Abstract
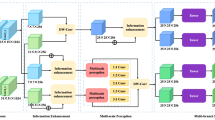
The backbone networks used in Siamese trackers are relatively shallow, such as AlexNet and VGGNet, resulting in insufficient features for tracking task. Therefore, this paper focuses on extracting more discriminative features to improve the performance of Siamese trackers. By comprehensive experimental validations, this goal is achieved through a simple yet effective framework referred as relation-aware Siamese region proposal network (Ra-SiamRPN). Firstly, the deep backbone network ResNet-50 is adopted to extract both low-level detail features and high-level semantic features of an image. Then we propose the feature fusion module (FFM), which can combine low-level detail features with high-level semantic features effectively. Furthermore, we propose the relation reasoning module (RRM) to perform the global relation reasoning in multiple disjoint regions. RRM can generate discriminative information to enhance the features generated by ResNet-50. Extensive experiments are conducted on the dataset OTB2015, VOT2016, VOT2018, UAV123 and LaSOT. The experiment results indicate that Ra-SiamRPN achieves competitive performance with the current advanced algorithms and shows good real-time performance. To be highlighted, in the experiments conducted on the large-scale dataset LaSOT, the success score and the normalized precision score of Ra-SiamRPN are 0.495 and 0.576, respectively. These performance indexes are better than the second best tracker MDNet 24.7% and 25.2%.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell S, Zitnick CL, Bala K, Girshick R (2016) Inside-outside net: detecting objects in context with skip pooling and recurrent neural networks. In: CVPR
Bertasius G, Torresani L, Yu SX, Shi J (2017) Convolutional random walk networks for semantic image segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 858–866
Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques JF, Vedaldi A, Torr PH (2016) Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In: ECCV, pp. 850–865
Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Golodetz S, Miksik O, Torr PH (2016) Staple: complementary learners for real-time tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 1401–1409
Bolme DS, Beveridge JR, Draper BA, Lui YM (2010) Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In: CVPR, pp. 2544–2550
Chandra S, Usunier N, Kokkinos I (2017) Dense and low-rank gaussian crfs using deep embeddings. In: ICCV, pp. 5103–5112
Che M, Wang R, Lu Y, Li Y, Zhi H, Xiong C (2018) Channel pruning for visual tracking. In: ECCVW, pp. 70–82
Choi J, Chang HJ, Fischer T, Yun S, Jin YC (2018) Context-aware deep feature compression for high-speed visual tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 479–488
Dai K, Wang D, Lu H, Sun C, Li J (2019) Visual tracking via adaptive spatially-regularized correlation filters. In: CVPR, pp. 4670–4679
Danelljan M, Häger G, Khan F, Felsberg M (2014) Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking. In: BMVC
Danelljan M, Hager G, Shahbaz Khan F, Felsberg M (2015) Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 4310–4318
Danelljan M, Hager G, Shahbaz Khan F, Felsberg M (2015) Convolutional features for correlation filter based visual tracking. In: ICCVW, pp. 58–66
Danelljan M, Robinson A, Khan FS, Felsberg M (2016) Beyond correlation filters: learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking. In: ECCV, pp. 472–488
Danelljan M, Bhat G, Shahbaz Khan F, Felsberg M (2017) Eco: efficient convolution operators for tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 6638–6646
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L-J, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR, pp. 248–255
Fan H, Ling H (2019) Siamese cascaded region proposal networks for real-time visual tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 7952–7961
Fan H, Lin L, Yang F, Chu P, Ling H (2018) LaSOT: a high-quality benchmark for large-scale single object tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 5374–5383.
Gao J, Zhang T, Xu C (2019) Graph convolutional tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 4649–4659
Grabner H (2006) On-line boosting and vision. In: CVPR
Guo Q, Feng W, Zhou C, Huang R, Wan L, Wang S (2017) learning dynamic siamese network for visual object tracking. In: ICCV, pp 1763-1771
Hare S, Golodetz S, Saffari A, Vineet V, Cheng MM, Hicks SL, Torr PHS (2016) Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. TPAMI 38(10):2096–2109
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp. 770–778
He A, Luo C, Tian X, Zeng W (2018) A twofold siamese network for real-time object tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 4834–4843
Held D, Thrun S, Savarese S (2016) Learning to track at 100 fps with deep regression networks. In: ECCV, pp. 749–765
Henriques JF, Rui C, Martins P, Batista J (2012) Exploiting the Circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In: ECCV, pp. 702–715
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P, Batista J (2014) High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. TPAMI 37(3):583–596
Hong Z, Zhe C, Wang C, Xue M, Tao D (2015) MUlti-store tracker (MUSTer): a cognitive psychology inspired approach to object tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 749–758
Kipf TN, Welling M (2016) Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv:1609.02907
Kong T, Sun F, Tan C, Liu H, Huang W (2018) Deep feature pyramid reconfiguration for object detection. In: ECCV, pp. 169–185
Kristan M, Leonardis A, Matas J, Felsberg M, Pflugfelder R, Cehovin Zajc L, Vojir T, Bhat G, Lukezic A, Eldesokey A (2018) The sixth visual object tracking vot2018 challenge results. In: ECCV, pp. 3–53
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS, pp. 1097–1105
Li B, Yan J, Wu W, Zhu Z, Hu X (2018) High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In: CVPR, pp. 8971–8980
Li F, Tian C, Zuo W, Zhang L, Yang M-H (2018) Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 4904–4913
Li B, Wu W, Wang Q, Zhang F, Xing J, Yan J (2019) Siamrpn++: evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In: CVPR, pp. 4282–4291
Li P, Chen B, Ouyang W, Wang D, Yang X, Lu H (2019) Gradnet: gradient-guided network for visual object tracking. In: ICCV, pp. 6162–6171
Lin TY, Maire M, Belongie S, Bourdev L, Girshick R, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Zitnick CL, Dollár P (2014) Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: ECCV, pp. 740–755
Lin T-Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, He K, Hariharan B, Belongie S (2017) Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: CVPR, pp. 2117–2125
Liu S, Qi L, Qin H, Shi J, Jia J (2018) Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 8759–8768
Lu X, Ma C, Ni B, Yang X, Yang M (2018) Deep regression tracking with shrinkage loss. In: ECCV, pp. 369–386
Lu X, Ma C, Ni B, Yang X (2019) Adaptive region proposal with channel regularization for robust object tracking. TCSVT 1–1
Lu X, Wang W, Ma C, Shen J, Shao L, Porikli F (2019) See more, know more: unsupervised video object segmentation with co-attention siamese networks. In: CVPR, pp. 3618–3627
Lukezic A, Vojir T, Cehovin Zajc L, Matas J, Kristan M (2017) Discriminative correlation filter with channel and spatial reliability. In: CVPR, pp. 6309–6318
Mueller M, Smith N, Ghanem B (2016) A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking. In: ECCV, pp. 445–461
Nam H, Han B (2016) Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 4293–4302
Pinheiro PO, Lin T-Y, Collobert R, Dollár P (2016) Learning to refine object segments. In: ECCV, pp. 75–91
Real E, Shlens J, Mazzocchi S, Xin P, Vanhoucke V (2017) YouTube-BoundingBoxes: a large high-precision human-annotated data set for object detection in video. In: CVPR, pp. 7464–7473
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 234-241
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M (2014) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. IJCV 115(3):211–252
Shen Y, Li H, Yi S, Chen D, Wang X (2018) Person re-identification with deep similarity-guided graph neural network. In: ECCV, pp. 508–526
Song Y, Ma C, Wu X, Gong L, Bao L, Zuo W, Shen C, Lau R, Yang MH (2018) VITAL: VIsual tracking via adversarial learning. In: CVPR, pp. 8990–8999
Tsafack N, Kengne J, Abd-El-Atty B, Iliyasu AM, Hirota K, Abd AA, EL-Latif (2020) Design and implementation of a simple dynamical 4-d chaotic circuit with applications in image encryption. Inf Sci 515:191–217
Valmadre J, Bertinetto L, Henriques J, Vedaldi A, Torr PH (2017) End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 2805–2813
Wang X, Gupta A (2018) Videos as space-time region graphs. In: ECCV, pp. 399–417
Wang W, Lu X, Shen J, Crandall D, Shao L (2019) Zero-shot video object segmentation via attentive graph neural networks. In: ICCV, pp. 9235–9244
Wang Q, Zhang L, Bertinetto L, Hu W, Torr PH (2019) Fast online object tracking and segmentation: a unifying approach. In: CVPR, pp. 1328–1338
Wang X, Zheng Z, He Y, Yan F, Zeng Z, Yang Y (2020). Progressive local filter pruning for image retrieval acceleration arXiv: 2001.08878
Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M-H (2015) Object tracking benchmark. TPAMI 37(9):1834–1848
Yan S, Xiong Y, Lin D (2018) Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: AAAI, pp. 7444–7452
Yang L, Zhu J (2014) A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration.
Zhang Z, Peng H (2019) Deeper and wider siamese networks for real-time visual tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 4591–4600
Zhang J, Ma S, Sclaroff S (2014) MEEM: robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization. In: ECCVW, pp. 254–256
Zhang Y, Wang L, Qi J, Wang D, Feng M, Lu H (2018) Structured siamese network for real-time visual tracking. In: ECCV, pp. 351–366
Zhu Z, Wang Q, Li B, Wu W, Yan J, Hu W (2018) Distractor-aware siamese networks for visual object tracking. In: ECCV, pp. 101–117
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 61971421 and 62071470).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Zhang, G., Zhou, S. et al. Relation-aware Siamese region proposal network for visual object tracking. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 15469–15485 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10574-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10574-z