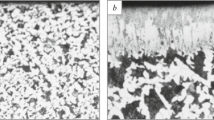
The structure and mechanical properties of steel with an elevated content of boron are studied after tensile tests at a high temperature. In its initial condition, the structure of the steel contains two types of borides [TiB2 and (Fe, Cr)2B] distributed uniformly in a ferritic matrix. The range of satisfactory process ductility is shown to be 1050 – 1150°C; at 1200°C the metal undergoes brittle fracture due to local fusion of individual regions of the structure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. E. Alshevskii, Yu. S. Kuzmichev, L. M. Kurochkina, et al., “Effect of ultrasound on the plasticity of high-boron stainless steel,” At. Energ., 20(5), 440 – 442 (1966).
L. He, Y. Liu, J. Li, and B. Li, “Effects of hot rolling and titanium content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of high boron Fe – B alloys,” Mater. Design, 36, 88 – 93 (2012).
Y. Liu, B. Li, J. Li, et al., “Effect of titanium on the ductilization of Fe – B alloys with high boron content,” Mater. Lett., 64, 1299 – 1301 (2010).
L. Zhong, C. Xiang, L. Yan-xiang, and H. Kai-hua, “High boron iron-based alloy and its modification,” J. Iron Steel Res., 16, 37 – 42 (2009).
K. Tanaka and T. Saito, “Phase equilibria in TiB2-reinforced high modulus steel,” J. Phase Equilibria, 20(3), 207 – 214 (1999).
V. Raghavan, “B – Cr – Fe – Ti (Boron – Chromium – Iron – Titanium),” J. Phase Equilibria, 24(5), 459 – 460 (2003).
G. V. Samsonov, T. I. Serebryakova, and V. A. Neronov, Borides [in Russian]. Atomizdat, Moscow (1975).
G. V. Samsonov, L. Ya. Markovskii, A. F. Zhigach, and M. G. Valyashko, Boron, Its Compounds and Alloys [in Russian]. Izd-vo AN Ukr. SSR, Kiev (1960).
A. A. Babakov and M. V. Pridantsev, Corrosion-Resistant Steels and Alloys [in Russian]. Metallurgiya, Moscow (1971).
This research was conducted with financial support from the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation for the realization of a project aimed at arranging for high-technology manufacturing in accordance with the theme: “Creation of Modern Facilities for the Production of Storage Racks for Heat-Releasing Rod Assemblies with the Use of High-Boron Steel.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 6, pp. 53 – 55, June, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Churyumov, A.Y., Khomutov, M.G., Pozdnyakov, A.V. et al. Study of the Structure and High-Temperature Mechanical Properties of a Steel with an Elevated Content of Boron. Met Sci Heat Treat 56, 336–338 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-014-9757-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-014-9757-2