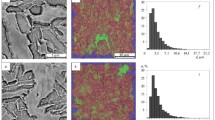
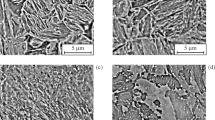
The structure of initially high-tempered steel 09G2S (quenched and tempered at 650°C) is studied quantitatively inside the zone of plastic strain formed by the force impact of the hammer of the impact machine under dynamic three-point bending. After the impact tests, the specimen exhibits features of plastic flow of the material and bands of adiabatic shear. Additional annealing at 600°C with a hold for from 7.5 to 24 h causes stage evolution of the structure of the bands.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. B. Neimark and M. A. Sokovnikov, “About the mechanism of adiabatic shear under high-speed loading of materials,” Matem. Model. Syst. Prots., 3, 71 – 76 (1995).
M. Sokovnikov, D. Bilalov, V. Oborin, et al., “Structural mechanisms of formation of adiabatic shear bands,” Frattura Integr. Strutturale, 10(38), 296 – 304 (2016).
C. G. Lee and Y. J. Lee, “Observation of adiabatic shear bands formed by ballistic impaction of aluminum-lithium alloys,” Scr. Metall. Mater., 32, 821 – 826 (1885).
Y. Yang, Z. Xinming, L. Zhenghua, and L. Qingyun, “Adiabatic shear band on the titanium side in the Ti – mild steel explosive cladding interface,” Acta Mater., 44(2), 561 – 565 (1996).
M. A. Meyers and H. R. Pak, “Observation of an adiabatic shear band in titanium by high-voltage transmission electron microscopy,” Acta Metall., 34, 2493 – 2499 (1986).
M. P. Bondar, S. G. Psakh’e, A. I. Dmitriev, and A. Yu. Nikonov, “Conditions of localization of strain and fragmentation of microstructure under rapid loading,” Fiz. Mesomekh., 16(2), 5 – 13 (2013).
T. W. Wright, The Physics and Mathematics of Adiabatic Shear Bands, University Press, Cambridge (2002), p. 240.
A. F. Belikova, S. N. Buravova, Yu. A. Gordopolov, and I. V. Saikov, “Nature of formation of bands of localized strain under dynamic loads,” Vest. TGU, 16(3), 908 – 909 (2010).
M. Yu. Simonov, O. B. Naimark, Yu. N. Simonov, et al., “Structural aspects of zones of plastic strain. Part I. Effect of adiabatic shear,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 10, 43 – 63 (2019).
M. Yu. Simonov, Yu. N. Simonov, and G. S. Shaimanov, “Structural and fractographic features of formation of splits in a low-alloy steel subjected to thermal deformation treatment,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 10, 5 – 15 (2019).
T. W. Wright and G. Ravichandran, “Canonical aspects of adiabatic shear bands,” Int. J. Plasticity, 13(4), 309 – 325 (1997).
Y. Z. Guo, Q. C. Ruan, S. X. Shu, et al., “Temperature rise associated with adiabatic shear band: Causality clarified,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 122(1), 015503 (2019).
A. Molinari and R. J. Clifton, “Analytical characterization of shear localization in thermoviscoplastic materials,” J. Appl. Mech., 54, 806 – 812 (1987).
D. Rittel, P. Landau, and A. Venkert, “Dynamic recrystallization as a potential cause for adiabatic shear failure,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 101, 165501 (2008).
T. J. Burns, “Does a shear band result from a thermal explosion,” Mech. Mater., 17(2 – 3), 261 – 271 (1994).
L. H. Zhang, D. Rittel, and S. Osovski, “Thermo-mechanical characterization and dynamic failure of near alpha and near beta titanium alloys.” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, Structural Mat. Prop. Microstr. Process., 729, 94 – 101 (2018).
C. Froustey, O. B. Naimark, I. A. Panteleev, et al., “Multiscale mechanisms of structural relaxation and adiabatic shear failure mechanisms,” Phys. Mesomech., 20(1), 31 – 42 (2017).
M. A. Sokovikov, D. A. Bilalov, V. V. Chudinov, et al., “Non equilibrium transitions in ensembles of defects attributed to dynamic localization of plastic deformation,” Tech. Phys. Lett., 40(12), 1075 – 1077 (2014).
D. A. Bilalov, M. A. Sokovikov, V. V. Chudinov, et al., “Numerical simulation and experimental study of plastic strain localization under dynamic loading of specimens in condition close to a pure shear,” J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys., 59(7), 1179 – 1188 (2018).
D. A. Bilalov, M. A. Sokovikov, and V. V. Chudinov, “Multiscale mechanisms of localization of plastic strain in piercing of obstacles,” Deform. Razrush. Mater., No. 5, 43 – 47 (2017).
D. Rittel, Z. G. Wang, and M. Merzer, “Adiabatic shear failure and dynamic stored energy of cold work,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 96, 075502 (1 – 4), 2006).
M. Yu. Simonov, M. N. Georgiev, G. S. Shaimanov, et al., “Comparative analysis of zones of plastic strain, dynamic crack resistance, structure and micromechanisms of crack growth of steels 09G2S, 25 and 40 in high-toughness condition,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 2, 39 – 48 (2016).
V. E. Panin, A. V. Panin, D. D. Moiseenko, et al., “The physical mesomechanics of deformable solid body as a multilevel system. II. Phenomenon of interpenetration of particles of unlike solids without disturbing continuity under the action of concentrated energy sources,” Fiz. Mezomekh., 4(9), 5 – 13 (2006).
M. Yu. Simonov, “Structural aspects of zones of plastic strain. Part II. Effect of mass transfer,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 10, 54 – 63 (2019).
M. N. Georgiev, M. Yu. Simonov, and Yu. N. Simonov, “Assessment of the fracture energy of impact specimens with side notches,” Zavod. Lab., Diagn. Mater., 78(9), 56 – 61 (2012).
M. Yu. Simonov, Yu. N. Simonov, A. M. Khanov, and G. S. Shaimanov, “Structure, dynamic crack resistance and fracture mechanisms of quenched and tempered structural steels,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 11, 32 – 29 (2012).
M. Yu. Simonov, M. N. Georgiev, Yu. N. Simonov, and G. S. Shaimanov, “Assessment of the sizes of the zone of plastic strain of high-toughness materials after dynamic tests by the method of systematic measuring of microhardness,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 11, 40 – 45 (2012).
M. Yu. Simonov, G. S. Shaimanov, and Yu. N. Simonov, “Formation of zones of plastic strain in quenched and tempered steel 09G2S during dynamic tests,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 12, 44 – 50 (2015).
The work has been performed within the state assignment conducted by the research stuff on a permanent base (No. 9.7893.2017∕ITR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 10, pp. 64 – 71, October, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonov, M.Y., Naimark, O.B., Simonov, Y.N. et al. Structural Aspects of Zones of Plastic Strain. Part III. Effect of Thermal Stability of Bands of Adiabatic Shear. Met Sci Heat Treat 61, 648–656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-020-00473-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-020-00473-9