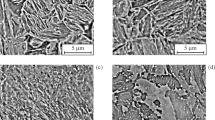
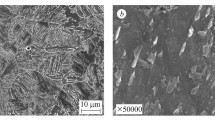
Comparative analysis of zones of plastic strain, dynamic crack resistance, structure, and micromechanisms of crack propagation in structural steels 09G2S, 25 and 40 in high-toughness condition is performed. The structure, the micromechanisms of crack growth, and the dynamic crack resistance of steels 09G2S, 25 and 40 are studied. Complete zones of plastic stain (CPSZ) under fracture surfaces are plotted after quenching and high tempering at 650°C. The levels of microhardness in the CPSZ are mapped for specially-designed specimens with additional 1-mm-deep side notches and relative crack length of 0.4 – 0.5. The sizes of the zones of plastic strain in the starting region are determined. Special features of the distribution of microhardness in local volumes of the CPSZ are determined. The structure under fracture surfaces of steels 09G2S, 25 and 40 is studied over the whole of the path of propagation of a dynamic crack.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. N. Georgiev, Toughness of Low-Carbon Steels [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1973), 224 p.
M. N. Georgiev and Yu. N. Simonov, Crack Resistance of Iron-Carbon Alloys, A Monograph [in Russian], Izd. PNIPU, Perm (2013), 418 p.
M. N. Georgiev and V. D. Kudin, “Classical brittle point in connection with the conditions of operating fracture,” Zavod. Lab., No. 6, 69 – 71 (1982).
Yu. N. Simonov, M. Yu. Simonov, G. S. Shaimanov, and L. E. Makarova, “A method for determining the plastic strain zone under fracture of a specimen, RF Patent 2516391, MPK G 01 No. 3/28, Patentee Perm National Research Polytechnic University,” Byull. Izobr. Polezn. Modeli, No. 14 (2014), Appl. 07.12.2012, Publ. 20.05.2014.
M. Yu. Simonov, G. S. Shaimanov, and Yu. N. Simonov, “Formation of zones of plastic strain in quenched and tempered steel 09G2S during dynamic tests,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 12 (2015).
Yu. N. Simonov, M. Yu. Simonov, D. O. Panov, A. V. Kasatkin, and D. P. Poduzov, “A method for evaluating the impact toughness of high-toughness sheet structural steels, RF Patent 2485476, MPK G 01 No. 3/30,” Byull. Izobr. Polezn. Modeli, No. 17 (2014), Appl. 10.01.2012, Publ. 20.06.2013.
M. Yu. Simonov, Yu. N. Simonov, A. M. Khanov, and G. S. Shaimiev, “Structure, dynamic crack resistance, and mechanisms of fracture of quenched and tempered structural steels,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 11, 32 – 39 (2012).
M. Yu. Simonov, G. S. Shaimanov, A. S. Pertsev, et al., “Structural and fractographic features of formation of high level of dynamic crack resistance and strength in steel 35Kh after cold radial forging,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 2 (2016).
M. Yu. Simonov, M. N. Georgiev, Yu. N. Simonov, and G. S. Shaimanov, “Evaluation of the sizes of plastic strain zone of high-toughness materials after dynamic testing by the method of systematic measurement of microhardness,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 11, 40 – 45 (2012).
Yu. N. Simonov, M. N. Georgiev, and M. Yu. Simonov, Fundamentals of Fracture Physics and Mechanics [in Russian], Izd. PNIPU, Perm (2012), 203 p.
M. N. Georgiev, Yu. N. Simonov, N. Ya. Mezhova, and V. N.Minaev, “Structural aspects of cyclic crack resistance of quenched and tempered steels,” Fiz. Khim. Mekhan. Mater., 21(5), 48 – 53 (1985).
M. N. Georgiev, M. Yu. Simonov, and Yu. N. Simonov, “Evaluation of fracture energy of impact specimens with side notches,” Zavod. Lab. Diagn. Mater., 78(9), 56 – 61 (2012).
A. A. Stepashkin, D. Yu. Ozherelkov, Yu. B. Sazonov, et al., “Evaluation of the fracture toughness of a discretely reinforced carbon-carbon composite material,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 4, 51 – 58 (2014).
A. A. Shanyavskii, “Rotational instability of deformation and fracture of metals under propagation of fatigue cracks at the mesoscopic and scale level. 1. Processes of plastic deformation at the tip of a crack,” Fiz. Mezomekhan., 4(1), 73 – 80 (2001).
O. B. Naimark, Yu. V. Bayandim, V. A. Leont’ev, and S. L. Permyakov, “On the thermodynamics of structure-scale transitions under plastic deformation of solids,” Fiz. Mezomekhan., 8(5), 23 – 29 (2005).
O. A. Panov, V. V. Chudinov, V. A. Leont’ev, and O. B. Naimark, “A study of special features of dissipation and accumulation of energy in submicrocrystalline titanium under quasi-static dynamic loading,” Vychisl. Mekhan. Sploshn. Sred, 1(4), 69 – 77 (2008).
S. I. Mednikov and D. M. Gureev, “On the problem of lowering the temperature of the start of phase transformation in steels under the action of plastic deformation,” Pis’ma Zh. Teor. Fiz., 18(5), 25 – 27 (1992).
D. O. Panov, Yu. N. Simonov, L. V. Spivak, and A. I. Smirnov, “Stages of austenitization of cold-deformed low-carbon steel in the intercritical temperature range,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 116(8), 846 (2015).
V. E. Panin, A. V. Panin, D. D. Moiseenko, et al., “The physical mesomechanics of deformable solid as a miltilevel system. II. Phenomenon of interpenetration of particles of unlike solids without disturbance of continuity under the action of lumped sources of energy,” Fiz. Mezomekhan., 4(9), 5 – 13 (2006).
R.W. Hertzberg, Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, John Wiley & Sons Inc., NJ (1996), 786 p.
E. A. Lyapunova, A. N. Petrova, I. G. Borodina, et al., “A study of the morphology of multiscale defect structures and localization of plastic strain due to puncturing of targets from steel A6061,” Pis’ma Zh. Teor. Fiz., 38(1), 13 – 20 (2012).
V. E. Panin and Yu. V. Grinyaev, “Physical mesomechanics: a new paradigm at the junction of the physics and mechanics of deformable solid,” Fiz. Mezomekhan., 6(4), 9 – 36 (2003).
T. F. Elsukova and E. V. Panin, “Effect of the scale levels of rotation modes of plastic yielding on strain resistance of polycrystals,” Fiz. Mezomekhan., 12(3), 5 – 13 (2009).
Jobu Awatani, Kazumune Katagiri, and Hiroshi Nakai, “Dislocation structures around propagating fatigue cracks in iron,” Metall. Trans. A, 9A, 111 – 116 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 2, pp. 39 – 48, February, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonov, M.Y., Georgiev, M.N., Shaimanov, G.S. et al. Comparative Analysis of Zones of Plastic Strain, Dynamic Crack Resistance, Structure and Micromechanisms of Crack Propagation in Structural Steels 09G2S, 25 and 40 in High-Toughness Condition. Met Sci Heat Treat 58, 97–105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-016-9970-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-016-9970-2