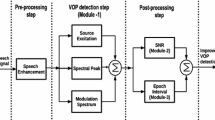
Abstract
People suffering from hearing loss have great difficulty to hear even with the help of hearing aids due to background noises. The problem of reducing noise in hearing aids still remains as a toughest problem to solve. A speech upgrade method to be specific, a modified spectral subtraction is proposed to decrease the different foundation noises and its execution is tried with target quality estimation parameter like signal to noise ratio (SNR) and perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ), and furthermore Vowels are thought to be voiced sounds with more vitality for discourse creation. And hence from the enhanced speech signal the formant frequency of the voiced vowels is extracted based on autocorrelation method and in future work thereby increase the intelligibility of the vowels by enhancing the formants for the hearing aid listeners.










Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 September 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13858-0
References
A Noisy Speech Corpus for Assessment of Speech enhancement Algorithms http://www.utdallas.edu/~Ioizou/speech/noizeus
Acoustical Solutions, Inc. Introduction to noise control, Acoustic Education
Anitha Sheela K et al Spectral subtraction technique for speech enhancement - A Review, ICRACVES-2014, ISSN (Online):2349–0020, ISSN (Print): 2394–4544
Berouti M, Schwartz R, Makhoul J (1979) Enhancement of speech corrupted by acoustic noise. In: Processing of International Conference of Acoustic, Speech and signal Processing, pp. 208–211
Cohen I (2003) Noise Spectrum estimation in adverse environment: Improved minima controlled recursive averaging. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 11:466–475
Cohen I (2005) Senior member, relaxed statistical model for speech enhancement and a priori SNR estimation. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 13(5)
Cohen I, Berdugo B (2001) Speech Enhancement for non-stationary noise environments. Signal Process 81(11):2403–2418
Dhivya E, Justin J (2016) Performance evaluation of speech enhancement techniques using wavelets. Proceedings of International conference on soft computing systems, Advances in Intelligence and computing 397CTU, pp. 47–49
Donoho DL (2015) Denoising by soft thresholding. IEEE Trans on Information Theory 41(3):613–627
Fry DB, Abramson AS, Eimas PD, Liberman AM (1962) The identification and discrimination of synthetic vowels. Lang Speech 5(4):171–189
Helmholtz HL (2009) On the sensations of tone as a physiological basis for the theory of music. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge
Hu Y, Loizou PC (2003) A perceptually motivated approach for speech enhancement. IEEE Trans Audio, Speech and Language Processing 11:457–465
Kamrul Hasan MD, Salahuddin S, Rezwan Khan M (2004) A modified A priori SNR for speech enhancement using spectral subtraction rules. IEEE Signal Processing Letters (4)
Kewley-Port D, Burkle TZ, Lee JH (2007) Contribution of consonant versus vowel information to sentence intelligibility for young normal hearing and elderly hearing-impaired listeners. J Acoust Soc Amer 122(4):2365–2375
Kuppusamy PG, Malini RRH (2012) An iterative and adaptive pixel wise maximum absolute difference (PMAD) based image filter for impulse noise removal. European Journal of Scientific Research
Parikh K, Loizou PC (2005) The influence of noise on vowel and consonant cues. J Acoust Soc Amer 118(6):3874–3888
Parlak K, Moreno OG (2012) Applied speech enhancement in mobile communication acoustics: background noise elimination with filtering algorithms. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing
Rao A, Carney LH (2014) Speech enhancement for hearing loss based on vowel coding in auditory midbrain. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 61(7)
Scalart P, Vieira-Filho J (1996) Speech enhancement based on a priori signal to noise estimation. In: Proceedings ICASSP, pp. 629–632
Upadhyay N, Karmakar A (2013) An Improved Multi-Band Spectral subtraction Algorithm for Enhancing Speech in Various Noise Environments, International Conference on Design and Manufacturing, IConDM 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng2013.09.103
Zahorian SA, Jagharghi AJ (1993) Spectral-shape features versus formants as acoustic correlates for vowels. J Acoust Soc Amer 94(4):1966–1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13858-0
About this article
Cite this article
Vanitha Lakshmi, M., Sudha, S. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Noise diminution and formant extraction on vowels for hearing aid users. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 3729–3741 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6914-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6914-4