Abstract
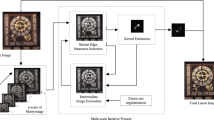
The goal of blind image deblurring is to estimate the blur kernel and restore the sharp latent image based on an input blur image. This paper proposes a novel blind image deblurring algorithm based on L0-regularization and kernel shape optimization. Firstly, the proposed objective function of the optimization model is formulated with L0-norm terms of the gradient and intensity of kernels, which results to good sparsity and less noise in the obtained kernel. Then, the coarse-to-fine iterative framework is adopted to estimate reliable salient image structures implicitly, which can reduce computation and accelerate convergence. Finally, the kernel shape is optimized by weighting method, which enables the obtained kernel closer to the ground-truth. Experimental results on public bench mark datasets demonstrate that restored images are clear with less ring-artifacts.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai JF, Ji H, Liu C, Shen Z (2012) Framelet-based blind motion deblurring from a single image. IEEE Trans Image Process A Publ IEEE Signal Process Soc 21(2):562–572
Cho S, Lee S (2009) Fast motion deblurring. ACM Trans Graph 28(5):1–8
Fergus R, Singh B, Hertzmann A, Roweis ST, Freeman WT (2006) Removing camera shake from a single photograph. ACM Trans Graph 25(25):787–794
Hirsch M, Schuler CJ, Harmeling S, Schölkopf B (2011) Blind deconvolution using a normalized sparsity measure. In: International conference on computer vision (ICCV). IEEE, Barcelona, pp 463–470
Hu Z, Yang MH (2015) Learning good regions to deblur images. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):345–362
Hu Z, Cho S, Wang J, Yang MH (2014) Deblurring low-light images with light streaks. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3382–3389
Jiang X, Yao H, Zhao S (2017) Text image deblurring via two-tone prior. Neurocomputing 242:1–14
Köhler R, Hirsch M, Mohler B, Schölkopf B, Harmeling S (2012) Recording and playback of camera shake: benchmarking blind deconvolution with a real-world database. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, Firenze, pp 27-40
Krishnan D, Tay T, Fergus R (2011) Blind deconvolution using a normalized sparsity measure. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE Computer Society, Colorado, pp 233-240
Kundur D, Hatzinakos D (1996) Blind image deconvolution. IEEE Signal Process Mag 13(3):43–64
Lam L, Lee SW, Suen CY (1992) Thinning methodologies-a comprehensive survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 14(9):869–885
Levin A, Weiss Y, Durand F, Freeman WT (2011) Efficient marginal likelihood optimization in blind deconvolution. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE Computer Society, Colorado, pp 2657–2664
Levin A, Weiss Y, Durand F, Freeman WT (2011) Understanding blind deconvolution algorithms. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(12):2354–2367
Li J, Lu W (2016) Blind image motion deblurring with l0-regularized priors. J Vis Commun Image Represent 40:14–23
Pan J, Liu R, Su Z, Gu X (2012) Kernel estimation from salient structure for robust motion deblurring. Signal Process Image Commun 28(9):1156–1170
Pan J, Hu Z, Su Z, Yang M (2014) Deblurring text images via L0-regularized intensity and gradient prior. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE Computer Society, Columbus, pp 2901–2908
Pan J, Hu Z, Su Z, Yang MH (2014) Deblurring face images with exemplars. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer International Publishing, Zürich, pp 47–62
Pan J, Sun D, Pfister H, Yang MH (2016) Blind image deblurring using dark channel prior. In: IEEE con- ference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE Computer Society, Las Vegas, pp 1628-1636
Ren W, Cao X, Pan J, Guo X, Zuo W, Yang M (2016) Image deblurring via enhanced low-rank prior. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(7):3426–3437
Roth S, Black MJ (2005) Fields of experts: a framework for learning image priors. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE Computer Society, San Diego, pp 860–867
Shan Q, Jia J, Agarwala A (2008) High-quality motion deblurring from a single image. ACM Trans Graph 27(3):1–10
Simoncelli EP (2005) Statistical modeling of photographic images. Handb Image Video Process 415(2):431–441
Sun S, Zhao H, Li B, Hao M, LvJ (2016) Kernel estimation for robust motion deblurring of noisy and blurry images. J Electron Imaging 25(3):033,019
Whyte O, Sivic J, Zisserman A, Ponce J (2010) Non-uniform deblurring for shaken images. IEEE, San Francisco, pp 491–498. http://www.di.ens.fr/willow/research/deblurring/
Xu L, Jia J (2010) Two-phase kernel estimation for robust motion deblurring. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, Heraklion, pp 157–170
Xu L, Lu C, Xu Y, Jia J (2011) Image smoothing via l0 gradient minimization. ACM Trans Graph 30(6):1–12
Xu L, Zheng S, Jia J (2013) Unnatural l0 sparse representation for natural image deblurring. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition, Oregon, pp 1107–1114
Yan Y, Ren W, Guo Y, Wang R, Cao X (2017) Image deblurring via extreme channels prior. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Hawaii, pp 6978–6986
Yuan XT, Liu X, Yan S (2012) Visual classification with multitask joint sparse representation. IEEE Trans Image Process A Publ IEEE Signal Process Soc 21 (10):4349
Zhao S, Yao H, Gao Y, Ji R, Ding G (2017) Continuous probability distribution prediction of image emotions via multitask shared sparse regression. IEEE Trans Multimed 19(3):632–645
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1736118), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (No. 2016A030313350), the Special Funds for Science and Technology Development of Guangdong (No. 2016KZ010103), the Key Project of Scientific Research Plan of Guangzhou (No. 201804020068), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 16lgjc83 and No. 17lgjc45).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Lu, W., Liu, H. et al. Natural image deblurring based on L0-regularization and kernel shape optimization. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 26239–26257 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5847-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5847-2