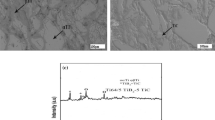
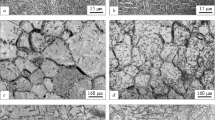
The properties of existing Ti-based alloys and composites are reviewed. The effect of various alloying elements, reinforcement, and technological parameters of the powder metallurgy on the physical and mechanical properties of Ti-based alloys and composites is studied. Post-treatment conditions are discussed and optimal ways to lower the residual porosity of the composites are suggested.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ahmed, D. G. Savvakin, O. M. Ivasishin, and E. V. Pereloma, “The effect of thermo-mechanical processing and ageing time on microstructure and mechanical properties of powder metallurgy near (titanium alloys,” J. Alloys Comd., 714, 610 – 618 (2017).
H. R. Zhang, H. Z. Niu, M. C. Zang, et al., “Microstructures and mechanical behavior of a near titanium alloy prepared by TiH2-based powder metallurgy,” Mat. Sci. Eng. A., 770, Art. 138570 (2020).
K. Yoganandam, V. Mohanavel, J. Vairamuthu, and V. Kannadhasan, “Mechanical properties of titanium matrix composites fabricated via powder metallurgy method,” Mater. Today: Proc., 33, 3243 – 3247 (2020).
R. Frykholm and B. Brash, “Press and sintering of titanium,” Key Eng. Mat., 704, 369 – 377 (2016).
A. Amigo, A. Vicente, C. R. M. Afonso, and V. Amigo, “Mechanical properties and the microstructure of β Ti-35Nb – 10Ta – xFe alloys obtained by powder,” Metals, 9(1), 76 (2019).
T. Childerhouse and M. Jackson, “Near net shape manufacture of titanium alloy components from powder and wire: A review of state-of-the-art process routes,” Metals, 9(6), 689 (2019).
R. Guo, B. Liu, R. Xu, et al., “Microstructure and mechanical properties of powder metallurgy high temperature titanium alloy with high Si content,” Mat. Sci. Eng. A., 777, Art. 138993 (2020).
N. Kumar, A. Bharti, M. Dixit, and A. Nigam, “Effect of powder metallurgy process and its parameters on the mechanical and electrical properties of copper-based materials: Literature review,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 59, 401 – 410 (2020).
N. Kumar, A. Bharti, and H. Tripathi, “Investigation of microstructural and mechanical properties of magnesium matrix hybrid composite,” in: Advances in Mechanical Engineering, Springer, Singapore (2020), pp. 661 – 669.
N. Kumar, A. Bharti, and K. K. Saxena, “A re-analysis of effect of various process parameters on the mechanical properties of Mg based MMCs fabricated by powder metallurgy technique,” Mater. Today: Proc., 26, 1953 – 1959 (2020).
Yu. A. Sokolov, N. V. Pavlushin, and S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, “New additive technologies based on ion beams,” Russ. Eng. Res., 36(12), 1012 – 1016 (2016).
S. M. Castillo, S. Munoz, P. Trueba, et al., “Influence of the compaction pressure and sintering temperature on the mechanical properties of porous titanium for biomedical applications,” Metals, 9, 12, 1249 (2019).
A. I. Rudskoy, S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, and Yu. A. Sokolov, “New approach to synthesis of powder and composite materials by electron beam. Part 1. Technological features of the process,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 58(1 – 2), 27 – 32 (2016).
S. Jiang, L. J. Huang, Q. An, et al., “Study on titanium-magnesium composites with bicontinuous structure fabricated by powder metallurgy and ultrasonic infiltration,” J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 81, 10 – 15 (2018).
A. R. Contreras, M. Punset, J. A. Calero, et al., “Powder metallurgy with space holder for porous titanium implants: A review,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 76, 129 – 149 (2021).
S. Yu. Kondrat’ev and Yu. A. Sokolov, “New approach to electron beam synthesis of powder and composite materials. Part 2. Practical results for alloy VT6,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 58(3 – 4), 165 – 169 (2016).
R. Yamanoglu, “Network distribution of molybdenum among pure titanium powders for enhanced wear properties,” Met. Powder Rep., 76(1), 32 – 39 (2020).
J. M. Oh, K. H. Heo, W. B. Kim, et al., “Sintering properties of Ti6Al4V alloys prepared using TiTiH2 powders,” Mater. Trans., 54, 119 – 121 (2013).
P. R. Mondi, R. Mariappan, C. R. Kumar, et al., “Effect of sintering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of powder metallurgy titanium composites,” Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res., 10, 33,389 – 33,392 (2015).
P. J. Teja, S. R. Shial, D. Chaira, and M. Masanta, “Development and characterization of Ti – TiC composites by powder metallurgy route using recycled machined Ti chips,” Mater. Today: Proc., 26, 3292 – 3296 (2020).
E. Reverte, S. A. Tsipas, and E. Gordo, “Oxidation and corrosion behavior of new low-cost Ti – 7Fe – 3Al and Ti – 7Fe – 5Cr alloys from titanium hydride powders,” Metals, 10(2), 254 (2020).
J. C. Z. Carrullo, A. D. Borras, V. A. Borras, et al., “Electrochemical corrosion behavior and mechanical properties of Ti – Ag biomedical alloys obtained by two powder metallurgy processing routes,” J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 112, Art. 104063 (2020).
Y. Alshammari, M. Jia, F. Yang, and L. Bolzoni, “The effect of α + β forging on the mechanical properties and microstructure of binary titanium alloys produced via a cost-effective powder metallurgy route,” Mat. Sci. Eng. A., 769, Art. 138496 (2020).
C. Zhang, F., Yang, Z. Guo, et al., “Oxygen scavenging, grain refinement and mechanical properties improvement in powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloys with CaB6,” Powder Technol., 340, 362 – 369 (2018).
C. Romero, F. Yang, C. Wei, and L. Bolzoni, “Thermomechanical processing of cost-affordable powder metallurgy Ti – 5Fe alloys from the blended elemental approach: Microstructure, tensile deformation behavior, and failure,” Metals, 10(11), 1405 (2020).
M. Guden, E. Celik, A. Hýzal, et al., “Effects of compaction pressure and particle shape on the porosity and compression mechanical properties of sintered Ti6Al4V powder compacts for hard tissue implantation,” J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part B. Appl. Biomater., 85(2), 547 – 555 (2008).
Y. F. Yang and M. Qian, “Spark plasma sintering and hot pressing of titanium and titanium alloys,” in: Titanium Powder Metallurgy, Elsevier, Butterworth-Heinemann (2015), pp. 219 – 235.
M. Rajadurai and A. R. Annamalai, “Effect of various sintering methods on microstructures and mechanical properties of titanium and its alloy (Ti – Al – V – X): A review, Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met+, 58, 434 – 448 (2017).
C. Yu, P. Cao, and M. I. Jones, “Titanium powder sintering in a graphite furnace and mechanical properties of sintered parts,” Metals, 7(3), 67 (2017).
L. Bolzoni, E. M. R. Navas, and E. Gordo, “Quantifying the properties of low-cost powder metallurgy titanium alloys,” Mat. Sci. Eng. A., 687, 47 – 53 (2017).
J. Lario, A. Vicente, and V. Amigo, “Evolution of the microstructure and mechanical properties of a Ti35Nb2Sn alloy post-processed by hot isostatic pressing for biomedical applications,” Metals, 11(7), 1027 (2021).
L. Bolzoni, E. M. R. Navas, D. L. Zhang, and E. Gordo, “Modification of sintered titanium alloys by hot isostatic pressing,” Key Eng. Mat., 520, 63 – 69 (2012).
O. Ivasishin, D. G. Savvakin, F. Froes, and K. Bondareva, “Synthesis of alloy Ti – 6Al – 4V with low residual porosity by a powder metallurgy method,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 41, 382 – 390 (2002).
L. Bolzoni, E. M. Ruiz-Navas, and E. Gordo, “Evaluation of the mechanical properties of powder metallurgy Ti – 6Al – 7Nb alloy,” J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 67, 110 – 116 (2017).
M. R. Baldissera, P. R. Rios, L. R. O. Hein, and H. R. Z. Sandim, “Three-dimensional characterization of pores in Ti – 6Al – 4V alloy,” Mater. Res., 14, 102 – 106 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 5, pp. 3 – 9, May, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Bharti, A. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Powder-Metallurgy-Processed Titanium Alloys and Composites: A Comparative Analysis. Met Sci Heat Treat 64, 245–251 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-022-00794-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-022-00794-x