Abstract
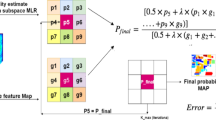
This paper introduces a two-step algorithm which deals with spectral mixing issue as well as performs the empirical study of continuous labelling in HSI images for over segmentation within class labels. In step-1, we have applied a subspace regression followed by an alpha expansion method to obtain the classified HSI image. This method better classifies the HSI image by removing the spectral mixing problem, which is a well-known problem in HSI domain. The classified image of step-1 is directly used in step-2 to improve the classification result by label update optimization using the energy of clusters. The optimization process in step-2 has performed in two phases. In the first phase of step-2, we have updated the cluster centers by the minimization of cluster energy. This energy minimization has stopped until some stopping criteria have met. The energy minimization has resulted in improved cluster centers. In the second phase of step-2, the RBF kernel based image function has updated using improved cluster centres, obtained from the phase-1. Classification probabilistic result from step-1 and updated image function from step-2 has transformed into a spectral data-cost. Subsequently, the data-cost of step-1 and step-2 have fused with the linear decision fusion method. Finally, The graph-cut method has applied to the fused spectral data-cost(Dc) and a spatial smoothness cost(Sc). Fusion of data-costs has resulted in a significant improvement in accuracy.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrieta C, Uribe S, Sing-Long C, Hurtado D, Andia M, Irarrazaval P, Tejos C (2017) Simultaneous left and right ventricle segmentation using topology preserving level sets. Biomed Signal Process Control 33:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2016.11.002, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S174680941630180X
Ayed I B, Mitiche A, Belhadj Z (2006) Polarimetric image segmentation via maximum-likelihood approximation and efficient multiphase level-sets. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(9):1493–1500. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2006.191
Bejinariu S, Luca R, Costin H (2016) Nature-inspired algorithms based multispectral image fusion. In: 2016 International Conference and Exposition on Electrical and Power Engineering (EPE), pp 010–015, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEPE.2016.7781293
Böhning D (1992) Multinomial logistic regression algorithm. Annals of the institute of statistical mathematics 44:197–200
Bioucas-Dias J M, Nascimento J M P (2008) Hyperspectral subspace identification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 46(8):2435–2445. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2008.918089
Boykov Y, Veksler O, Zabih R (2001) Fast approximate energy minimization via graph cuts. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(11):1222–1239. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.969114
Boykov Y, Veksler O, Zabih R (2001) Fast approximate energy minimization via graph cuts. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(11):1222–1239. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.969114
Boykov Y, Kolmogorov V (2004) An experimental comparison of min-cut/max- flow algorithms for energy minimization in vision. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26(9):1124–1137. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2004.60
Boykov Y, Funka-Lea G (2006) Graph cuts and efficient n-d image segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 70(2):109–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-006-7934-5
Camps-Valls G, Bruzzone L (2005) Kernel-based methods for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 43(6):1351–1362. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2005.846154
Chan T F, Vese L A (2001) Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(2):266–277. https://doi.org/10.1109/83.902291
Chan T F, Vese L A (2001) Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(2):266–277. https://doi.org/10.1109/83.902291
Chang H, Yang Q, Auer M, Parvin B (2007) Modeling of front evolution with graph cut optimization. In: 2007 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, vol 1, pp I–241–I–244. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2007.4378936
Cremers D, Rousson M, Deriche R (2007) A review of statistical approaches to level set segmentation: Integrating color, texture, motion and shape. Int J Comput Vis 72(2):195–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-006-8711-1
Dai S, Lu K, Dong J, Zhang Y, Chen Y (2015) A novel approach of lung segmentation on chest ct images using graph cuts. Neurocomputing 168:799 – 807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.05.044, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231215007201
Delong A, Osokin A, Isack H N, Boykov Y (2012) Fast approximate energy minimization with label costs. Int J Comput Vis 96(1):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-011-0437-z
Dhillon I S, Guan Y, Kulis B (2007) Weighted graph cuts without eigenvectors a multilevel approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(11):1944–1957. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1115
Du Q, Younan N H (2008) On the performance improvement for linear discriminant analysis-based hyperspectral image classification. In: 2008 IAPR Workshop on pattern recognition in remote sensing (PRRS, vol 2008, pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/PRRS.2008.4783168
ElZehiry N, Xu S, Sahoo P, Elmaghraby A (2007) Graph cut optimization for the mumford-shah model. In: The Seventh IASTED International Conference on Visualization, Imaging and Image Processing, VIIP ’07. ACTA Press, Anaheim, pp 182–187. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1659167.1659203
El-Zehiry N, Xu S, Sahoo P, Elmaghraby A (2007) Graph cut optimization for the mumford-shah model, pp 182–187
Farhi L, Yusuf A, Raza RH (2017) Adaptive stochastic segmentation via energy-convergence for brain tumor in mr images. J Vis Commun Image Represent 46:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2017.04.013, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1047320317301001
Fukui K (2014) Subspace methods
Jaroszewicz S, Simovici DA (2002) Support approximations using bonferroni-type inequalities. In: Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Principles of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=645806.670302. Springer, London, pp 212–224
Jia S, Tang G, Zhu J, Li Q (2016) A novel ranking-based clustering approach for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(1):88–102. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2015.2450759
Keshava N, Mustard J F (2002) Spectral unmixing. IEEE Signal Proc Mag 19(1):44–57. https://doi.org/10.1109/79.974727
Li J, Bioucas-Dias J M, Plaza A (2010) Semisupervised hyperspectral image segmentation using multinomial logistic regression with active learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 48(11):4085–4098. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2010.2060550
Li J, Bioucas-Dias J M, Plaza A (2011) Hyperspectral image segmentation using a new bayesian approach with active learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 49(10):3947–3960. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2011.2128330
Li J, Bioucas-Dias J M, Plaza A (2012) Spectral–spatial hyperspectral image segmentation using subspace multinomial logistic regression and markov random fields. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 50(3):809–823. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2011.2162649
Liu C, Liu W, Xing W (2017) An improved edge-based level set method combining local regional fitting information for noisy image segmentation. Signal Process 130:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.06.013, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165168416301256
Muller K, Mika S, Ratsch G, Tsuda K, Scholkopf B (2001) An introduction to kernel-based learning algorithms. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12 (2):181–201. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.914517
Mumford D, Shah J (1989) Optimal approximation by piecewise smooth function and associated variational problems. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics 42(5):577–685. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpa.3160420503. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cpa.3160420503
Niu S, Chen Q, deSisternes L, Ji Z, Zhou Z, Rubin DL (2017) Robust noise region-based active contour model via local similarity factor for image segmentation. Pattern Recogn 61:104 – 119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.07.022, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031320316301728
ODuda R, EHArt P, GStork D (2001) Pattern classification
Oja, E (1983)
Poulsen J, French A (2004) Discriminant function analysis
Pratondo A, Chui CK, Ong SH (2017) Integrating machine learning with region-based active contour models in medical image segmentation. J Vis Commun Image Represent 43:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2016.11.019, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1047320316302486
Rother C, Kolmogorov V, Blake A (2004) Grabcut: Interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. ACM Transaction on Graphics 23:309–314
Salah MB, Mitiche A, Ayed IB (2011) Multiregion image segmentation by parametric kernel graph cuts. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(2):545–557. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2066982
Schoenemann T, Cremers D (2006) Near real-time motion segmentation using graph cuts. In: Franke K, Müller KR, Nickolay B, Schäfer R (eds) Pattern Recognition. Springer, Berlin, pp 455–464
Stefano CD, Cioppa AD, Marcelli A (2002) An adaptive weighted majority vote rule for combining multiple classifiers. In: Object recognition supported by user interaction for service robots, vol 2, pp 192–195. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2002.1048270
Sun K, Geng X, Chen J, Ji L, Tang H, Zhao Y, Xu M (2016) A robust and efficient band selection method using graph representation for hyperspectral imagery. Int J Remote Sens 37(20):4874–4889. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1225173
Sun W, Zhang L, Zhang L, Lai Y M (2016) A dissimilarity-weighted sparse self-representation method for band selection in hyperspectral imagery classification. IEEE Jo Sel Top Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 9(9):4374–4388. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2539981
Sun W, Du Q (2018) Graph-regularized fast and robust principal component analysis for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56 (6):3185–3195. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2794443
Thrun S (2002) Exploring artificial intelligence in the new millennium, chapter robotic mapping: A survey, pp 1–35
Veksler O (1999) Efficient graph-based energy minimization methods in computer vision. PhD thesis, Ithaca, pp aAI9939932
Vu N, Manjunath BS (2008) Shape prior segmentation of multiple objects with graph cuts. In: 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587450
Watanabe S, Pakvasa N (1973) Subspace method to pattern recognition
Yang J M, Kuo B C, Yu P T, Chuang C H (2010) A dynamic subspace method for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 48 (7):2840–2853. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2010.2043533
Zeng X, Chen W, Peng Q (2006) Efficiently solving the piecewise constant mumford-shah model using graph cuts
Zeng X, Chen W, Peng Q (2006) Efficiently solving the piecewise constant mumford-shah model using graph cuts
Zheng Q, Li H, Fan B, Wu S, Xu J (2018) Integrating support vector machine and graph cuts for medical image segmentation. J Vis Commun Image Represent 55:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.06.005, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1047320318301305
Zhong Y, Ma A, soon Ong Y, Zhu Z, Zhang L (2018) Computational intelligence in optical remote sensing image processing. Appl Soft Comput 64:75–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.11.045, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568494617307081
Zhong Y, Wang X, Xu Y, Wang S, Jia T, Hu X, Zhao J, Wei L, Zhang L (2018) Mini-uav-borne hyperspectral remote sensing: From observation and processing to applications. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Mag 6(4):46–62. https://doi.org/10.1109/MGRS.2018.2867592
Zhou S, Wang J, Zhang S, Liang Y, Gong Y (2016) Active contour model based on local and global intensity information for medical image segmentation. Neurocomputing 186:107 – 118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.12.073, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231215020469
Zhu SC, Lee TS, Yuille AL (1995) Region competition: unifying snakes, region growing, energy/bayes/mdl for multi-band image segmentation. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 416–423. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.1995.466909
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, V., Biswas, B. A subspace regression and two phase label optimization for High Dimensional Image classification. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 5897–5918 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08477-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08477-1