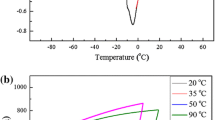
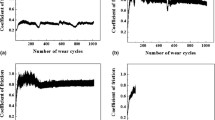
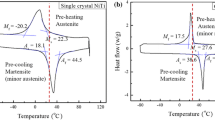
The effect of load and sliding rate on wear resistance of a NiTi alloy in martensitic and austenitic conditions with dry friction by a ball–disk scheme is studied. Martensitic transformation temperature and wear mechanism are analyzed using differential calorimetry, scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive spectrum analysis. It is shown that friction coefficient decreases by about 40% with increase in load, and sliding rate has a smaller and ambiguous effect on NiTi alloy friction characteristics. Austenitic phase exhibits a slower wear rate than martensitic phase with all of the friction regimes used.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 February 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-023-00859-5
References
B. O. Kucukyildirim, “The effect of aging under loading on the phase transformation behavior of near-equiatomic niti shape memory alloy,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 24, 3228 – 3240 (2015).
V. Di. Cocco, F. Iacoviello, and S. Natali, “Fatigue microstructural evolution in pseudo elastic NiTi alloy,” Proc. Struct. Integrity, 2, 1457 – 1464 (2016).
L. Qian, Z. Zhou, and Q. Sun, “The role of phase transition in the fretting behavior of NiTi shape memory alloy,” Wear, 259(6), 309 – 318 (2005).
K. Nurveren, A. Akdonan Eker, and W. M. Huang, “Evolution of transformation characteristics with heatingcooling rate in NiTi shape memory alloys,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 196(1–3), 129 – 134 (2008).
W. Tillmann and S. Momeni, “Influence of in-situ and post annealing technique on tribological performance of NiTi SMA thin films,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 276, 286 – 295 (2015).
M. Mehdi, K. Farokhzadeh, and A. Edrisy, “Dry sliding wear behavior of superelastic Ti – 10V – 2Fe – 3Al – titanium alloy,” Wear, 350 – 351(1), 10 – 20 (2016).
N. Levintant-Zayonts, G. Starzynski, M. Kopec, and S. Kucharski, “Characterization of NiTi SMAin its unusual behaviour in wear tests,” Tribol. Int., 137, 313 – 323 (2019).
L. Yan, Y. Liu, and E. Liu, “Wear behaviour of martensitic NiTi shape memory alloy under ball-on-disk sliding tests,” Tribol. Int., 66(1), 219 – 224 (2013).
W. Yan, “Theoretical investigation of wear-resistance mechanism of superelastic shape memory alloy NiTi,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 427(1–2), 348 – 355 (2006).
A. P. Markopoulos, I. S. Pressas, and D. E. Manolakos, “Manufacturing processes of shape memory alloys,” Mater. Form. Machining: Res. Devel., 1, 155 – 180 (2016).
Z. Yang, M. Stossel, and J. Wang, “Microstructural evolution and surface strengthening of pulse-laser treated TiNi multilayer thin films,” Extreme Mechan. Lett., 4(1), 45 – 51 (2015).
W. Y. Yan, Q. P. Sun, X. Q. Feng, and L. M. Qian, “Analysis of spherical indentation of superelastic shape memory alloys,” Int. J. Solids Struct., 44(1), 1 – 17 (2007).
O. G. Zotov and S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, “Antifriction properties of copper alloys with convertible martensite in the structure,” Trenie Iznos, 14(2), 419 – 422 (1993).
N. G. Kolbasnikov, S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, and S. G. Fomin, “Mechanical properties of alloys with reverse martensite transformations,” Probl. Proch., 3, 34 – 42 (1992).
N. G. Kolbasnikov, S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, S. G. Fomin, and S. V. Shchukin, “Mechanical properties of alloys with reversible martensitic transformation,” Strength Mater., 24(3), 262 – 269 (1992).
S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, O. G. Zotov, G. Ya. Yaroslavskii, et al., “Investigation of interrelationship between damping capacity and mechanical properties as well as morphology of martensite in alloys with reversible martensite transformation,” Probl. Proch., 14B(3), 79 – 82 (1983).
S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, G. Y. Yaroslavskii, B. S. Chaikovskii, and V. V. Matveev, “Effect of doping and hardening conditions on mechanical properties and microstructure of Br.A10 alloy,” Probl. Proch., 7(145), 98 – 101 (1981).
L. Yan and Y. Liu, “Effect of deformation mode on the wear behavior of NiTi shape memory alloys,” Shape Memory Superelasticity, 2(2), 204 – 217 (2016).
M. Abedini, H. M. Ghasemi, and M. NiliAhmadabad, “Tribological behavior of NiTi alloy in martensitic and austenitic states,” Mater. Design, 30(10), 4493 – 4497 (2009).
L. Yan and Y. Liu, “Wear behavior of austenitic NiTi shape memory alloy,” Shape Memory Superelasticity, 1(1), 56 – 68 (2015).
L. Zorko and R. Rudolf, “Metallographic sample preparation of orthodontic Ni – Ti wire,” Assoc. Metall. Eng., 15(4), 267 – 274 (2009).
K. Heinz and Z. Gahr, “Sliding wear,” Tribol. Ser., 10, 351 – 495 (1987).
M. Abedini, H. M. Ghasemi, and M. N. Ahmadabadi, “Tribological behavior of NiTi alloy against 52100 steel and WC at elevated temperatures,” Mater. Charact., 61(7), 689 – 695 (2010).
R. Aliasgarian, H. M. Ghasemi, and M. Abedini, “Tribological behavior of heat treated Ni-rich NiTi alloy,” J. Tribol., 133(3), 1 – 6 (2011).
H. Wang, Y. Kalchev, H. Wang, et al., “Surface modification of NiTi alloy by ultrashort pulsed laser shock peening,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 394(1), 125899 (2020).
We would like to thank Advanced Materials Research Group (AMRG) from Yildiz Technical University, Mechanical Engineering Department, for providing the laboratory conditions during our studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 4, pp. 23 – 31, April, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Avcil, A., Eker, A.A. & Kucukyildirim, B.O. Influence of Sliding Rate and Load with Friction on NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Wear Resistance. Met Sci Heat Treat 64, 211–218 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-022-00786-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-022-00786-x