Abstract
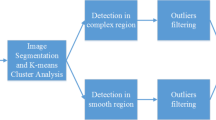
Copy-move forgery is one of the most common types of image forgeries, where a region from one part of an image is copied and pasted onto another part, thereby concealing the image content in the latter region. Keypoint based copy-move forgery detection approaches extract image feature points and use local visual features, rather than image blocks, to identify duplicated regions. Keypoint based approaches exhibit remarkable performance with respect to computational cost, memory requirement, and robustness. But unfortunately, they usually do not work well if smooth background areas are used to hide small objects, as image keypoints cannot be extracted effectively from those areas. It is a challenging work to design a keypoint-based method for detecting forgeries involving small smooth regions. In this paper, we propose a new keypoint-based copy-move forgery detection for small smooth regions. Firstly, the original tampered image is segmented into nonoverlapping and irregular superpixels, and the superpixels are classified into smooth, texture and strong texture based on local information entropy. Secondly, the stable image keypoints are extracted from each superpixel, including smooth, texture and strong texture ones, by utilizing the superpixel content based adaptive feature points detector. Thirdly, the local visual features, namely exponent moments magnitudes, are constructed for each image keypoint, and the best bin first and reversed generalized 2 nearest-neighbor algorithm are utilized to find rapidly the matching image keypoints. Finally, the falsely matched image keypoints are removed by customizing the random sample consensus, and the duplicated regions are localized by using zero mean normalized cross-correlation measure. Extensive experimental results show that the newly proposed scheme can achieve much better detection results for copy-move forgery images under various challenging conditions, such as geometric transforms, JPEG compression, and additive white Gaussian noise, compared with the existing state-of-the-art copy-move forgery detection methods.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Qershi OM, BE Khoo (2015) Enhanced matching method for copy-move forgery detection by means of Zernike moments. 13th International Workshop on Digital-Forensics and Watermarking (IWDW 2014), LNCS 9023, pp 485–497
Amerini I, Ballan L, Caldelli R, Del Bimbo A, Del Tongo L, Serra G (2013) Copy-move forgery detection and localization by means of robust clustering with J-Linkage. Signal Process Image Commun 28(6):659–669
Amerini I, Ballan L, Caldelli R (2011) A SIFT-based forensic method for copy-move attack detection and transformation recovery. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 6(3):1099–1110
Ardizzone E, Bruno A, Mazzola G (2015) Copy-move forgery detection by matching triangles of keypoints. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(10):2084–2094
Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, Gool LV (2008) Speeded up robust features (SURF). Comput Vis Image Underst 110(3):346–359
Bi X, Pun CM, Yuan XC (2016) Multi-level dense descriptor and hierarchical feature matching for copy-move forgery detection. Inf Sci 345:226–242
Bravo-Solorio S, Nandi AK (2011) Exposing duplicated regions affected by reflection, rotation and scaling. 2011 I.E. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, pp 1880–1883
Caldelli R, Amerini I, Ballan L (2012) On the effectiveness of local warping against SIFT-based copy-move detection. Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Communications, Control and Signal Processing, Rome, Italy, pp 1–5
Chambers J, Yan W, Garhwal A (2015) Currency security and forensics: a survey. Multimedia Tools Appl 74(11):4013–4043
Chen L, Lu W, Ni J, Sun W (2013) Region duplication detection based on Harris corner points and step sector statistics. J Vis Commun Image Represent 24(3):244–254
Chen B, Shu H, Coatrieux G (2015) Color image analysis by quaternion-type moments. J Math Imaging Vision 51(1):124–144
Christlein V, Riess C, Jordan J (2012) An evaluation of popular copy-move forgery detection approaches. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 7(6):1841–1854
Costanzo A, Amerini I, Caldelli R (2014) Forensic analysis of SIFT keypoint removal and injection. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 9(9):1450–1464
Cozzolino D, Poggi G, Verdoliva L (2014) Copy-move forgery detection based on patchmatch. 2014 I.E. International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, pp 5312–5316
Cozzolino D, Poggi G, Verdoliva L (2015) Efficient dense-field copy-move forgery detection. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(11):2284–2297
Da S (2009) Research on density based image processing algorithms and application. Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin
Davarzani R, Yaghmaie K, Mozaffari S (2013) Copy-move forgery detection using multiresolution local binary patterns. Forensic Sci Int 231(1–3):61–72
Fattah SA, Ullah MMI, Ahmed M (2014) A scheme for copy-move forgery detection in digital images based on 2D-DWT. IEEE 57th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), College Station, TX, pp 801–804
Imamoglu M, Ulutas G, Ulutas M (2013) Detection of copy-move forgery using Krawtchouk moment. 2013 8th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Bursa, Turkey, pp 311–314
Jaberi M, Bebis G, Hussain M (2014) Accurate and robust localization of duplicated region in copy-move image forgery. Mach Vis Appl 25(2):451–475
Jie Z, Guo J (2013) Passive forensics for copy-move image forgery using a method based on DCT and SVD. Forensic Sci Int 233(1–3):158–166
Kakar P, Sudha N (2012) Exposing postprocessed copy-paste forgeries through transform-invariant features. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 7(3):1018–1028
Ketenci S, Ulutas G, Ulutas M (2014) Detection of duplicated regions in images using 1D-Fourier transform. International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing, Dubrovnik, Croatia, pp 171–174
Lee JC (2015) Copy-move image forgery detection based on Gabor magnitude. J Vis Commun Image Represent 31:320–334
Lee J, Chang C, Chen W (2015) Detection of copy–move image forgery using histogram of orientated gradients. Inf Sci 321:250–262
Li J, Li X, Yang B (2015) Segmentation-based image copy-move forgery detection scheme. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(3):507–518
Li Y, Wang S, Tian Q (2015) A survey of recent advances in visual feature detection. Neurocomputing 149:736–751
Liu MY, Tuzel O, Ramalingam S, Chellappa R (2011) Entropy rate superpixel segmentation. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, Colorado, USA, pp 2097–2104
Meng M, Ping ZL (2011) Decompose and reconstruct images based on exponential Fourier moments. J Inner Mongolia Norm Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 40(3):258–260
Muhammad G, Hussain M, Bebis G (2012) Passive copy move image forgery detection using undecimated dyadic wavelet transform. Digit Investig 9(1):49–57
Pun CM, Yuan XC, Bi XL (2015) Image forgery detection using adaptive oversegmentation and feature point matching. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(8):1705–1716
Qureshi MA, Deriche M (2015) A bibliography of pixel-based blind image forgery detection techniques. Signal Process Image Commun 39(Part A):46–74
Ryu SJ, Kirchner M, Lee MJ (2013) Rotation invariant localization of duplicated image regions based on Zernike moments. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 8(8):1355–1370
Silva E, Carvalho T, Ferreira A (2015) Going deeper into copy-move forgery detection: exploring image telltales via multi-scale analysis and voting processes. J Vis Commun Image Represent 29:16–32
Sitara K, Mehtre BM (2016) Digital video tampering detection: an overview of passive techniques. Digit Investig 18:8–22
Ustubioglu B, Ayas S, Doganl H (2015) Image forgery detection based on color SIFT. The IEEE Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference, Malatya, Turkey, pp 1741–1744
Wang X, Liu Y, Li S, Yang H, Niu P, Zhang Y (2015) A new robust digital image watermarking using local polar harmonic transform. Comput Electr Eng 46:403–418
Wu YJ, Yu D, Duan HB (2014) Dual tree complex wavelet transform approach to copy-rotate-move forgery detection. Sci China Inf Sci 57(1):1–12
Xia Z, Wang X, Sun X (2016) Steganalysis of LSB matching using differences between nonadjacent pixels. Multimedia Tools and Applications 75(4):1947–1962
Yan L, Nian L, Bin Z, Kai-guo Y, Yang Y (2015) Image multiple copy-move forgery detection algorithm based on reversed-generalized 2 nearest-neighbor. J Electron Inf Technol 7:1767–1773
Yu L, Han Q, Niu X (2016) Feature point-based copy-move forgery detection: covering the non-textured areas. Multimedia Tools Appl 75(2):1159–1176
Zhou Z, Wang Y, Jonathan Wu QM, Yang C-N, Sun X (2006) Effective and efficient global context verification for image copy detection. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur. doi:10.1109/TIFS.2016.2601065
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61472171 & 61272416, the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China under Grant No. 201602463, A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center on Atmospheric Environment and Equipment Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XY., Li, S., Liu, YN. et al. A new keypoint-based copy-move forgery detection for small smooth regions. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 23353–23382 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4140-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4140-5