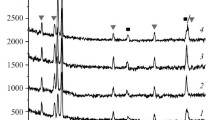
Ti – Zr-based alloys with a high zirconium content prepared by vacuum-arc remelting with nonconsumable tungsten electrode are studied. The optimum number of remelting operations and melting conditions in order to achieve a highly uniform distribution of components and low content of impurities in the alloy are determined. Optimum thermomechanical treatment (cold rolling) and post-deformation annealing regimes are proposed. X-ray studies are conducted at room temperature and after thorough cooling in order to determine the crystallographic resource of alloy reversible deformability. Alloy susceptibility towards superelastic behavior at room temperature, cyclic endurance and its dependence on annealing atmosphere are evaluated in the course of tension-compression mechanical tests.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Here and throughout the text, apart from stipulated cases, alloy chemical composition is provided in at.%.
References
D. Carter, W. Caler, D. Spengler, and V. Frankel, “Fatigue behavior of adult cortical bone: the influence of mean strain and strain range,” Acta Orthop., 52(5), 481 – 490 (1981).
S. Shabalovskaya, “On the nature of the biocompatibility and on the medical applications of NiTi shape memory alloys,” Bio-Med. Mater. Eng., 6(4), 267 – 289 (1996).
V. Brailovski, S. Prokoshkin, K. Inaekyan, and V. Demers, “Functional properties of nanocrystalline, submicrocrystalline and polygonized Ti – Ni alloys processed by cold rolling and post deformation annealing,” J. Alloys Compd., 509(5), 2066 – 2075 (2011).
I. Khmelevskaya, I. Trubitsyna, S. Prokoshkin, et al., “Thermomechanical treatment of Ti – Ni-based shape memory alloys using severe plastic deformation,” Mater. Sci. Forum, 426 – 432(3), 2765 – 2770 (2003).
S. Prokoshkin, V. Brailovski, K. Inaekyan, et al., “Thermomechanical treatment of TiNi intermetallic-based shape memory alloys,” in: N. Resnina and V. Rubanik (eds.), Shape Memory Alloys: Properties, Technologies, Opportunities, Trans Tech Publ., Pfaffikon, Switzerland (2015).
J. Kim, H. Kim, T. Inamura, et al., “Shape memory characteristics of Ti – 22 Nb – (2 – 8) Zr (at.%) biomedical alloys,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 403(1 – 2), 334 – 339 (2005).
H. Kim, T. Sasaki, K. Okutsu, et al., “Texture and shape memory behavior of Ti – 22Nb – 6Ta alloy,” Acta Mater., 54(2), 423 – 433 (2006).
P. Buenconsejo, H. Kim, H. Hosoda, and S. Miyazaki, “Shape memory behavior of Ti – Ta and its potential as a high-temperature shape memory alloy,” Acta Mater., 57(4), 1068 – 1077 (2009).
J. Fu, H. Kim, and S. Miyazaki, “Effect of annealing temperature on microstructure and superelastic properties of a Ti – 18Zr– 4.5Nb – 3Sn – 2Mo alloy,” J. Mech. Behav. Biomed., 65(1), 716 – 723 (2017).
H. Hosoda, N. Hosoda, and S. Miyazaki, “Development and characterization of Ni-free Ti-base shape memory and superelastic alloys,” Trans. Mat. Res. Soc. J., 26, 243 – 246 (2001).
T. Ahmed and H. Rack, “Martensitic transformations in Ti – (16 – 26) at.% Nb alloys,” J. Mater. Sci., 31, 4267 – 4276 (1996).
H. Kim, H. Satoru, J. Kim, et al., “Mechanical properties and shape memory behavior of Ti – Nb alloys,” Mat. Trans., 45, 2443 – 2448 (2004).
V. Sheremetyev, V. Brailovski, S. Prokoshkin, et al., “Functional fatigue behavior of superelastic beta Ti – 22Nb – 6Zr (at.%) alloy for load-bearing biomedical applications,” Mater. Sci. Eng., 58, 935 – 944 (2016).
V. Brailovski, S. Prokoshkin, M. Gauthier, et al., “Bulk and porous metastable beta Ti – Nb – Zr(Ta) alloys for biomedical applications,” Mat. Sci. Eng., 31(3), 543 – 657 (2011).
H. Kim, J. Fu, H. Tobe, et al., “Crystal structure, transformation strain, and superelastic property of Ti – Nb – Zr and Ti – Nb –Ta alloys,” Shape Memory Superelasticity, 1, 107 – 116 (2015).
A. Konopatsky, S. Dubinskiy, Y. Zhukova, et al., “Ternary Ti –Zr – Nb and quaternary Ti – Zr – Nb – Ta shape memory alloys for biomedical applications: Structural features and cyclic mechanical properties,” Mat. Sci. Eng., A702, 301 – 311 (2017).
Work was carried out with financial support of the Federal Target program (measure 1.2 “Development of technology for creating intrabone implants with a biopolymer coating based on superelastic titanium alloys,” unique identifier RFMEF167517XO158).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 6, pp. 3 – 9, June, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konopatskii, A.S., Dubinskii, S.M., Zhukova, Y.S. et al. Experimental Search for Chemical Compositions of Superelastic Titanium Alloys with Enhanced Functional Properties. Met Sci Heat Treat 61, 333–339 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-019-00426-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-019-00426-x