Abstract
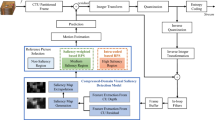
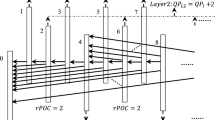
Video delivery over error prone channels suffer from packet loss, which significantly deteriorates the reconstructed video quality. Multiple description coding (MDC) is an effective error resilient coding scheme for transmission of video over unreliable networks, where video is encoded into multiple descriptions having redundancy between them. The amount of redundancy between these descriptions has an important role in MDC, because it provides error resilience. In this paper, a new redundancy allocation scheme using visual saliency model is presented with an aim of achieving high decoding quality, when one or more than one descriptions are received at the decoder. The proposed MDC method splits the input video sequence into even and odd subsequences, which are independently encoded by using high efficiency video coding (HEVC) encoder. The missing frames in each description are predicted by using pixel interpolation and motion interpolation. The residual information is generated by using the interpolated frame and its adjacent frame from the other description, which represents the redundancy in each description. Residual information is encoded based on a visual saliency mask, which is generated using a global contrast based visual saliency model. In this work, two different modes are proposed for visual saliency based redundancy allocation to provide better perceptual quality, while decoding the descriptions. The proposed scheme is implemented on HEVC reference software HM 16.2 and compared with two state-of-the-art temporal subsampling based multiple description video coding methods. Experiments show that the proposed method performs better than the reference methods, both in lossless and packet erasure channel conditions.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adedoyin S, Fernando WAC, Karim HA, Hewage CT, Kondoz AM (2008) Scalable multiple description coding with side information using motion interpolation. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 54(4):2045–2052
Bai H, Lin W, Zhang M, Wang A, Zhao Y (2014) Multiple description video coding based on human visual system characteristics. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 24(8):1390–1394
Chen J, Cai C, Li L, Li C (2016) Layered multiple description video coding using dual-tree discrete wavelet transform and h. 264/avc. Multimed Tools Appl 75 (5):2801–2814
Cheng M-M, Mitra NJ, Huang X, Torr PH, Hu S-M (2015) Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):569–582
Choupani R, Wong S, Tolun M (2014) Multiple description coding for snr scalable video transmission over unreliable networks. Multimed Tools Appl 69(3):843–858
Chung D-M, Wang Y (1998) Multiple description image coding based on lapped orthogonal transforms. In: ICIP 98. Proceedings. 1998 International Conference on Image Processing, vol 1. IEEE, pp 664–668
Crave O, Pesquet-Popescu B, Guillemot C (2010) Robust video coding based on multiple description scalar quantization with side information. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 20(6):769–779
Franchi N, Fumagalli M, Lancini R, Tubaro S (2005) Multiple description video coding for scalable and robust transmission over ip. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 15(3):321–334
Frank B, David F, Karl S, Suhring K (2014) Hevc reference software hm 16.2 reference manual. Technical report, ITU-T/ISO/IEC JCTVC HEVC reference software manual
Ghahremani S, Ghanbari M (2017) Error resilient video transmission in ad hoc networks using layered and multiple description coding. Multimed Tools Appl 76 (6):9033–9049
Goyal VK (2001) Multiple description coding: Compression meets the network. IEEE Signal Process Mag 18(5):74–93
Goyal VK, Kovacevic J, Arean R, Vetterli M (1998) Multiple description transform coding of images. In: ICIP 98. Proceedings. 1998 International Conference on Image Processing, vol 1. IEEE, pp 674–678
Hellge C, Gomez-Barquero D, Schierl T, Wiegand T (2011) Layer-aware forward error correction for mobile broadcast of layered media. IEEE Trans Multimed 13(3):551–562
Heng BA, Apostolopoulos JG, Lim JS (2006) End-to-end rate-distortion optimized md mode selection for multiple description video coding. EURASIP J Appl Signal Process 2006:261–261
Huo Y, El-Hajjar M, Hanzo L (2013) Inter-layer fec aided unequal error protection for multilayer video transmission in mobile tv. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 23(9):1622–1634
Huo Y, Zhu C, Hanzo L (2013) Spatio-temporal iterative source–channel decoding aided video transmission. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 62(4):1597–1609
Huo Y, Hellge C, Wiegand T, Hanzo L (2015) A tutorial and review on inter-layer fec coded layered video streaming. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 17 (2):1166–1207
Karim HA, Hewage CT, Worrall S, Kondoz AM (2008) Scalable multiple description video coding for stereoscopic 3d. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 54(2):745–752
Kazemi M, Sadeghi KH, Shirmohammadi S, Moallem P (2015) Rate/distortion optimization in multiple description video coding. Signal Process Image Commun 36:95–105
Kim IK, Cho NI (2006) Hybrid multiple description video coding using optimal dct coefficient splitting and sd/md switching. Signal Process Image Commun 21(4):293–305
Kim C-K, Lee H-r, Jung T-j, Kim B-G, Seo K-d (2016) An efficient delay-constrained arq scheme for mmt packet-based real-time video streaming over ip networks. J Real-Time Image Process 12(2):257–271
Lin C, Tillo T, Zhao Y, Jeon B (2011) Multiple description coding for h. 264/avc with redundancy allocation at macro block level. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 21(5):589–600
Majid M, Abhayaratne C (2009) Multiple description image coding using several multiple description scalar quantizers. In: IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging, International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp 725711–725711
Majid M, Abhayaratne C (2009) Multiple description scalar quantization with successive refinement. In: Signal Processing Conference, 2009 17th European, IEEE, pp 2268–2272
Majid M, Abhayaratne C (2010) Successive refinement of overlapped cell side quantizers for scalable multiple description coding. In: Picture Coding Symposium (PCS) 2000. IEEE, pp 286–289
Majid M, Abhayaratne C (2012) Inter-description motion vector redundancy control for scalable multiple description video coding. In: IET Conference on Image Processing (IPR)
Majid M, Abhayaratne C (2012) Redundancy controllable scalable unbalanced multiple description bitstream generation for peer-to-peer video streaming. Signal Process Image Commun 27(5):496–512
Servetto SD, Ramchandran K, Vaishampayan VA, Nahrstedt K (2000) Multiple description wavelet based image coding. IEEE Trans Image Process 9(5):813–826
Stephan W (1999) Error patterns for internet video experiments, ITU-T SG16 Document Q15-I-16-R1, pp 2004–2005
Sullivan GJ, Ohm J, Han W-J, Wiegand T (2012) Overview of the high efficiency video coding (hevc) standard. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 22 (12):1649–1668
Sun G, Samarawickrama U, Liang J, Tu C, Tran T (2007) Multiple description image coding with prediction compensation. In: Proceedings of 2007 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp 513–516
Tillo T, Grangetto M, Olmo G (2008) Redundant slice optimal allocation for h. 264 multiple description coding. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 18(1):59–70
Vaishampayan VA (1993) Design of multiple description scalar quantizers. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 39(3):821–834
Vaishampayan VA (1996) Application of multiple description codes to image and video transmission over lossy networks. In: Proceedings of 7th International Workshop Packet Video, pp 55–60
Verdicchio F, Munteanu A, Gavrilescu AI, Cornelis J, Schelkens P (2006) Embedded multiple description coding of video. IEEE Trans Image Process 15 (10):3114–3130
Wang Y, Orchard MT, Reibman AR (1997) Multiple description image coding for noisy channels by pairing transform coefficients. In: 1997., IEEE First Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, IEEE, pp 419–424
Wang Y, Orchard MT, Vaishampayan V, Reibman AR (2001) Multiple description coding using pairwise correlating transforms. IEEE Trans Image Process 10 (3):351–366
Wang Y, Reibman AR, Lin S (2005) Multiple description coding for video delivery. Proc IEEE 93(1):57–70
Wu J, Yuen C, Chen J (2015) Leveraging the delay-friendliness of tcp with fec coding in real-time video communication. IEEE Trans Commun 63(10):3584–3599
Xie X, Zaitsev Y, Velasquez-Garcia L, Teller S, Livermore C (2014) Compact, scalable, highresolution, mems-enabled tactile displays. In: Proceedings of Solid-State Sensors, Actuators, and Microsystems Workshop, pp 127–30
Xie X, Zaitsev Y, Velásquez-García LF, Teller S, Livermore C (2014) Scalable, mems-enabled, vibrational tactile actuators for high resolution tactile displays. J Micromech Microeng 24(12):125014
Xu Y, Zhu C (2013) End-to-end rate-distortion optimized description generation for h. 264 multiple description video coding. IEEE Trans Circ Sys Video Technol 23(9):1523–1536
Yang M, Gadgil N, Comer ML, Delp EJ (2016) Adaptive error concealment for temporal–spatial multiple description video coding. Signal Process Image Commun 47:313–331
Zhang M, Bai H (2012) Adaptive multiple description video coding and transmission for scene change. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 2012(1):265
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Mr. Muhammad Zeeshan for his help in the analysis of visual saliency model for noisy inputs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majid, M., Owais, M. & Anwar, S.M. Visual saliency based redundancy allocation in HEVC compatible multiple description video coding. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 20955–20977 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5499-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5499-7