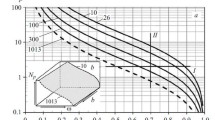
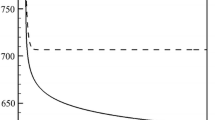
Materials and methods of study of nitriding parameters and nitriding atmospheres obtained under different dilution conditions and at different pressures of undiluted ammonia and the reactions occurring in them are described. Calculated relations characterizing the dependence of the nitrogen potential on the characteristics of the medium and the effect of the degree of dissociation of ammonia on the content of nitrogen in the atmosphere are suggested.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. J. Somers and E. J. Mittemeijer, “Layer, growth, kinetics on gaseous nitriding of pure iron: evolution of diffusion coefficients for nitrogen in iron nitrides,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 26, 57 – 74 (1995).
L. Maldzinski, Thermodynamic, Kinetic and Technological Aspects of Producing Nitrided Layers on Iron and Steel in Processes of Gas Nitriding, Poznan University of Technology, Poznan (2002).
D. Jordan, H. Antes, V. Osterman, and T. Jones, “Vacuum nitriding of 4140 steel,” Heat Treat. Prog., 3 – 4, 33 – 38 (2008).
J. Michalski, “Using nitrogen availability as a nitriding process parameter,” Ind. Heat., 10, 63 – 68 (2012).
J. Michalski, Characteristics and Calculations of Atmospheres for Controlled Gas Nitriding of Steel, Institute of Precision Mechanics, Warsaw (2010).
E. Lehrer, “Über das Eisen-Wasserstoff-Amoniak-Gleichgewicht,” Z. für Elektrochem., 36, 383 – 392 (1930).
E. J. Mittemeijer and M. A. Somers, “Thermodynamics, kinetics, and process control of nitriding,” Surf. Eng., 13, 483 – 497 (1997).
A. V. Smirnov and Y. S. Kuleshov, “Calculations for nitriding with diluted ammonia,” Metall. Sci. Heat Treat., 8, 385 – 403 (1966) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00649318).
H. J. Grabke, “Reaktionen von Ammoniak, Stickstoff und Wasserstoff an der Oberfläche von Eisen,” Berichte Bunsenges für Phys. Chem., 4, 533 – 548 (1968).
N. I. Kardonina, A. S. Yurovskikh, and A. S. Kolpakov, “Transformations in the Fe – Ni system,” Metall. Sci. Heat Treat., 52, 457 – 467 (2010).
W. Arabczyk and J. Zamlynny, “Study of the ammonia decomposition over iron catalysts,” Catal. Lett., 60, 167 – 171 (1999).
R. Wróbel and W. Arabczyk, “Solid-gas reaction with adsorption as the rate limiting step,” J. Phys. Chem. A, 110, 9219 – 24 (2006) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp061947b).
J. Kunze, Nitrogen and Carbon in Iron and Steels Thermodynamics, Akademie Verlag, Berlin (1990).
B. Kooi, M. A. J. Somers, and E. J. Mittemeijer, “An evaluation of the FeN phase diagram considering long range order of N atoms, γ′-Fe4N(1–x)and ε-Fe2N(1–z),” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 27, 1064 – 1071 (1996).
J. R. Jennings, Catalytic Ammonia Synthesis Fundamentals and Practice, Plenum Press, New York (1991).
K. Aika, L. J. Christiansen, I. Dybkjaer, et al., Ammonia Catalysis and Manufacture, Springer Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg (1995).
K. H. Jack, “The occurrence and the crystal structure of α-iron nitride; A new type of interstitial alloy formed during the tempering of nitrogen-martensite,” Proc. R. Soc. Lond., 208, 216 – 224 (1951).
K. H. Jack, “Iron-nitrogen system: The crystal structures of e-phase iron nitrides,” Acta Crystallogr., 5, 404 – 411 (1952).
L. Małdziñski and J. Tacikowski, “Concept of an economical and ecological process of gas nitriding of steel,” HTM Hartereitechnische Mitteilungen, 61, 296 – 302 (2006) (doi: https://doi.org/10.3139/105.100399).
N. L. Anichkina, V. S. Bogolyubov, V. V. Boiko, et al., “Comparison of methods of gas, ionic and vacuum nitriding,” Metall. Sci. Heat Treat., 31, 170 – 174 (1989).
M. Yang and R. D. Sisson, “Alloy effects on the gas nitriding process, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 23, 4181 – 4186 (2014) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1187-1).
L. Barrallier, “Classical nitriding of heat treatable steel,” Thermochem. Surf. Eng. Steels, Elsevier (2015), pp. 393 – 412 (doi: https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857096524.3.393).
K. T. Cho, K. Song, S. H. Oh, et al., “Enhanced surface hardening of AISI D2 steel by atomic attrition during iron nitriding,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 251, 115 – 121 (2014) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.04.011).
D. Manova, D. Hirsch, J. W. Gerlach, et al., “In situ investigation of phase formation during low energy ion nitriding of Ni80Cr20 alloy,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 259, 434 – 441 (2014) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.10.054).
I. Rosales, H. Martinez, and R. Guardian, “Mechanical performance of thermally post-treated ion-nitrided steels,” Appl. Surf. Sci., 371, 576 – 582 (2016) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.048).
D. Hoche, J. Kaspar, and P. Schaaf, “Laser nitriding and carburization of materials,” in: J. R. Lawrence, C. Dowding, D. Waugh, and J. B. Griffiths (eds.), Laser Surf. Eng., Elsevier (2015), pp. 33 – 58 (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-78242-074-3.00002-7).
P. Kula, E. Wolowiec, R. Pietrasik, et al., “Non-steady state approach to the vacuum nitriding for tools,” Vacuum, 88, 1 – 7 (2013) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2012.08.001).
S. M. Soshkin, Y. M. Lakhtin, and Y. D. Kogan, “Structure of the diffusion layer with vacuum nitriding,” Metall. Sci. Heat Treat., 26, 521 – 523 (1984).
Y. M. Lakhtin, Y. D. Kogan, and S. M. Soshkin, “Nitriding of steels in vacuum,” Metall. Sci. Heat Treat., 22, 635 – 638 (1980).
M. Perez and F. J. Belzunce, “A comparative study of salt-bath nitrocarburizing and gas nitriding followed by post-oxidation used as surface treatments of H13 hot forging dies,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 305, 146 – 157 (2016) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016. 08.003).
Z. Zhou, M. Dai, Z. Shen, and J. Hu, “Effect of D.C. electric field on salt bath nitriding for 35 steel and kinetics analysis,” J. Alloys Compd., 623, 261 – 265 (2015) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom. 2014.10.146).
Y. M. Lakhtin and Y. D. Kogan, “Controlled nitriding processes,” Metall. Sci. Heat Treat., 20, 667 – 671 (1978) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00780806).
J. Tacikowski and J. Zysk, Method of Gas Nitriding, PL 85924 (1977).
M. Kulka, D. Panfil, J. Michalski, and P. Wach, “The effects of laser surface modification on the microstructure and properties of gas-nitrided 42CrMo4 steel,” Opt. Laser Technol., 82, 203 – 219 (2016) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2016.02.021).
D. Panfil, M. Kulka, P. Wach, et al., “Nanomechanical properties of iron nitrides produced on 42CrMo4 steel by controlled gas nitriding and laser heat treatment,” J. Alloys Compd., 706, 63 – 75 (2017) (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.02.220).
L. Maldzinski and J. Tacikowski, “ZeroFlow gas nitriding of steels,” in: M. A. Mitemeijer and J. Somers (eds.), Thermochem. Surf. Eng. Steels, Elsevier (2015), pp. 459 – 483 (doi: https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857096524.3.459).
M. Bazel, M. Korecki, L. Maldzinski, et al., “Industrial experiences with controlled nitriding using a ZeroFlow method,” Heat Treat. Prog., 7 – 8, 19 – 22 (2009).
P. Kula, R. Pietrasik, and E. Stañczyk-Wo3owiec, Method of Nitriding Tools Made of Iron Alloys, PL 219125 (2014).
V. M. Zinchenko, V. Y. Syropyatov, V. V. Barelko, and L. A. Bykov, “Gas nitriding in catalytically prepared ammonia media,” Metall. Sci. Heat Treat., 39, 280 – 284 (1977).
W. S. Krylov, E. H. Goralczyk, and G. W. Szerbiednickij, “Features of nitriding of iron and steel in an ammonia pressure below atmospheric pressure,” Metally, 4, 175 – 178 (1977).
E. Wołowiec, P. Kula, B. Januszewicz, and M. Korecki, “Mathematical modelling the low-pressure nitriding process,” Appl. Mech. Mater., 421, 377 – 383 (2013).
B. J. Lightfoot and K. H. Jack, “Kinetics of nitriding with and without white layer formation,” in: Proc. Heat Treat.’73, The Metals Society, London (1973), pp. 59 – 66 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 3, pp. 44 – 52, March, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michalski, J., Wołowiec-Korecka, E. A Study of Parameters of Nitriding Processes. Part 1. Met Sci Heat Treat 61, 183–190 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-019-00398-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-019-00398-y