Abstract
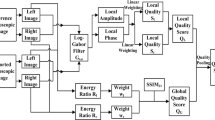
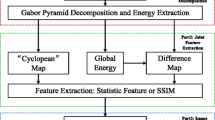
Objective image quality assessment is proposed with the intention to substitute human-rated subjective evaluation by using computational method. Several types of two dimensional (2D) image quality metrics were proposed in the last decade to evaluate the quality of 2D images. When three dimensional (3D) or stereoscopic imaging gradually become popular in different areas of application, new objective quality assessments for 3D images had also been proposed. In this paper, a new method for assessing 3D image quality is proposed. This method is an improvement of the popular 2D structural similarity (SSIM) method with the addition of depth information to measure similarity between distorted and reference 3D images. The proposed method was tested on benchmark 3D image databases to gauge its performance. Experiment results show that predicted quality scores, as calculated from the proposed algorithm, are highly correlated with the corresponding subjective scores from manual evaluation. The significance and effectiveness of the proposed method were also evaluated by comparing its performance to other state-of-the-art 3D quality metrics.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter R, Sazzad Z, Horita Y, Baltes J (2010) No reference stereoscopic image quality assessment. In: Proc SPIE 7524 Stereoscopic displays and application XXI. doi:10.1117/12.838775
Battisti F, Bosc E, Carli M, Le Callet P, Perugia S (2015) Objective image quality assessment of 3D synthesized views. Signal Process Image Commun 30:78–88. doi:10.1016/j.image.2014.10.005
Benoit A, Le Callet P, Campisi P, Cousseau R (2009) Quality assessment of stereoscopic images. EURASIP J Image Video Process 2008(1):1–13
Bong D B L, Khoo B E (2014) An efficient and training-free blind image blur assessment in the spatial domain. IEICE Trans Inf Syst 97(7):1864–1871. doi:10.1587/transinf.e97.d.1864
Bong D B L, Khoo B E (2014) Blind image blur assessment by using valid reblur range and histogram shape difference. Signal Process Image Commun 29(6):699–710. doi:10.1016/j.image.2014.03.003
Bong DBL, Khoo BE (2015) Objective blur assessment based on contraction errors of local contrast maps. Multimed Tools Appl 74(17):7355–7378. doi:10.1007/s11042-014-1983-5
Chandler DM, Hemami SS (2007) VSNR: a wavelet-based visual signal-to-noise ratio for natural images. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(9):2284–98. doi:10.1109/tip.2007.901820
Chen MJ, Su CC, Kwon DK, Cormack LK, Bovik AC (2013) Full-reference quality assessment of stereopairs accounting for rivalry. Signal Process Image Commun 28(9):1143–1155. doi:10.1016/j.image.2013.05.006
Chen MJ, Cormack LK, Bovik AC (2013) No-reference quality assessment of natural stereopairs. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(9):3379–339. doi:10.1109/tip.2013.2267393
Gorley P, Holliman N (2008) Stereoscopic image quality metrics and compression. In: SPIE Conference on stereoscopic displays and applications, vol XIX, pp 6803. doi:10.1117/12.763530
Hewage CTER, Martini MG (2010) Reduced-reference quality metric for 3D depth map transmission. IEEE Int Conf Image Process. doi:10.1109/3dtv.2010.5506205
Hosni A, Rhemann C, Bleyer M, Rother C, Gelautz M (2013) Fast cost-volume filtering for visual correspondence and beyond. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(2):504–511. doi:10.1109/cvpr.2011.5995372
Howard IP, Rogers BJ (1996) Binocular vision and stereopsis. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195084764.001.0001
ITU-R BT. 500-11 (2002) Methodology for the subjective assessment of the quality of television pictures. International Telecommunication Union
Jiang Q, Shao F, Jiang G, Yu M, Peng Z (2016) Leveraging visual attention and neural activity for stereoscopic 3D visual comfort assessment. Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-016-3548-2
Lee JS, Goldmann L, Ebrahimi T (2013) Paired comparison-based subjective quality assessment of stereoscopic images. Multimed Tools Appl 67(1):31–48. doi:10.1007/s11042-012-1011-6
Lin YH, Wu JL (2014) Quality assessment of stereoscopic 3D image compression by binocular integration behaviors. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(4):1527–1542. doi:10.1109/tip.2014.2302686
Liu X, Sun C, Yang LT (2015) DCT-based objective quality assessment metric of 2D/3D image. Multimed Tools Appl 74(8):2803–2820. doi:10.1007/s11042-013-1698-z
Liu Y, Yang J, Meng Q, Lv Z, Song Z, Gao Z (2016) Stereoscopic image quality assessment method based on binocular combination saliency model. Signal Process 31(125):237–48. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.01.019
Mittal A, Moorthy A K, Bovik A C (2012) No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(12):4695–708. doi:10.1109/tip.2012.2214050
Moorthy AK, Su CC, Mittal A, Bovik AC (2012) Subjective evaluation of stereoscopic image quality. Signal Process Image Commun 28(8):870–883. doi:10.1016/j.image.2012.08.004
Saad MA, Bovik AC, Charrier C (2010) A DCT statistics-based blind image quality index. IEEE Signal Process Lett 17(6):583–6. doi:10.1109/lsp.2010.2045550
Shao F, Lin W, Gu S, Jiang G, Srikanthan T (2013) Perceptual full-reference quality assessment of stereoscopic images by considering binocular visual characteristics. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(5):1940–1953. doi:10.1109/tip.2013.2240003
Sheikh HR, Bovik AC (2006) Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(2):430–444. doi:10.1109/tip.2005.859378
Shen L, Yang J, Zhang Z (2009) Stereo picture quality estimation based on a multiple channel HVS model. In: The Second IEEE international congress on image and signal processing, pp 1–4. doi:10.1109/cisp.2009.5301128
Voo KHB, Bong DBL (2015) Quality assessment for stereoscopic images with JPEG compression errors. In: IEEE International conference on consumer electronics-taiwan (ICCE-TW), vol 2015, pp. 220-221. doi:10.1109/icce-tw.2015.7216865
Wang Z, Bovik AC (2009) Mean squared error: love it or leave it? - A new look at signal fidelity measures. IEEE Signal Process Mag 26(1):98–117. doi:10.1109/msp.2008.930649
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error measurement to structural similarity. IEEE Signal Process Lett 13(4):600–612. doi:10.1109/tip.2003.819861
Wang X, Kwong S, Zhang Y (2011) Considering binocular spatial sensitivity in stereoscopic image quality assessment. In: IEEE Visual communications and image processing (VCIP), pp 1–4. doi:10.1109/vcip.2011.6116015
Wang J, Da Silva MP, Le Callet P, Ricordel (2013) Computational model of stereoscopic 3D visual saliency. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(6):2151–2165. doi:10.1109/tip.2013.2246176
Yang J, Hou C, Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Guo J (2009) Objective quality assessment method of stereo images. In: 3DTV Conference: the true vision-capture, transmission and display of 3D video, pp 1–4. doi:10.1109/3dtv.2009.5069615
Yang J, Liu Y, Gao Z, Chu R, Song Z (2015) A Perceptual stereoscopic image quality assessment model accounting for binocular combination behavior. J Vis Commun Image Represent 31:138–145. doi:10.1016/j.jvcir.2015.06.002
Yang J, Lin Y, Gao Z, Lv Z, Wei W, Song H (2015) Quality index for stereoscopic images by separately evaluating adding and subtracting. PloS one 10 (12):e0145800. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0145800
Yang J, Wang Y, Li B, Lu W, Meng Q, Lv Z, Zhao D, Gao Z (2016) Quality assessment metric of stereo images considering cyclopean integration and visual saliency. Inf Sci 373:251–68. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2016.09.004
You J, Xing L, Perkis A, Wang X (2010) Perceptual quality assessment for stereoscopic images based on 2D image quality metrics and disparity analysis. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on video processing and quality metrics for consumer electronics. Scottsdale
Zhang Y, Chandler DM (2015) 3D-MAD: a full reference stereoscopic image quality estimator based on binocular lightness and contrast perception. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(11):3810–3825. doi:10.1109/TIP.2015.2456414
Zhu Z, Wang Y (2009) Perceptual distortion metric for stereo video quality evaluation. WSEAS Trans Signal Process 5(7):241–250
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Ministry of Education Malaysia, for the provision of research grant: FRGS/TK03(01)/1063/2013(09) and Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Sarawak for the provision of research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voo, K.H.B., Bong, D.B.L. Quality assessment of stereoscopic image by 3D structural similarity. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 2313–2332 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4361-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4361-2