Abstract
Most of current crowd simulation methods have considered the impact of interindividual emotion on the agent’s behavior pattern during emergency evacuations. However, the emotion contagion is not only at the individual level, but also at the contagion in groups. Psychological researches show that the third-party authority also has an impact on emotion contagion. For example, security guards can guide individuals to find exits and calms them; and teachers can lead their students safely evacuate from multi-layer teaching buildings, etc. In this paper, we propose a unified framework to simulate the emergency evacuations in virtual environment. This framework considers four kinds of agents: third-party authority agents, group leaders, members and isolated agents. Firstly, we randomly assign each agent a specific personality and initialize its emotion. Secondly, the emotion contagion in this paper is considered with three aspects: intra-group contagion, inter-group contagion and third-party authority based emotion contagion. We simulate inter-group aggregated behaviors by improving the ASCRIBE and provide a threshold model to simulate inter-group switching behaviors. The third-party authorities exhibit a calm effect on the agents during an evacuation, and we set their negative emotion very low and keep unchanged. Meanwhile, we perform high-level path planning to explore the environments and obtain a cognitive map for navigation purposes. Through quantitative and qualitative experiments, simulation results demonstrate that our proposed model can simulate the emotion contagion in groups during emergency evacuations, and our model outperforms some existing works.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 July 2018
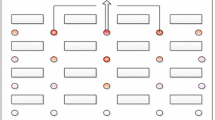
In the original publication, Figs. 1 and 4 contain an error. Figure 1 on page 7, in the lower right corner of the image below “Leader 2” should be corrected to “Group 2” instead of “Group 1”. Figure 4 on page 12, on the left part of the image, “Group 3” should be corrected to “Group 1.”
References
Barsade SG (2002) The ripple effect: emotional contagion and its influence on group behavior. Adm Sci Q 47:644–675. https://doi.org/10.2307/3094912
Barsade SG, Gibson DE (1998) Group emotion: a view from top and bottom. Research on managing groups and teams 1:81–102
BBC news (2015) Shanghai new year crush kills 36. BBC News. http://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-china-30646918. Accessed 1 Jan 2015
Bellomo N, Gibelli L (2016) Behavioral crowds: modeling and Monte Carlo simulations toward validation. Comput Fluids 141:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2016.04.022
Bellomo N, Clarke D, Gibelli L, Townsend P, Vreugdenhil B (2016) Human behaviours in evacuation crowd dynamics: from modelling to “big data” toward crisis management. Phys Life Rev 18:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plrev.2016.05.014
BNO news (2016) Oromia: Stampede at Ethiopia protest leaves 52 dead. BBC News. http://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-37534387. Accessed 3 Oct 2016
BNO news (2017) Panic erupts during Champions League viewing in Italy, injuring 1,500. BNO News. http://bnonews.com/news/index.php/news/id5974. Accessed 3 June 2017
Bosse T, Duell R, Memon ZA, Treur J, van der Wal CN (2015) Agent based modeling of emotion contagion in groups. Cogn Comput 7:111–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-014-9277-9
Bruneau J, Olivier A-H, Pettre J (2015) Going through, going around: a study on individual avoidance of groups. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 21:520–528. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2015.2391862
Cao M, Zhang G, Wang M, Lu D, Liu H (2017) A method of emotion contagion for crowd evacuation. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 483:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.04.137
Doulamis N (2009) Evacuation planning through cognitive crowd tracking. In: Systems, Signals and Image Processing 16th International Conference on: 1–4. doi:10.1109/IWSSIP.2009.5367704
Doulamis N, Doulamis A, Makantasis K, Karantzalos K, Loupos K (2015) Micro-scale thermal behavioral analysis for active evacuation routes. Proceedings of the 8th ACM International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments 50:51–54. https://doi.org/10.1145/2769493.2769575
Durupinar F, Pelechano N, Allbeck J, Gudukbay U, Badler NI (2011) How the ocean personality model affects the perception of crowds. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 31:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCG.2009.105
Durupınar F, Güdükbay U, Aman A, Badler NI (2016) Psychological parameters for crowd simulation: from audiences to mobs. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 22:2145–2159. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2015.2501801
Eysenck HJ (1991) Dimensions of personality. In: Explorations in temperament. Springer 87–103. doi:10.1007/978-1-4899-0643-4_7
Faroqi H, Mesgari M-S (2015) Agent based crowd simulation considering emotion contagion for emergency evacuation problem. The International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 40:193. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsarchives-XL-1-W5-193-2015
Gebhard P (2005) ALMA: a layered model of affect. In: Proceedings of the fourth international joint conference on Autonomous agents and multiagent systems 29–36. doi:10.1145/1082473.1082478
Guy SJ, Kim S, Lin MC, Manocha D (2011) Simulating heterogeneous crowd behaviors using personality trait theory. In: Proceedings of the 2011 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on computer animation 43–52. doi:10.1145/2019406.2019413
Hatfield E, Cacioppo JT, Rapson RL (1993) Emotional contagion. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 2:96–100
He W, Chen JX, Zhang W (2016) Crowd simulation using DC model and density information. Multimedia Tools and Applications 75:5981–5998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2561-1
Helbing D, Molnar P (1995) Social force model for pedestrian dynamics. Phys Rev E 51:4282–4286. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.51.4282
Helbing D, Farkas I, Vicsek T (2000) Simulating dynamical features of escape panic. Nature 407:487–490. https://doi.org/10.1038/35035023
Hughes RL (2002) A continuum theory for the flow of pedestrians. Transp Res B Methodol 36:507–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-2615(01)00015-7
Jaklin N, Kremyzas A, Geraerts R (2015) Adding sociality to virtual pedestrian groups. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology 163–172. doi:10.1145/2821592.2821597
Kim S, Guy SJ, Manocha D, Lin MC (2012) Interactive simulation of dynamic crowd behaviors using general adaptation syndrome theory. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games 55–62. doi:10.1145/2159616.2159626
Kim S, Guy SJ, Manocha D (2013) Velocity based modeling of physical interactions in multi-agent simulations. In: Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on computer animation:125–133. doi:10.1145/2485895.2485910
Mehrabian A (1996) Pleasure-arousal-dominance: a general framework for describing and measuring individual differences in temperament. Curr Psychol 14:261–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02686918
Narain R, Golas A, Curtis S, Lin MC (2009) Aggregate dynamics for dense crowd simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 28(122):121–128. https://doi.org/10.1145/1661412.1618468
O'Connor S, Liarokapis F, Jayne C (2015) Perceived realism of crowd behaviour with social forces. In: Information Visualisation (iV), 2015 19th International Conference on: 494–499. doi:10.1109/iV.2015.88
Ortony A, Clore GL, Collins A (1990) The cognitive structure of emotions. Cambridge university press
Park SI, Quek F, Cao Y (2012) Modeling social groups in crowds using common ground theory. In: Simulation Conference (WSC), Proceedings of the 2012 Winter 1–12. doi:10.1109/WSC.2012.6465119
Pelechano N, O'Brien K, Silverman B, Badler N (2005) Crowd simulation incorporating agent psychological models, roles and communication. A: International Workshop on Crowd Simulation. First International Workshop on Crowd Simulation 1–10
Pelechano N, Allbeck JM, Badler NI (2007) Controlling individual agents in high-density crowd simulation. In: Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation 99–108
Reynolds CW (1987) Flocks, herds and schools: a distributed behavioral model. ACM SIGGRAPH computer graphics 21:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1145/37401.37406
Sabeur Z, Doulamis N, Middleton L, Arbab-Zavar B, Correndo G, Amditis A (2015) Multi-modal computer vision for the detection of multi-scale crowd physical motions and behavior in confined spaces. In: International Symposium on Visual Computing: 162–173. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-27857-5_15
Sinclair J, Lui CSM (2015) Integrating personality and emotion for human crowd simulation. In: The Fifteenth International Conference on Electronic Business: 300–307
Staff BP (2015) PM Modi condoles loss of Lives during Stampede at Mina in Saudi Arabia. Biharprabha News Copyright. http://news.biharprabha.com/2015/09/pm-modi-condoles-loss-of-lives-during-stampede-at-mina-in-saudi-arabia/. Accessed 24 Sept 2015
Stamatopoulou I, Sakellariou I, Kefalas P (2012) Formal agent based modelling and simulation of crowd behaviour in emergency evacuation plans. In: Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), 2012 I.E. 24th International Conference on 1:1133–1138. doi:10.1109/ICTAI.2012.161
Sung M, Gleicher M, Chenney S (2004) Scalable behaviors for crowd simulation. In:. Computer Graphics Forum 23:519–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8659.2004.00783.x
Taffou M, Ondřej J, O’Sullivan C, Warusfel O, Viaud-Delmon I (2017) Judging crowds’ size by ear and by eye in virtual reality. Journal on Multimodal User Interfaces 11:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12193-016-0228-5
Treuille A, Cooper S, Popović Z (2006) Continuum crowds. In: ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 25:1160–1168. doi:10.1145/1141911.1142008
Tsai J, Fridman N, Bowring E, Brown M, Epstein S, Kaminka G, Marsella S, Ogden A, Rika I, Sheel A (2011) ESCAPES: evacuation simulation with children, authorities, parents, emotions, and social comparison. In: The 10th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems 2:457–464
Van Toll WG, Cook AF, Geraerts R (2012) Real-time density-based crowd simulation. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds 23:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/cav.1424
Vicovaro M, Hoyet L, Burigana L, O'sullivan C (2014) Perceptual evaluation of motion editing for realistic throwing animations. ACM Transactions on Applied Perception (TAP) 10:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1145/2617916
Vreugdenhil B, Bellomo N, Townsend PS (2015) Using Crowd Modelling in Evacuation Decision Making. ISCRAM
Wang H, Ondřej J, O'Sullivan C (2016) Path patterns: Analyzing and comparing real and simulated crowds. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games:49–57. doi:10.1145/2856400.2856410
Wiggins JS (1996) The five-factor model of personality: Theoretical perspectives. Guilford Press
Winch J, and Sherwell P, Editor A, Latifi A (2015) 12 schoolgirls trampled to death in Afghanistan earthquake. Telegraph. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/pakistan/11954666/Major-earthquake-strikes-northern-Afghanistan-live-updates.html. Accessed 26 Oct 2015
Wong SK, Tang PK, Li FS, Wang ZM, Yu ST (2015) Guidance path scheduling using particle swarm optimization in crowd simulation. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds 26:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1002/cav.1636
Yin Y, Tang W, Li W (2012) Modeling Group Emotion Based on Emotional Contagion. In: Intelligent Information Processing VI 240–247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(MP4 7339 kb)
ESM 2
(MP4 5388 kb)
ESM 3
(MP4 4305 kb)
ESM 4
(MP4 5845 kb)
ESM 5
(MP4 5239 kb)
ESM 6
(MP4 9166 kb)
ESM 7
(MP4 5772 kb)
ESM 8
(MP4 4057 kb)
ESM 9
(MP4 3484 kb)
ESM 10
(MP4 3158 kb)
ESM 11
(MP4 3892 kb)
ESM 12
(MP4 2206 kb)
ESM 13
(MP4 3584 kb)
ESM 14
(MP4 3624 kb)
ESM 15
(MP4 4613 kb)
ESM 16
(MP4 2844 kb)
ESM 17
(MP4 2285 kb)
ESM 18
(MP4 2304 kb)
ESM 19
(MP4 3143 kb)
ESM 20
(MP4 1878 kb)
ESM 21
(MP4 1867 kb)
ESM 22
(MP4 3171 kb)
ESM 23
(MP4 2115 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Y., Yang, S., Li, Z. et al. Personality trait and group emotion contagion based crowd simulation for emergency evacuation. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 3077–3104 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6069-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6069-3