 10:87
Cronk C, Schall J, Tanner JM, Marshall WA, Healy MJR, Goldstein H (1987) Assessment of skeletal maturity and prediction of adult height (tw2 method)
Dahlberg PS, Mosdol A, Ding Y, Bleka Rolseth V, Straumann GH, Skjerven-Martinsen M, Delaveris GJ, Vist GE (2019) A systematic review of the agreement between chronological age and skeletal age based on the Greulich and Pyle atlas. Eur Radiol 29(6):2936–2948
Da Silva AMM, Olabarriaga SD, Dietrich CA, Schmitz CA (2001) On determining a signature for skeletal maturity. In Proceedings of XIV Brazilian Symposium on Computer Graphics and Image Processing. IEEE pp 246-251
Dinesh MS, Prakash B, Rao A (1995) Vision system for bone measurement from digital hand radiograph, In Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 1995 and 14th Conference of the Biomedical Engineering Society of India. An International Meeting, Proceedings of the First Regional Conference., IEEE, pp SPC9-SP10
El Soufi K, Kabbara Y, Shahin A, Khalil M, Nait-Ali A (2013) Cimor: An automatic segmentation to extract bone tissue in hand x-ray images. In 2013 2nd International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME). IEEE pp 171–174
Frisch H, Riedl S, Waldhor T (1996) Computer-aided estimation of skeletal age and comparison with bone age evaluations by the method of greulich-pyle and tanner-whitehouse. Pediatr Radiol 26(3):226–231
Gertych A, Zhang A, Sayre J, Pospiech-Kurkowska S, Huang HK (2007) Bone age assessment of children using a digital hand atlas. Comput Med Imaging Graph 31(4):322–331
Gertych A, Zhang A, Sayre J, Pospiech-Kurkowska S, Huang HK (2007) Bone age assessment of children using a digital hand atlas. Comput Med Imaging Graph 31(4–5):322–331
Giordano D, Kavasidis I, Spampinato C (2016) Modeling skeletal bone development with hidden Markov models. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 124:138–147
Greulich WW, Pyle SI (1959) Radiographic atlas of skeletal development of the hand and wrist. Am J Med Sci 238(3):393
Hackman L, Black S (2013) Age estimation from radiographic images of the knee. J Forensic Sci 58(3):732–737
Hackman L, Davies CM, Black S (2013) Age estimation using foot radio graphs from a modern scottish population. J Forensic Sci 58(s1)
Halabi SS, Prevedello LM, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Mamonov AB, Bilbily A, Cicero M, Pan I et al (2019) The RSNA pediatric bone age machine learning challenge. Radiology 29(2):498–503
Han S-H, Kim S-H, Ahn Y-W, Huh G-Y, Kwak D-S, Park D-K, Lee U, Kim Y-S (2009) Microscopic age estimation from the anterior cortex of the femur in Korean adults. J Forensic Sci 54(3):519–522
Hsieh C-W, Liu T-C, Jong T-L, Chen C-Y, Tiu C-M, Chan D-Y (2011) Fast and fully automatic phalanx segmentation using a grayscale-histogram morphology algorithm. Opt Eng 50(8):087007
Hue TTM, Kim JY, Fahriddin M (2011) Hand bone radiograph image segmentation with roi merging, In Proceedings of the 13th IASME/WSEAS International Conference on Mathematical Methods and Computational Techniques in Electrical Engineering conference on Applied Computing. World Scientific and Engineering Academy and Society (WSEAS) pp 147–154
Iscan MY, Loth SR, Wright RK (1984) Age estimation from the rib by phase analysis: white males. J Forensic Sci 29(4):1094–1104
Jing F, Li M, Zhang H-J, Zhang B (2003) Unsupervised image segmentation using local homogeneity analysis. In Proceedings of the 2003 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. IEEE vol. 2, p 2
Kashif M, Deserno TM, Haak D, Jonas S (2016) Feature description with SIFT, SURF, BRIEF, BRISK, or FREAK? A general question answered for bone age assessment. Comput Biol Med 68:67–75
Kimmerle EH, Konigsberg LW, Jantz RL, Baraybar JP (2008) Analysis of age-at-death estimation through the use of pubic symphyseal data. J Forensic Sci 53(3):558–568
Lee H, Tajmir S, Lee J, Zissen M, Yeshiwas BA, Alkasab TK, Choy G, Do S (2017) Fully automated deep learning system for bone age assessment. J Digit Imaging 30(4):427–441
Lehmann TM, Abel J, Weiβ C (2006) The impact of lossless image compression to radiographs. International Society for Optics and Photonics In Medical Imaging p 614516
Mahalakshmi BV, Anand MJ (2014) Adaptive wavelet packet decomposition for efficient image denoising by using neighsuren shrink method. Int J Comput Sci Inf Technol 5(4):5003
Martell M, Fescina RH, Martinez E, Bolivar N (1997) Estimation of gestational age by the length of the dorsal spine. J Perinat Med-Official Journal of the WAPM 25(2):168–172
Materka A, Strzelecki M (1998) Texture analysis methods a review. Technical university of lodz, institute of electronics, COST B11 report, Brussels pp 9-11
Michael DJ, Nelson AC (1989) Handx: a model-based system for automatic segmentation of bones from digital hand radiographs. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 8(1):64–69
Perona P, Malik J (1990) Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 12(7):629–639
Powers DM (2011) Evaluation: from precision, recall and f-measure to roc, informedness, markedness and correlation
Pietka E, McNitt-Gray MF, Kuo ML, Huang HK (1991) Computer assisted phalangeal analysis in skeletal age assessment. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 10(4):616–620
Raj RG (2012) Automated web based system for bone age assessment using historam technique. Malays J Comput Sci 25(3):107–121
Rajith B, Srivastava M, Agarwal S (2016) Edge preserved de-noising method for medical x-ray images using wavelet packet transformation, In Emerging Research in Computing, Information, Communication and Applications. Springer pp 449-467
Rajitha B, Tiwari A, Agarwal S (2015) A new local homogeneity analysis method based on pixel intensities for image defect detection, In IEEE 2nd International Conference on Recent Trends in Information Systems (ReTIS) pp 200-206
Rajitha B, Agarwal S (2015) An iterative thresholding method for epiphysis ROI segmentation for radiographic images. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advanced Research in Computer Science Engineering and Technology (ICARCSET 2015). ACM p 16
Ren X, Li T, Yang X, Wang S, Ahmad S, Xiang L, Stone SR et al (2018) Regression convolutional neural network for automated pediatric bone age assessment from hand radiograph. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23(5):2030–2038
Schmidt S, Nitz I, Schulz R, Schmeling A (2008) Applicability of the skeletal age determination method of tanner and whitehouse for forensic age diagnostics. Int J Legal Med 122(4):309–314
Schneider MK, Fieguth PW, Karl WC, Willsky AS (2000) Multiscale methods for the segmentation and reconstruction of signals and images. IEEE Trans Image Process 9(3):456–468
Seok J, Kasa-Vubu J, DiPietro M, Girard A (2016) Expert system for automated bone age determination. Expert Syst Appl 50:75–88
Stolojescu-CriSan C, Holban S (2013) A comparison of x-ray image segmentation techniques. Adv Electr Comput Eng 13(3)
Tanner J, Oshman D, Bahhage F, Healy M (1997) Tanner-Whitehouse bone age reference values for North American children. J Pediatr 131(1):34–40
Thodberg HH, Kreiborg S, Juul A, Pedersen KD (2008) The BoneXpert method for automated determination of skeletal maturity. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(1):52–66
Thodberg HH, Kreiborg S, Juul A, Pedersen KD (2009) The bonexpert method for automated determination of skeletal maturity. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(1):52–66
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Westerberg E (2020) AI-based age estimation using X-ray hand images: A comparison of object detection and deep learning models. BSc thesis, Department of Software Engineering, Blekinge Institute of Technology
Wu E, Kong B, Wang X, Bai J, Lu Y, Gao F, Zhang S, Cao K, Song Q, Lyu S, Yin Y (2019) Residual attention based network for hand bone age assessment. In 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019) pp 1158-1161
Yildiz M, Guvenis A, Guven E, Talat D, Haktan M (2011) Implementation and statistical evaluation of a webbased software for bone age assessment. J Med Syst 35(6):1485–1489
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to express thanks to Dr. K.V.S.S.B.R.K Subramanyam, Retd. Dy. Cheif Medical Officer, The Singereni Collaries Co.Ltd and Dr. Shailendra Kumar Mishra, Medical Officer In-charge, MNNIT Allahabad for their support and kind help in conducting the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajitha, B., Agarwal, S. Segmentation of Epiphysis Region-of-Interest (EROI) using texture analysis and clustering method for hand bone age assessment. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 1029–1054 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11531-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11531-6