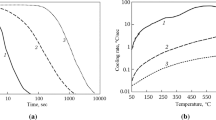
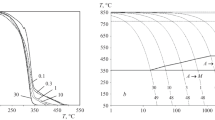
The effect of hot plastic deformation on decomposition of supercooled austenite in some structural and die steels with different contents of carbon and alloying elements is investigated. It is shown that high-temperature plastic deformation accelerates the transformation of supercooled austenite by the diffusion mechanism and decelerates the development of bainitic transformations by raising the hardenability of the steels. The general laws of formation of mechanical properties under high-temperature thermomechanical treatment of structural and die steels after low- and high-temperature tempering are studied.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. V. Smirnov, E. N. Sokolkov, and V. D. Sadovskii, “Effect of plastic deformation in austenitic condition on the temper brittleness of structural steels,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 103(4), 609 – 610 (1955).
E. N. Sokolkov and V. D. Sadovskii, “High-temperature thermomechanical treatment of metals and alloys,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 19(2), 226 – 240 (1965).
M. M. Shteinberg, V. I. Filatov, T. S. Shilkova, et al., “Effect of high-temperature plastic deformation on the kinetics of decomposition of supercooled austenite,” Izv. Vysh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., No. 10, 117 – 119 (1973).
M. M. Shteinberg, M. A. Smirnov, and V. I. Filatov, “High-temperature thermomechanical treatment of alloy steels with different carbon contents,” Fiz. Khim. Obrab. Mater., No. 1, 100 – 106 (1978).
A. N. Monoshkov, Yu. I. Pashkov, and V. A. Vlasov, “About the choice of specimen and mode of its loading for determining the resistance of materials to crack propagation,” Zavod. Lab., No. 3, 338 – 341 (1973).
M. A. Smirnov, L. V. Smirnov, V. M. Schastlivtsev et al, “Effect of high-temperature thermomechanical treatment on the intercrystalline brittleness of structural steels,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 67(5), 950 – 958 (1989).
M. A. Smirnov, M. M. Shteinberg, L. G. Gurevich, et al., “Strengthening of die steels under high-temperature thermomechanical treatment,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 9, 29 – 31 (1973).
M. A. Smirnov, M. M. Shteinberg, and L. G. Gurevich, “Effect of high-temperature thermomechanical treatment on mechanical properties of die steels,” in: Volume Die Forming [in Russian], MDNTP, Moscow (1973), pp. 141 – 146.
M. A. Smirnov, M. M. Shteinberg, L. G. Gurevich, et al., “Mechanical properties of die steels after HTTMT,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 11, 53 – 59 (1977).
M. A. Smirnov, M. M. Shteinberg, L. G. Gurevich, and V. I. Filatov, “Effect of HTTMT on the thermal fatigue strength of die steels,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 3, 29 – 31 (1979).
M. A. Smirnov, M. M. Shteinberg, V. I. Filatov, and L. G. Gurevich, “Effect of high-temperature deformation on the embrittlement of steel 3Kh2V8F at elevated loading temperatures,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Metally, No. 1, 167 – 169 (1980).
Yu. F. Balandin and M. A. Zolotukhina, “A new method for evaluation of thermal fatigue of structural materials,” Zavod. Lab., No. 1, 63 – 66 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 9, pp. 15 – 21, September, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smirnov, V.A., Filatov, V.I. High-Temperature Thermomechanical Treatment of Alloyed Structural and Tool Steels. Met Sci Heat Treat 56, 470–476 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-015-9784-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-015-9784-7