Abstract
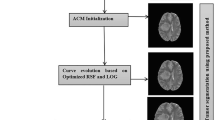
Segmentation and precise volume estimation of abnormalities is one of the main focus in medical image processing field for the purpose of diagnosis and treatment planning. The precise estimation of volume of the abnormality aids better prognosis, treatment planning and dose estimation. The work put forth in this paper has proposed and implemented a semi-automatic technique that yields appropriate segmented regions from MR brain images. The Segmentation technique here utilizes fusion of information beyond human perception from MR images to develop a fused feature map. The information beyond human perception include second order derivatives that are computed from an image which are discussed in detail in relevant section of this paper. This obtained feature map acts as a stopping function for the initialized curve in the framework of an active contour model to obtain a well segmented region of interest. The segmentation is carried out in all the slices of a particular dataset with initialization of the active contour required only on the first slice which makes this method fast. The obtained segmentation results are compared with ground truth segmentation results obtained from experts manually using Jackard’s Co-efficient of Similarity and Overlap index. The boundaries of the segmented regions are utilized in surveyor’s algorithm to compute the volume of the tumors with high accuracy. The efficacy of this volume estimation technique is illustrated with comparison to mostly used ABC/2 method and cavalieri method. The results obtained on various case studies like Craniophryngioma, High grade Glioma and Microadenoma show a good efficacy of the overall method.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bezdek JC (1981) Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms. Plenum Press, New York
Bilgic S, Sahin B, Sonmez OF, Odaci E, Colakoglu S, Kaplan S et al (2005) A new approach for the estimation of intervertebral disc volume using the cavalieri principle and computed tomography images. Clin Nuerol Neurosurg 107:282–288
Caselles V, Kimmel R, Sapiro G (1997) Geodesic active contours. Int J Comput Vis 22(1):61–79
Chakraborty A, Staib LH, Duncan JS (1996) Deformable boundary finding in medical images by integrating gradient and region information. IEEE Trans Med Imag 15(6):859–870
Chan TF, Vese LA (2001) Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(2):266–277
Clausi DA, Deng H (2005) Design-based texture feature fusion using Gabor filters and co-occurrenceprobabilities. IEEETrans Image Process 14(7):925–936
Clausi DA, Deng H (2005) Design-based texture feature fusion using Gabor filters and co- occurrence probabilities. IEEE Trans Image Process 14(7):925–936
Coleman GB, Andrews HC (1979) Image segmentation by clustering. Proc IEEE 67(5):773–785
Cremers D, Rousson M, Deriche R (2007) A review of statistical approaches to level set segmentation: integrating color, texture, motion and shape. Int J Comput Vis 72(2):195–215
del Fresno M, Venere M, Clausse A (2009) A combined region growing and deformable model method for extraction of closed surfaces in 3D CT and MRI scans. Comput Med Imaging Graph 33(5):369–376
Dou WB, Ruan S, Chen YP, Bloyet D, Constans JM (2007) A framework of fuzzy information fusion for the segmentation of brain tumor tissues on MR images. Image Vis Comput 25(2):164–171
Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG (2001) Pattern classification, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Dunn JC (1973) A fuzzy relative of the ISODATA process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters. J Cybernet: Trans Am Soc Cybernet 3(3):32–57
Gabel JM, Sila CA, Sloan MA et al (1998) comparison of ABC/2 estimation technique to computer assisted volumetric analysis of intraparenchymal and subdural hematomas complicating the GUSTO-1 trial. Stroke 29:1799–1801
Gebel JM, Sila CA, Sloan MA, Granger CB, Weisenberger JP, Green CL (1998) Comparison of the ABC/2 estimation technique to computer-assisted volumet- ric analysis of intraparenchymal and subdural hematomas complicating the gusto-1 trial. Stroke 29:1799–1801
Haffner JPE, Bouyé S, Puech P, Leroy X, Lemaitre L, Villers A (2009) Peripheral zone prostate cancers: location and intraprostatic patterns of spread at histopathology. Prostate 69(3):276–282
Hansasuta A, Choi CY, Gibbs IC, Soltys SG, Tse VC, Lieberson RE et al (2011) Multisession stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwanno- mas: single-institution experience with 383 cases. Neurosurgery 69:1200–1209
Haralick RM () A texturecontext feature extraction algorithm 1241, Mar. 1973. for remotely sensed imagery. Roc I971 I1971EEE Decisim Confrol Conf. (Gainde, FL), 650–657
Huttner HB, Steiner T, Hartman M et al (2006) Comparison of ABC/2 estimation technique to computer assisted planimetric analysis in warafin related intracerebral parenchymal hemorrhage. Stroke 37:404–408
Jayadevappa D, Srinivas Kumar S, Murty DS (2011) Medical image segmentation algorithms using deformable models: a review. IETE Tech Rev 28(3)
Kapur T, Eric W, Grimson L, Wells WM III, Kikinis R (1996) Segmentation of brain tissue from magnetic resonance images. Med Image Anal 1(2):109–127
Kass M, Witkin A, Terzopoulos D (1988) Snakes: active contour models. Int J Comput Vis 1(4):321–331
Kichenassamy S, Kumar A, Olver P, Tannenbaum A, Yezzy A (1995) “Gradient flows and geometric active contour models,”. 22 Comput Math Methods Med Proc 5th Int Conf Comput Vision (ICCV’95), 810–815
Kothari RU, Brott T, Broderick JP, Barson WG, Sauerbeck LR, Zuccarello M et al (1996) The ABCs of measuring intracerebral hemorrhage volumes. Stroke 27:1304–1305
Li BN, Chui CK, Chang S, Ong SH (2011) Integrating spatial fuzzy clustering with level set methods for automated medical image segmentation. Comput Biol Med 41(1):1–10
Li B, Huang DS (2008) Locally linear discriminant embedding: an efficient method for face recognition. Pattern Recogn 41(12):3813–3821
Li C, Huang R, Ding Z, Gatenby JC, Metaxas DN, Gore JC (2011) A level set method for image segmentation in the presence of intensity inhomogeneities with application to MRI. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(7):2007–2016
Liew AW-C, Yan H (2006) Current methods in the automatic tissue segmentation of 3D magnetic resonance brain images. Curr Med Imag Rev 2(1):91–103
Logeswari T, Karnan M (2010) An improved implementation of brain tumor detection using segmentation based on hierarchical self-organizing map. Int J Comput Theory Eng 2(4):1793–8201, LONI (2014)
Luby M, Hong J, Merino JG, Lynch JK, Hsia AW, Magadan A, Song SS, Latour LL, Warach S Stroke mismatch volume with the use of ABC/2 is equivalent to planimetric stroke mismatch volume. J Nucl Med, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34; 1901–07
Magi-Galluzzi C et al (2011) International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP)Consensus Conference on Handling and Staging of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Working group 3: extraprostatic extension, lymphovascular invasion and locally advanced disease. Modern Pathol : Off J United States Can Acad Pathol, Inc 24(1):26–33
Malladi R, Sethian JA, Vemuri BC (1995) Shape modelling with front propagation: a level set approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 17(2):158–175
Massick DD, Welling DB, Dodson EE, Scholfield M, Nagaraja HN, Schmalbrock P et al (2000) Tumor growth and audiometric change in vestibular schwannomas managed conservatively. Laryngoscope 110:1843–1849
Masutani Y, Schiemann T, Hohne KH (1998) Vascular shape segmentation and structure extraction using a shape based region-growing model. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Interventation—MICCAI'98. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference Cambridge, MA, USA, October 11–13, 1998, vol 1496 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 1242–1249, Springer, Berlin, Germany
Mir AH, Hanmandlu M, Tandon SN (1995) Texture analysis of CT images. Eng Med Biol Mag, IEEE 14(6):781–786. doi:10.1109/51.473275
Montironi R et al (2003) Handling and pathology reporting of radical prostatectomy specimens. Eur Urol 44(6):626–636
Olabaoriago SD, Smeulders AWM (2001) Interaction in the segmentation of medical image analysis. Nuero Image 5:127–142
Ortiz A, Gorriz JM, Ramirez J, Salas-Gonzalez D (2014) Improving MR brain image segmentation using self-organising maps and entropy-gradient clustering. Inf Sci 262:117–136. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2013.10.002
Osher S, Sethian JA (1988) Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J Comp Phys 79:12–49
Passat N, Ronse C, Baruthio J, Armspach J-P, Maillot C, Jahn C (2005) Region-growing segmentation of brain vessels: an atlas-based automatic approach. J Magn Reson Imaging 21(6):715–725
Pham DL, Xu CY, Prince JL (2000) A survey of current methods in medical image segmentation. Ann Rev Biomed Eng 2:315–337 [Technical report version, JHU/ECE 99–01, Johns Hopkins University]
Pitas L (1993) Digital image processing algorithms. Pentice Hall
Sezgin M, Sankur B (2004) Survey over image thresholding techniques and quantitative performance evaluation. J Electron Imag 13(1):146–168
Shang L, Huang DS, Du JX, Zheng CH (2006) Palm-print recognition using fast ICA algorithm and radial basis probabilistic neural network. Neuro-computing 69(13–15):1782–1786
Solberg AHS, Jain AK (1997) Texture fusion and feature selection applied to SAR imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 35(2):475–479
Unal B, Kara A, Aksak S, Unal D (2010) A stereological assessment method for estimating the surface area of cycloids. T Eurasian J Med 42:66–73
Van der Kwast TH et al (2011) International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Handling and Staging of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. working group 2: T2 substaging and prostate cancer volume. Modern Pathol : Off J United States Can Acad Pathol, Inc 24(1):16–25
Wang J, Kong J, Lu Y, Qi M, Zhang B (2008) A modified FCM algorithm for MRI brain image segmentation using both local and non-local spatial constraints. Comput Med Imaging Graph 32(8):685–698. doi:10.1016/j.compmedimag.2008.08.004, ISSN 0895–6111
Warfield SK, Kaus M, Jolesz FA, Kikinis R (2000) Adaptive, template moderated, spatially varying statistical classification. Med Image Anal 4(1):43–55
Weglinski T, Fabijanska A (201) Brain tumor segmentation from MRI data sets using region growing approach. Proc 7th Int Confe Perspect Technol Methods MEMS Design (MEMSTECH’11), 185–188
Wells WM III, Crimson WEL, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA (1996) Adaptive segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 15(4):429–442
Xu C, Prince JL (Mar. 1998) Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans Image Process 7(3):359–369
Xue J-H, Pizurica A, Philips W, Kerre E, van de Walle R, Lemahieu I (2003) An integrated method of adaptive enhancement for unsupervised segmentation of MRI brain images. Pattern Recogn Lett 24(15):2549–2560
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zhang N, Ruan S, Lebonvallet S, Liao Q, Zhu Y (2011) Kernel feature selection to fuse multi-spectral MRI images for brain tumor segmentation. Comput Vis Image Underst 115(2):256–269, ISSN 1077–3142
Zhao ZQ, Huang DS, Sun BY (2004) Human face recognition based on multiple features using neural networks committee. Pattern Recognit Lett 25(12):1351–1358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banday, S.A., Mir, A.H. Statistical textural feature and deformable model based brain tumor segmentation and volume estimation. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 3809–3828 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3979-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3979-9