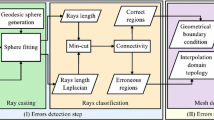
Abstract
Medical images have a very significant impact in the diagnosing and treating process of patient ailments and radiology applications. For many reasons, processing medical images can greatly improve the quality of radiologists’ job. While 2D models have been in use for medical applications for decades, wide-spread utilization of 3D models appeared only in recent years. The proposed work in this paper aims to segment medical volumes under various conditions and in different axel representations. In this paper, we propose an algorithm for segmenting Medical Volumes based on Multiresolution Analysis. Different 3D volume reconstructed versions have been considered to come up with a robust and accurate segmentation results. The proposed algorithm is validated using real medical and Phantom Data. Processing time, segmentation accuracy of predefined data sets and radiologist’s opinions were the key factors for methods validations.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MN, Yamany SM, Mohamed N, Farag AA, Moriarty T (2002) A modified fuzzy c-means algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of mri data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21(3):193–199. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.996338
Al-Ayyoub M, Abu-Dalo AM, Jararweh Y, Jarrah M, Al Sa’d M (2015) A gpu-based implementations of the fuzzy c-means algorithms for medical image segmentation. J Supercomput 71(8):3149–3162
Al-Ayyoub M, AlZu’bi S, Jararweh Y, Shehab MA, Gupta BB (2018) Accelerating 3d medical volume segmentation using gpus. Multimedia Tools and Applications 77(4):4939–4958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4218-0
Al-Zu’bi S, Al-Ayyoub M, Jararweh Y, Shehab MA (2017) Enhanced 3d segmentation techniques for reconstructed 3d medical volumes: robust and accurate intelligent system. Procedia Computer Science 113:531–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.08.318. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877050917317283, the 8th international conference on emerging ubiquitous systems and pervasive networks (EUSPN 2017)
AlZu’bi S, Amira A (2010) 3d medical volume segmentation using hybrid multiresolution statistical approaches. Adv Artificial Intellegence 2010:520,427:1–520,427:15
AlZubi S, Sharif MS, Abbod M (2011a) Efficient implementation and evaluation of wavelet packet for 3d medical image segmentation. In: 2011 IEEE international symposium on medical measurements and applications., pp 619–622 https://doi.org/10.1109/MeMeA.2011.5966667
AlZubi S, Sharif MS, Islam N, Abbod M (2011b) Multi-resolution analysis using curvelet and wavelet transforms for medical imaging. In: 2011 IEEE international symposium on medical measurements and applications, pp 188–191. https://doi.org/10.1109/MeMeA.2011.5966687
AlZubi S, Jararweh Y, Shatnawi R (2012) Medical volume segmentation using 3d multiresolution analysis. In: 2012 international conference on innovations in information technology (IIT), pp 156–159
AlZu’bi S, Shehab M, Al-Ayyoub M, Jararweh Y, Gupta B (2018a) Parallel implementation for 3d medical volume fuzzy segmentation. Pattern Recognition Letters. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.07.026. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016786551830326X
AlZu’bi SM (2011) A 3d multiresolution statistical approaches for accelerated medical image and volume segmentation. PhD thesis, School of Engineering and Design, Brunel University - London
Badura P (2017) Virtual bacterium colony in 3d image segmentation. Comput Med Imaging Graph https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2017.04.004
Berg JV, Kruecker J, Schulz H, Meetz K, Sabczynski J (2004) A hybrid method for registration of interventional ct and ultrasound images. Int Congr Ser 1268:492–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ics.2004.03.171
Bezdek JC (1981) Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell
Clark K, Vendt B, Smith K, Freymann J, Kirby J, Koppel P, Moore S, Phillips S, Maffitt D, Pringle M, Tarbox L, Prior F (2013) Maintaining and operating a public information repository. J Digit Imaging 23(6):1045–1057
Computerized Imaging Reference Systems I (2013) Triple modality 3D abdominal phantom, Model 057A. CIRS
Cook S (2012) CUDA programming: a developer’s guide to parallel computing with GPUs. Applications of GPU Computing Series, Elsevier Science
Doi K (2007) Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: historical review, current status and future potential. Comput Med Imaging Graph 31(4):198–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2007.02.002. Computer-aided Diagnosis (CAD) and Image-guided Decision Support
Drebin RA, Carpenter L, Hanrahan P (1988) Volume rendering. SIGGRAPH Comput Graph 22(4):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1145/378456.378484
Dunn JC (1973) A fuzzy relative of the isodata process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters. J Cybern 3(3):32–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/01969727308546046
Eklund A, Dufort P, Forsberg D, LaConte SM (2013) Medical image processing on the gpu – past, present and future. Med Image Anal 17(8):1073–1094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2013.05.008
El-Dahshan ESA, Mohsen HM, Revett K, Salem ABM (2014) Computer-aided diagnosis of human brain tumor through mri: a survey and a new algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 41(11):5526–5545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.01.021
Engel K, Kraus M, Ertl T (2001) High-quality pre-integrated volume rendering using hardware-accelerated pixel shading. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/EUROGRAPHICS workshop on graphics hardware, ACM, New York, NY, USA, HWWS ’01, pp 9–16 https://doi.org/10.1145/383507.383515
Eschrich S, Ke J, Hall LO, Goldgof DB (2003) Fast accurate fuzzy clustering through data reduction. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 11(2):262–270. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2003.809902
Figueiredo O (1999) Advances in discrete geometry applied to the extraction of planes and surfaces from 3d volumes. PhD thesis, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Fishman EK, Ney DR, Heath DG, Corl FM, Horton KM, Johnson PT (2006) Volume rendering versus maximum intensity projection in ct angiography: what works best, when, and why. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc 26(3):905–22
Fulkerson B, Soatto S (2012) Really quick shift: image segmentation on a gpu. In: Trends and topics in computer vision, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 350–358
Gletsos M, Mougiakakou SG, Matsopoulos GK, Nikita KS, Nikita AS, Kelekis D (2003) A computer-aided diagnostic system to characterize ct focal liver lesions: design and optimization of a neural network classifier. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 7(3):153–162. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2003.813793
Gonzalez RC, Woods RE (2006) Digital image processing, 3rd. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA
Haralick RM, Shapiro LG (1985) Image segmentation techniques. Computer Vision Graphics, and Image Processing 29 (1):100–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-189X(85)90153-7
Hwang C, Rhee FCH (2007) Uncertain fuzzy clustering: interval type-2 fuzzy approach to c-means. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15(1):107–120. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2006.889763
(IEC) IEC, (NEMA) NEMA (2001) Nema standards publication no. nu2. National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) http://jrtassociates.com/pdfs/Pro-NM/20NEMA/20NU2.pdf
Jayashree K, Sandy N (2015) Multi-site collection of lung ct data with nodule segmentations. J Digit Imaging. https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2015.1BUVFJR7, Binsheng Z
Kostrzewa M, Rathmann N, Kara K, Schoenberg SO, Diehl SJ (2015) Accuracy of percutaneous soft-tissue interventions using a multi-axis, c-arm ct system and 3d laser guidance. Eur J Radiol 84(10):1970–1975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.06.028
Lacroute P, Levoy M (1994) Fast volume rendering using a shear-warp factorization of the viewing transformation. In: Proceedings of the 21st annual conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH ’94, pp 451–458. https://doi.org/10.1145/192161.192283
Lee RK, Ihm I (2000) On enhancing the speed of splatting using both object- and image-space coherence. Graph Model 62(4):263–282. https://doi.org/10.1006/gmod.2000.0524
Levoy M (1988) Display of surfaces from volume data. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 8(3):29–37. https://doi.org/10.1109/38.511
Li J, Wu Y, Zhao J, Lu K (2016a) Multi-manifold sparse graph embedding for multi-modal image classification. Neurocomputing 173:501–510
Li J, Zhao J, Lu K (2016b) Joint feature selection and structure preservation for domain adaptation. In: IjCAI, pp 1697–1703
Li J, Wu Y, Zhao J, Lu K (2017a) Low-rank discriminant embedding for multiview learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 47(11):3516–3529
Li J, Lu K, Huang Z, Zhu L (2018) Transfer independently together: a generalized framework for domain adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics
Li Z, Nie F, Chang X, Yang Y (2017b) Beyond trace ratio: weighted harmonic mean of trace ratios for multiclass discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 29(10):2100–2110
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, van der Laak JA, van Ginneken B, Sánchez CI (2017) A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 42:60–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005
Lum EB, Wilson B, Ma KL (2004) High-quality lighting and efficient pre-integration for volume rendering. In: VISSYM’04
Luo M, Chang X, Li Z, Nie L, Hauptmann AG, Zheng Q (2017) Simple to complex cross-modal learning to rank. Comput Vis Image Underst 163:67–77
M Al-Ayyoub DAZ (2013) Determining the type of long bone fractures in x-ray images. WSEAS Trans Inf Sci Appl 10(8):261–270
Ma Z, Chang X, Yang Y, Sebe N, Hauptmann AG (2017) The many shades of negativity. IEEE Trans Multimedia 19(7):1558–1568
Max N, Hanrahan P, Crawfis R (1990) Area and volume coherence for efficient visualization of 3d scalar functions. In: Computer Graphics, pp 27–33
McInerney T, Terzopoulos D (1996) Deformable models in medical image analysis: a survey. Med Image Anal 1(2):91–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1361-8415(96)80007-7
Montgomery D (2006) Multiscale compression and segmentation of volumetric oncological pet imagery. PhD thesis, The Queen’s University of Belfast
Mortensen EN, Barrett WA (1998) Interactive segmentation with intelligent scissors. Graphical Models and Image Processing 60(5):349–384. https://doi.org/10.1006/gmip.1998.0480
Nikolaidis D (2001) 3-D image processing algorithms. PhD thesis, The Queen’s University of Belfast
Osher S, Fedkiw R (2002) Level set methods and dynamic implicit surfaces. Applied Mathematical Sciences. Springer, New York
Pawel B, Kawa J, Czajkowska J, Rudzki M, Pietka E (2011) Fuzzy connectedness in segmentation of medical images, a look at the pros and cons. International Conference on Fuzzy Computation Theory and Applications 2011:486–492
Pham DL, Xu C, Prince JL (2000) Current methods in medical image segmentation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2(1):315–337. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bioeng.2.1.315. pMID: 11701515
Pietka E, Kawa J, Badura P, Spinczyk D (2010) Open architecture computer-aided diagnosis system. Expert Syst 27(1):17–39
Shih F (2009) Image Processing and Mathematical Morphology: Fundamentals and Applications. CRC Press
Silverstein JC, Parsad NM, Tsirline V (2008) Automatic perceptual color map generation for realistic volume visualization. J Biomed Inform 41(6):927–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2008.02.008
Stytz MR, Frieder G, Frieder O (1991) Three-dimensional medical imaging: algorithms and computer systems. ACM Comput Surv 23:421–499
Udupa JK, Samarasekera S (1996) Fuzzy connectedness and object definition: theory, algorithms, and applications in image segmentation. Graphical Models and Image Processing 58(3):246–261. https://doi.org/10.1006/gmip.1996.0021
Vázquez V, Eugenio M, Pedro G, Manlio FVC, Felipe n C, Eduardo AV, Claudio VS, Kirby GV, Manuel D, Javier P (2017) Assessment of intraoperative 3d imaging alternatives for ioert dose estimation. Zeitschrift fü,r Medizinische Physik 27(3):218–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.zemedi.2016.07.002
Wiecawek W, Pitka E (2008) Fuzzy clustering in segmentation of abdominal structures based on ct studies. In: Pietka E, Kawa J (eds) Information technologies in biomedicine, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 93–104
Wieclawek W, Pietka E (2007) Live-wire-based 3d segmentation method. In: 2007 29th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, pp 5645–5648. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4353627
Wieclawek W, Pietka E (2015) Watershed based intelligent scissors. Comput Med Imaging Graph 43:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2015.01.003
Won HJ, Kim N, Kim GB, Seo JB, Kim H (2017) Validation of a ct-guided intervention robot for biopsy and radiofrequency ablation: experimental study with an abdominal phantom. Diagn Interv Radiol 23:233–237
Xu R, Wunsch D (2005) Survey of clustering algorithms. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16(3):645–678. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2005.845141
Zarychta P, Konik H, Zarychta-bargieła A (2012) Computer assisted location of the lower limb mechanical axis. In: Information technologies in biomedicine, Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 93–100
Zhang Y, Matuszewski BJ, Shark LK, Moore CJ (2008) Medical image segmentation using new hybrid level-set method. In: 2008 fifth international conference biomedical visualization: information visualization in medical and biomedical informatics, pp 71–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/MediVis.2008.12
Zhao B (2015) Data from lung phantom. The cancer imaging archive https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2015.08A1IXOO
Zhu L, Shen J, Jin H, Xie L, Zheng R (2015a) Landmark classification with hierarchical multi-modal exemplar feature. IEEE Trans Multimedia 17(7):981–993
Zhu L, Shen J, Jin H, Zheng R, Xie L (2015b) Content-based visual landmark search via multimodal hypergraph learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 45(12):2756–2769
Zhu L, Huang Z, Liu X, He X, Sun J, Zhou X (2017a) Discrete multimodal hashing with canonical views for robust mobile landmark search. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 19(9):2066–2079
Zhu L, Shen J, Xie L, Cheng Z (2017b) Unsupervised topic hypergraph hashing for efficient mobile image retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 47(11):3941–3954
Zhu L, Shen J, Xie L, Cheng Z (2017c) Unsupervised visual hashing with semantic assistant for content-based image retrieval. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 29(2):472–486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AlZu’bi, S., Jararweh, Y., Al-Zoubi, H. et al. Multi-orientation geometric medical volumes segmentation using 3D multiresolution analysis. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 24223–24248 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-7003-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-7003-4