Abstract
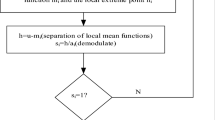
The performance of interpolation algorithm used in bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition directly affects its popularization and application. Therefore, the research on interpolation algorithm is more reasonable, accurate and fast. So far, in the interpolation algorithm adopted by the bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition, an adaptive interpolation algorithm can be proposed according to the image characteristics. In view of this, this paper proposes an image interpolation algorithm based on the particle swarm and fractal. Its procedure includes: to analyze the given image by using the fractal brown function, to pick up the feature quantity from the image, and then to operate the adaptive image interpolation in terms of the obtained feature quantity. The parameters involved in the interpolation process are optimized by particle swarm optimization algorithm, and the optimal parameters are obtained, which can solve the problem of low efficiency and low precision of interpolation algorithm used in bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition. It solves the problem that the image cannot be decomposed to obtain accurate and reliable bi-dimensional intrinsic modal function, and realize the fast decomposition of the image. It lays the foundation for the further popularization and application of the bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition algorithm.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akima H, Gebhardt A, Petzoldt T (2013) “akima: interpolation of irregularly spaced data,” R package version 0.5–11, URL http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=akima
Al-Baddai S, Al-Subari K, Tomé AM (2016) A Green’s function-based bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition. Inf Sci 348:305–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.089
Bernini MB, Federico A, Kaufmann GH (2008) Noise reduction in digital speckle pattern interferometry using bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition. Appl Opt 47(14):2592–2598. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.47.002592
Bernini MB, Federico A, Kaufmann GH (2009) Normalization of fringe patterns using the bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert transform. Appl Opt 48(36):6862–6869. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.48.006862
Bhuiyan SMA, Attoh-Okine NO, Barner KE (2009) Bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition using various interpolation techniques. Adv Adapt Data Anal 1(2):309–338. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536909000084
Bornert M, Doumalin P, Dupré JC (2017) Shortcut in DIC error assessment induced by image interpolation used for subpixel shifting. Opt Lasers Eng 91:124–133
Clerc M (2010) Particle swarm optimization. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 321–389
De Boor C, Höllig K, Sabin M (1987) High accuracy geometric Hermite interpolation. Comput Aided Geom Des 4(4):269–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8396(87)90002-1
Falconer K, Fractal geometry: mathematical foundations and applications. Hoboken: Wiley, 2004, pp. 109–139
Falconer K (2012) Fractals: theory and applications in engineering: theory and applications in engineering. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin, pp 201–289
Goldberg DE (2013) The design of innovation: lessons from and for competent genetic algorithms. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin, pp 138–165
Grefenstette JJ (2013) Genetic algorithms and their applications: proceedings of the second international conference on genetic algorithms. Psychology Press, London, pp 309–337
Grefenstette JJ (2013) Genetic algorithms and their applications: proceedings of the second international conference on genetic algorithms. Psychology Press, London, pp 109–138
He Z, Wang Q, Shen Y (2013) Multivariate gray model-based BEMD for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 62(5):889–904. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2013.2246917
Ke Y, Sukthankar R (2004) PCA-SIFT: A more distinctive representation for local image descriptors. Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on. IEEE, USA, p 506–513
Lei D, Xiaolin H, Feng L (2011) Support vector machines-based method for restraining end effects of B-spline empirical mode decomposition. J Vib Meas Diagn 31(3): 344–347. 3: 1–19
Li T, Wang Y (2011) Biological image fusion using a NSCT based variable-weight method. Inform Fusion 12(2):85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2010.03.007
Lin DC, Guo ZL, An FP (2012) Elimination of end effects in empirical mode decomposition by mirror image coupled with support vector regression. Mech Syst Signal Process 31(1):13–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.02.012
Linderhed A (2005) Variable sampling of the empirical mode decomposition of two-dimensional signals. Int J Wavelets Multiresolution Inf Process 3(3):435–452. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219691305000932
Liu Z, Wang H, Peng S (2004) Texture segmentation using directional empirical mode decomposition. In: Proc. ICIP'04, USA, p 279–282
Nunes JC, Bouaouue Y, Delechelle E (2003) Image analysis by bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition. Image Vis Comput 21(12):1019–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0262-8856(03)00094-5
Nunes JC, Guyot S, Delechelle E (2005) Texture analysis based on local analysis of the bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition. Mach Vis Appl 16(3):177–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-004-0170-5
Panichella A, Dit B, Oliveto R (2013) How to effectively use topic models for software engineering tasks? An approach based on genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Software Engineering, USA, p 522–531
Rubin SG, Khosla PK (1977) Polynomial interpolation methods for viscous flow calculations. J Comput Phys 24(3):217–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(77)90036-5
Sadeghi B, Yu R, Wang R (2018) Shifting interpolation kernel toward orthogonal projection. IEEE Trans Signal Process 66(1):101–112
Sastry K, Goldberg DE, Kendall G (2014) Genetic algorithms. Springer US, Berlin, pp 93–117
Scrucca L (2013) GA: a package for genetic algorithms in R [J]. J Stat Softw 53(4):1–37
Steeb WH (2014) The nonlinear workbook: chaos, fractals, cellular automata, genetic algorithms, gene expression programming, support vector machine, wavelets, hidden Markov models, fuzzy logic with C++, Java and SymbolicC++ programs. World Scientific Publishing Co Inc, Singapore, pp 307–334
Torres IC, Rubio JMA, Ipsen R (2012) Using fractal image analysis to characterize microstructure of low-fat stirred yoghurt manufactured with microparticulated whey protein. J Food Eng 109(4):721–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.11.016
Wang Z, Bovik AC (2009) Mean squared error: love it or leave it? A new look at signal fidelity measures. IEEE Signal Process Mag 26(1):98–117
Wielgus M, Patorski K (2011) Evaluation of amplitude encoded fringe patterns using the bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition and the 2D Hilbert transform generalizations. Appl Opt 50(28):5513–5523. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.50.005513
Wu Z, Huang NE, Chen X (2009) The multi-dimensional ensemble empirical mode decomposition method. Adv Adapt Data Anal 1(3):339–372. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536909000187
Xu G, Cheng Q, Zuo R (2016) Application of improved bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition (BEMD) based on Perona–Malik to identify copper anomaly association in the southwestern Fujian. J Geochem Explor 164:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.013
Yin S, Cao L, Ling Y (2010) One color contrast enhanced infrared and visible image fusion method. Infrared Phys Technol 53(2):146–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2009.10.007
Zhao J, Zhao P, Chen Y (2016) Using an improved BEMD method to analyse the characteristic scale of aeromagnetic data in the Gejiu region of Yunnan, China. Comput Geosci 88(2016):132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2015.12.016
Zhou Y, Li H (2011) Adaptive noise reduction method for DSPI fringes based on bi-dimensional ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Opt Express 19(19):18207–18215. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.19.018207
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Science Foundation Project of P. R. China (No. 61701188).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, FP., Liu, ZW. Bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition (BEMD) algorithm based on particle swarm optimization-fractal interpolation. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 17239–17264 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-7097-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-7097-8