Abstract
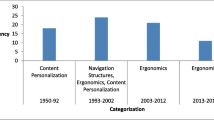
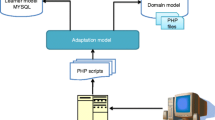
This research drill presents a perspective on modeling an Adaptive Hypermedia Instructional System (AHIS), by integrating investigational research findings on technology and education. In the past decade, a number of adaptive hypermedia learning systems have been developed. Most of these systems deliver instructions according to learner prior knowledge. Each learner, process and organize instruction in a different way. An effective and efficient instruction significantly affect student learning. Thus, researchers and practitioners are investigating ways to design and develop effective and efficient instructions. Proposed Adaptive Hypermedia Instructional System based on Component Display Theory (CDT) given by (Merrill, 1983) present guidelines to design effective and efficient instruction. Present study showed that an instruction is a balanced combination of - Graphic Aesthetic, Ergonomics, Hypermedia and Media building blocks. As a consequence, critical survey was conducted. Survey included 60 studies out which 30 studies were on adaptive systems (14 were peer reviewed journals). Survey revealed that little adaptation focus has been laid on Instructional Strategies and Components of Instruction. As a result, described framework (AHIS) assists in formulating efficient and effective instruction to achieve desired learning outcome. The design, development and improvement of learning instructions in AHIS are based on Media Worthiness, Ergonomics, Hypermedia, Attributes and Methods building blocks. Framework is at more abstract and coarse-grain level and calls for its evolution into Shell. Thus, we conceived the Modelling of Adaptive Hypermedia Instructional System (AHIS) by integrating the research findings of micro-studies on various aspects of Ergonomic, Hypermedia and Media. Effectiveness of instructions was evaluated by forty-four undergraduate students. Results indicate that instructions designed through Adaptive Hypermedia Instructional System were learner engaging and considerably affect learner performance. The implications of these results for the design of Adaptive Hypermedia Instructional System are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agelight L (2001) Interface design guidelines for users of all ages. URL: http://www.agelight.com/webdocs/designguide. …,. Available: http://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&btnG=Search&q=intitle:Interface+Design+Guidelines+for+Users+of+All+Ages#0%5Cnhttp://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&btnG=Search&q=intitle:Interface+design+guidelines+for+users+of+all+ages#0
Allen WH (1966) Reading in educational media theory and research. 14(2):157–183
Altaboli A, Lin Y (2011) Investigating Effects of Screen Layout Elements on Interface and Screen Design Aesthetics. Adv Human-Computer Interact 2011:1–10
Andre T (1990) Type of Inserted Question and the Study-Posttest Delay. J Exp Educ 58(2):77–86
Anglin GJ (1986) Effect of pictures on recall of written prose: how durable are picture effects? Annual Convention of the Association for Educational Communications and Technology, Las Vegas
Atkinson RK (2002) Optimizing Learning From Examples Using Animated Pedagogical Agents. J Educ Psychol 94(2):416–427
Bajraktarevic N, Hall W, Fullick P (2003) Incorporating learning styles in hypermedia environment: Empirical evaluation. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Adaptive Web-Based Systems, no. 1999, pp. 41–52
Bajraktarevic N, Hall W, Fullick P (2003) ILASH: Incorporating learning strategies in hypermedia. In Twelfth International World Wide Web Based Systems, no. 1993, pp. 1–9
Benabou R, Triole J (2003) Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation. Rev Econ Stud 70(2):489–520
Bernard M, Linda B, Riley S, Hackler T, Janzen K (2002) A Comparison of Popular online Fonts: Which Size and Type is Best,” Usability News, 3
Bernard, M, Mills M, Peterson M (2001) A Comparison of Popular Online Fonts: Which is Best and When?,” Usability News, 3. Available: http://psychology.wichita.edu/surl/usabilitynews/3S/usability_news.html
Bodemer D, Ploetzner R, Feuerlein I, Spada H (2004) The active integration of information during learning with dynamic and interactive visualisations. Learn Instr 14:325–341
G. H. Bower and E. R. Hilgard, Theories of Learning, vol. 3. 1948
Carver CA, Howard RA, Lane WD (1999) Enhancing Student Learning Through Hypermedia Courseware and Incorporation of Student Learning Styles. IEEE Trans Educ 42(1):33–38
Chanijani SSM, Bukhari SS, Dengel A (2015) Analysis of text layout quality using wearable eye trackers. In IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), pp. 1–6
Chiu C, Tseng JCR, Hsu TY (2017) Blended context-aware ubiquitous learning in museums : environment , navigation support and system development. Pers Ubiquit Comput 21(2):355–369
Corder PR (1994) Instructional System And Method For Improving Communication SKills. 5302132
Del Corso D, Ovcin E, Morrone G, Gianesini D, Salojarvi S, Kvist T (2001) 3DE: An Environment For The Development Of Learner-Centered Custom Educational Packages. In 31 ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference, vol. 2
Dias P, Gomes MJ, Correia AP (1999) Dissorientation in Hypermedia Enviornments: Mechanism To Support Navigation. J Educ Comput Res 20(2)
Dyson MC (2004) How physical text layout affects reading from screen. Behav Inform Technol 23(6):377–393
Gilbert JE, Han CY (2002) Arthur: A personalized instructional system. J Comput High Educ 14(1):113–129
Hartely J (1996) Text Design. In Handbook of research for eduactional comunications and technology, pp. 795–820
Hasan EHR (2001) Instructional Design and Media Selection. University of Twente
Hoffler TN, Leutner D (2007) Instructional animation versus static pictures: A meta-analysis. Learn Instr 17:722–738
IMS (2003) web.pdf. Available: www.imsglobal.org
Jeong H (2016) UX based adaptive e-learning hypermedia system (U-AEHS): an integrative user model approach. Multimed Tools Appl 13193–13209
Jonassen D (1988) Designing Structured Hypertext and Structuring Access to Hypertext. J. Educ. Technol
Keller JM (1979) Motivation and Instructional Design: A Theoretical Perspective. J Instr Dev 2(4):26–34
King A (2017) Method and System For Facilitating Provisioning Of Media For Instructional Use. US 20170358231A1
Kozma RB (1991) Learning with Media. Rev Educ Res 61(2):179–211
Kruk P, Muter RS (1984) Reading of Continuous Text on Video Screens. Hum Factors 3(26):339–345
Latham AM, Crockett KA, McLean DA, Edmonds B, O’Shea K (2010) Oscar: An intelligent conversational agent tutor to estimate learning styles. In: 2010 IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, WCCI 2010, 44
Lin CF, Hung YH, Chang RI, Hung SH (2014) Developing a problem-solving learning system to assess the effects of different materials on learning performance and attitudes. Comput Educ 77:50–66
Mangen A, Walgermo BR, Brønnick K (2013) Reading linear texts on paper versus computer screen : Effects on reading comprehension. Int J Educ Res 58:61–68
Martinez M (2001) Key Design Considerations for Personalized Learning on the Web. Educ Technol Soc 10(1):26–40
Mayer RE (2005) Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning. In The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning, pp. 31–48
Mayer R, Gallini JK (1990) When is an illustration worth ten thousand words? J Educ Psychol 82
Mayer RE, Heiser J, Lonn S (2001) Cognitive Constraints on Multimedia Learning: When Presenting More Material Results in Less Understanding. J Educ Psychol 93(1):187–198
Mayer G, Lingle J, Usselman M (2017) Experiences of Advanced High School Students in Synchronous Online Recitations. Educ Technol Soc 20(2):15–26
Mayer G, Lingle J, Usselman M (2017) Experiences of Advanced High School Students in Synchronous Online Recitations. Int Forum Educ Technol Soc 20(2):15–26
Merrill MD (1983) The descriptive component display theory. In: Instructional Design Theories and Models: An overview of their current status, pp. 282–333
Moore DMM, Burton JK, Myers RJ (1994) Multiple-channel communication: the theoretical and research foundations of multimedia. In: Handbook of Research for Educational Communications and Technology, 851–875, pp. 979–1006
Mørch AI, Engeness I, Cheng VC, Cheung WK, Wong KC (2017) EssayCritic : Writing to Learn with a Knowledge-Based Design Critiquing System. Int Forum Educ Technol Soc 20(2):213–223
Ngo DCL, Teo LS, Byrne JG (2000) Formalising guidelines for the design of screen layouts. Displays 21:3–15
Norma DB Pribadi S, Wadlow MG (1990) The use of color in computer interfaces: preliminary research
Özyurt Ö, Özyurt H, Baki A (2013) Design and development of an innovative individualized adaptive and intelligent e-learning system for teaching – learning of probability unit : Details of UZWEBMAT. Expert Syst Appl 40:2914–2940
Papanikolaou KA, Grigoriadou M, Kornilakis H, Magoulas GD (2003) Personalizing the interaction in a web-based educational hypermedia system: The case of INSPIRE. User Model User-Adapted Interact 13(3):213–267
Park O, Lee J (2003) Adaptive instructional systems. Handb Res Educ Commun Technol 1911:651–684
Pena C, Marzo J-L, de la Rosa J-L (2004) Curriculum sequencing for an e-learning system. Inf Tecnol Based High Educ Train: 167–172
Peter SE, Bacon E, Dastbaz M (2010) Adaptable, personalised e-learning incorporating learning styles. Campus-Wide Inf Syst 27(2):91–100
Pezdek K, Stevens E (1984) Children ’ s Memory for Auditory and Visual Information on Television. Dev Psychol 20(2):212–218
Popescu E (2010) Adaptation provisioning with respect to learning styles in a Web-based educational system : an experimental study. J Comput Assist Learn 26:243–257
Porion A, Aparicio X, Megalakaki O, Robert A (2016) The impact of paper-based versus computerized presentation on text comprehension and memorization. Comput Hum Behav 54:569–576
Prieto M, García F (2006) METHADIS: Methodology for the Design of Adaptive Hypermedia Systems for Learning based on Learning and Cognitive Styles. In: Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies
Ragan T, Smith P (2004) Conditions theory and models for designing instructions. Handb Res Educ Commun Technol 623–650
Rahadian RB, Budiningsih CA (2018) What are the suitable instructional strategy and media for student learning styles in middle schools? Int J Integr Technol Educ 6(4):25–39
Rakes TA, Kutzman SK (1982) The Selection And Use Of Reading Games And Activities. Read Horizons 49(2):67–70
Rangan TJ, Smith PL (2004) Conditions based models for designing instruction. In: Handbook of research for eduactional comunications and technology, pp. 623–649
Sancho P, Martínez I, Fernández-Manjón B (2005) Semantic Web Technologies Applied to e-learning Personalization in <e-aula>. J Univ Comput Sci 11(9):1470–1481
Schiaffino S, Garcia P, Amandi A (2008) eTeacher: Providing personalized assistance to e-learning students. Comput Educ 51:1744–1754
Shang Y, Shi H, Chen S-S (2001) An intelligent distributed environment for active learning. ACM J Educ Resour Comput 1(2):308–315
Siadaty M, Taghiyareh F (2007) PALS2: Pedagogically adaptive learning system based on Learning Styles In: Seventh IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT 2007), pp. 2–4
Tennyson RD, Cocchiarella MJ (1986) An Empirically Based Instructional Design Theory for Teaching Concepts. Am Educ Res Assoc 56(1):40–71
Tolhurst D (1992) A Checklist for Evaluating Content Based Hypertext Computer Software. J. Educ. Technol
Triantafillou E, Pomportsis A, Demetriadis S (2003) The design and the formative evaluation of an adaptive educational system based on cognitive style. Comput Educ 41:87–103
Wang H, Li T, Chang C (2004) A Web-based Tutoring System with Styles-matching Strategy for Learning Spatial Geometry. In International Computer Symposium
Williams R (2004) Non-Designer’s Design Book
Wolf C (2007) Construction of an adaptive e-learning environment to address styles and an investigation of the effect of media choice. RMIT University, Melbourne
Wu T, Huang Y (2017) A Mobile Game-Based English Vocabulary Practice System Based on Portfolio Analysis. Int Forum Educ Technol Soc 20(2):265–277
Wu WV, Scott J, Hsieh C, Yang JC (2017) Creating an online learning community in a flipped classroom to enhance EFL learners ’ oral proficiency. Int Forum Educ Technol Soc 20(2)
Young M (2004) An ecological psychology of instructional design: Learning and thinking by perceiving – acting systems. Handb Res Educ Commun Technol: 169–178
Zatarain R, Lucía M, Estrada B, Alberto C, García R (2011) EDUCA: A web 2 . 0 authoring tool for developing adaptive and intelligent tutoring systems using a Kohonen network. Expert Syst Appl 38(8):9522–9529
Zengin Y (2017) Investigating the Use of the Khan Academy and Mathematics Software with a Flipped Classroom Approach in Mathematics Teaching. J Educ Technol Soc 20(2):89–100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.J., Mustafa, K. Modelling adaptive hypermedia instructional system: a framework. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 14397–14424 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6819-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6819-2