Abstract
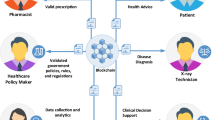
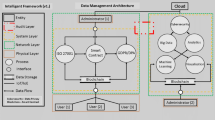
With the rapid increase in urbanisation, the concept of smart cities has attracted considerable attention. By leveraging emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence and cloud computing, smart cities have the potential to improve various indicators of residents’ quality of life. However, threats to data integrity may affect the delivery of such benefits, especially in the IoT environment where most devices are inherently dynamic and have limited resources. Prior work has focused on ensuring integrity of data in a piecemeal manner and covering only some parts of the smart city ecosystem. In this paper, we address integrity of data from an end-to-end perspective, i.e., from the data source to the data consumer. We propose a holistic framework for ensuring integrity of data in smart cities that covers the entire data lifecycle. Our framework is founded on three fundamental concepts, namely, secret sharing, fog computing and blockchain. We provide a detailed description of various components of the framework and also utilize smart healthcare as use case.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alghamdi WY, Wu H, Kanhere SS (2017) Reliable and secure end-to-end data aggregation using secret sharing in wsns. In: Wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), 2017 IEEE, pp 1–6
Bakıcı T, Almirall E, Wareham J (2013) A smart city initiative: the case of barcelona. J Knowl Econ 4(2):135–148
Baliga A (2017) Understanding blockchain consensus models. Persistent
Banerjee M, Lee J, Choo K-KR (2017) A blockchain future for internet-of-things security: a position paper. Digital Communications and Networks
Biswas K, Muthukkumarasamy V (2016) Securing smart cities using blockchain technology. In: , 2016 IEEE 18th international conference on high performance computing and communications; IEEE 14th international conference on smart city; IEEE 2nd international conference on data science and systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), IEEE, pp 1392–1393
Chakrabarty S, Engels DW (2016) A secure iot architecture for smart cities. In: Consumer communications & networking conference (CCNC), 2016 13th IEEE annual, IEEE, pp 812–813
Chang X, Yu Y-L, Yang Y, Xing EP (2017) Semantic pooling for complex event analysis in untrimmed videos. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(8):1617–1632
Dorri A, Kanhere SS, Jurdak R (2017) Towards an optimized blockchain for iot. In: Proceedings of the second international conference on internet-of-things design and implementation, ACM, pp 173–178
Farooq MU, Waseem M, Khairi A, Mazhar S (2015) A critical analysis on the security concerns of internet of things (iot). Int J Comput Appl 7:111
Ferreira C, Walsh R, Ferreira A (2018) Degradation in urban areas. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health
Gope P, Hwang T (2016) Bsn-care: a secure iot-based modern healthcare system using body sensor network. IEEE Sens J 16(5):1368–1376
Jararweh Y, Al-Ayyoub M, Benkhelifa E, et al. (2018) An experimental framework for future smart cities using data fusion and software defined systems: the case of environmental monitoring for smart healthcare. Future Generation Computer Systems
Jose J, Jose J, Princy M (2014) A survey on privacy preserving data aggregation protocols forwireless sensor networks. J Comput Inf Technol 22(1):1–20
Li X, Jiang P, Chen T, Luo X, Wen Q (2017) A survey on the security of blockchain systems. Future Generation Computer Systems
Liu B, Yu XL, Chen S, Xu X, Zhu L (2017) Blockchain based data integrity service framework for iot data. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on Web services (ICWS), IEEE, pp 468–475
Liu C, Yang C, Zhang X, Chen J (2015) External integrity verification for outsourced big data in cloud and iot: a big picture. Futur Gener Comput Syst 49:58–67
Mazieres D (2015) The stellar consensus protocol: a federated model for internet-level consensus. Stellar Development Foundation
Patil NS, Patil P (2010) Data aggregation in wireless sensor network. In: IEEE international conference on computational intelligence and computing research, vol 6
Perera C, Qin Y, Estrella JC, Reiff-Marganiec S, Vasilakos AV (2017) Fog computing for sustainable smart cities: a survey. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 50(3):32
Rezvani M, Ignjatovic A, Bertino E, Jha S (2015) Secure data aggregation technique for wireless sensor networks in the presence of collusion attacks. IEEE Trans Dependable Secure Comput 12(1):98–110
Rifi N, Rachkidi E, Agoulmine N, Taher NC (2017) Towards using blockchain technology for iot data access protection. In: 2017 IEEE 17th international conference on ubiquitous wireless broadband (ICUWB), IEEE, pp 1–5
Sagirlar G, Carminati B, Ferrari E, Sheehan JD, Ragnoli E (2018) Hybrid-iot: Hybrid blockchain architecture for internet of things-pow sub-blockchains. arXiv:1804.03903
Salama U, Yao L, Wang X, Paik H-Y, Beheshti A (2017) Multi-level privacy-preserving access control as a service for personal healthcare monitoring. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on Web services (ICWS), IEEE, pp 878–881
Sandhu RS (1993) On five definitions of data integrity. In: DBSec, pp 257–267
Sharma PK, Chen M-Y, Park JH (2018) A software defined fog node based distributed blockchain cloud architecture for iot. IEEE Access 6:115–124
Sharma PK, Moon SY, Park JH (2017) Block-vn: a distributed blockchain based vehicular network architecture in smart city. J Inf Process Syst 13(1):84
Sheng M, Qin Y, Yao L, Benatallah B (2017) Managing the Web of things: linking the real world to the web. Morgan Kaufmann
Sivathanu G, Wright CP, Zadok E (2005) Ensuring data integrity in storage: techniques and applications. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ACM workshop on storage security and survivability, ACM, pp 26–36
Song T, Li R, Mei B, Yu J, Xing X, Cheng X (2017) A privacy preserving communication protocol for iot applications in smart homes. IEEE Internet Things J 4(6):1844–1852
Su K, Li J, Fu H (2011) Smart city and the applications. In: 2011 International conference on electronics, communications and control (ICECC), IEEE, pp 1028–1031
Yang Y, Wang X, Zhu S, Cao G (2008) Sdap: a secure hop-by-hop data aggregation protocol for sensor networks. ACM Trans Inf Syst Secur (TISSEC) 11(4):18
Yao L, Sheng QZ, Dustdar S (2015) Web-based management of the internet of things. IEEE Internet Comput 19(4):60–67
Yao L, Sheng QZ, Ngu AH, Li X (2016) Things of interest recommendation by leveraging heterogeneous relations in the internet of things. ACM Trans Internet Technol (TOIT) 16(2):9
Yi S, Li C, Li Q (2015) A survey of fog computing: concepts, applications and issues. In: Proceedings of the 2015 workshop on mobile big data, ACM, pp 37–42
Zeng Z, Li Z, Cheng D, Zhang H, Zhan K, Yang Y (2018) Two-stream multirate recurrent neural network for video-based pedestrian reidentification. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 14(7):3179–3186
Zheng Z, Xie S, Dai H-N, Wang H (2016) Blockchain challenges and opportunities: a survey. Work Pap.–2016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altulyan, M., Yao, L., Kanhere, S.S. et al. A unified framework for data integrity protection in people-centric smart cities. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 4989–5002 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7182-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7182-7