Abstract
Background
In recent decades, phytotherapy has remained as a key therapeutic option for the treatment of various cancers. Evodiamine, an excellent phytocompound from Evodia fructus, exerts anticancer activity in several cancers by modulating drug resistance. However, the role of evodiamine in cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells is not clear till now. Therefore, we have used evodiamine as a chemosensitizer to overcome cisplatin resistance in NSCLC.
Methods
Here, we looked into SOX9 expression and how it affects the cisplatin sensitivity of cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells. MTT and clonogenic assays were performed to check the cell proliferation. AO/EtBr and DAPI staining, ROS measurement assay, transfection, Western blot analysis, RT-PCR, Scratch & invasion, and comet assay were done to check the role of evodiamine in cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells.
Results
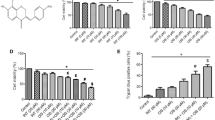
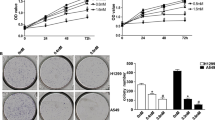
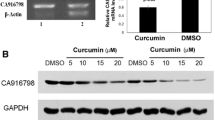
SOX9 levels were observed to be higher in cisplatin-resistant A549 (A549CR) and NCI-H522 (NCI-H522CR) compared to parental A549 and NCI-H522. It was found that SOX9 promotes cisplatin resistance by regulating β-catenin. Depletion of SOX9 restores cisplatin sensitivity by decreasing cell proliferation and cell migration and inducing apoptosis in A549CR and NCI-H522CR. After evodiamine treatment, it was revealed that evodiamine increases cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in A549CR and NCI-H522CR cells through increasing intracellular ROS generation. The combination of both drugs also significantly inhibited cell migration by inhibiting epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT). Mechanistic investigation revealed that evodiamine resensitizes cisplatin-resistant cells toward cisplatin by decreasing the expression of SOX9 and β-catenin.
Conclusion
The combination of evodiamine and cisplatin may be a novel strategy for combating cisplatin resistance in NSCLC.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL, Paz-Ares L (2017) Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 389(10066):299–311
Fennell DA, Summers Y, Cadranel J, Benepal T, Christoph DC, Lal R, Das M, Maxwell F, Visseren-Grul C, Ferry D (2016) Cisplatin in the modern era: the backbone of first-line chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 44:42–50
Min HY, Lee HY (2021) Mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Arch Pharm Res 44(2):146–164
Wang L, Liu X, Ren Y, Zhang J, Chen J, Zhou W, Guo W, Wang X, Chen H, Li M, Yuan X, Zhang X, Yang J, Wu C (2017) Cisplatin-enriching cancer stem cells confer multidrug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via enhancing TRIB1/HDAC activity. Cell Death Dis 8(4):e2746
Tanabe S, Quader S, Cabral H, Ono R (2020) Interplay of EMT and CSC in cancer and the potential therapeutic strategies. Front Pharmacol 11:904
Kohno K, Uchiumi T, Niina I, Wakasugi T, Igarashi T, Momii Y, Yoshida T, Matsuo K, Miyamoto N, Izumi H (2005) Transcription factors and drug resistance. Eur J Cancer 41(16):2577–2586
Vishnoi K, Viswakarma N, Rana A, Rana B (2020) Transcription factors in cancer development and therapy. Cancers 12(8):2296
Kawai T, Yasuchika K, Ishii T, Miyauchi Y, Kojima H, Yamaoka R, Katayama H, Yoshitoshi EY, Ogiso S, Kita S, Yasuda K, Fukumitsu K, Komori J, Hatano E, Kawaguchi Y, Uemoto S (2016) SOX9 is a novel cancer stem cell marker surrogated by osteopontin in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep 6:30489
Voronkova MA, Rojanasakul LW, Kiratipaiboon C, Rojanasakul Y (2020) The SOX9-aldehyde dehydrogenase axis determines resistance to chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Cell Biol 40(2):e00307-e319. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00307-19
Panda M, Tripathi SK, Biswal BK (2021) SOX9: An emerging driving factor from cancer progression to drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1875(2):188517
Huang JQ, Wei FK, Xu XL, Ye SX, Song JW, Ding PK, Zhu J, Li HF, Luo XP, Gong H, Su L, Yang L, Gong LY (2019) SOX9 drives the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small-cell lung cancer through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Transl Med 17(1):143
Ma F, Ye H, He HH, Gerrin SJ, Chen S, Tanenbaum BA, Cai C, Sowalsky AG, He L, Wang H, Balk SP, Yuan X (2016) SOX9 drives WNT pathway activation in prostate cancer. J Clin Invest 126(5):1745–1758
Sakunrangsit N, Kalpongnukul N, Pisitkun T, Ketchart W (2016) Plumbagin enhances tamoxifen sensitivity and inhibits tumor invasion in endocrine resistant breast cancer through EMT regulation. Phytother Res 30(12):1968–1977
Shaikh S, Shaikh J, Naba YS, Doke K, Ahmed K, Yusufi M (2021) Curcumin: reclaiming the lost ground against cancer resistance. Cancer Drug Resist 4(2):298–320
Gavaraskar K, Dhulap S, Hirwani RR (2015) Therapeutic and cosmetic applications of evodiamine and its derivatives–a patent review. Fitoterapia 106:22–35
Liao CH, Pan SL, Guh JH, Chang YL, Pai HC, Lin CH, Teng CM (2005) Antitumor mechanism of evodiamine, a constituent from chinese herb evodiae fructus, in human multiple-drug resistant breast cancer NCI/ADR-RES cells in vitro and in vivo. Carcinogenesis 26(5):968–975
Sui H, Zhou LH, Zhang YL, Huang JP, Liu X, Ji Q, Fu XL, Wen HT, Chen ZS, Deng WL, Zhu HR, Li Q (2016) Evodiamine suppresses ABCG2 mediated drug resistance by inhibiting p50/p65 NF-κB pathway in colorectal cancer. J Cell Biochem 117(6):1471–1481
Liu L, Sun X, Guo Y, Ge K (2022) Evodiamine induces ROS-dependent cytotoxicity in human gastric cancer cells via TRPV1/Ca(2+) pathway. Chem Biol Interact 351:109756
Kleih M, Böpple K, Dong M, Gaißler A, Heine S, Olayioye MA, Aulitzky WE, Essmann F (2019) Direct impact of cisplatin on mitochondria induces ROS production that dictates cell fate of ovarian cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 10(11):851
Xue DF, Pan ST, Huang G, Qiu JX (2020) ROS enhances the cytotoxicity of cisplatin by inducing apoptosis and autophagy in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 122:105732
Rojas E, Lopez MC, Valverde M (1999) Single cell gel electrophoresis assay: methodology and applications. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 722(1–2):225–254
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674
Khine HEE, Ecoy GAU, Roytrakul S, Phaonakrop N, Pornputtapong N, Prompetchara E, Chanvorachote P, Chaotham C (2021) Chemosensitizing activity of peptide from lentinus squarrosulus (Mont.) on cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Sci Rep 11(1):4060. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-83606-1
Zhang C, He LJ, Zhu YB, Fan QZ, Miao DD, Zhang SP, Zhao WY, Liu XP (2019) Piperlongumine inhibits akt phosphorylation to reverse resistance to cisplatin in human non-small cell lung cancer cells via ROS regulation. Front Pharmacol 10:1178
Yang J, Zhao X, Tang M, Li L, Lei Y, Cheng P, Guo W, Zheng Y, Wang W, Luo N, Peng Y, Tong A, Wei Y, Nie C, Yuan Z (2017) The role of ROS and subsequent DNA-damage response in PUMA-induced apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 8(14):23492–23506
Ribatti D, Tamma R, Annese T (2020) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cancer: a historical overview. Transl Oncol 13(6):100773
Tsoukalas N, Aravantinou-Fatorou E, Tolia M, Giaginis C, Galanopoulos M, Kiakou M, Kostakis ID, Dana E, Vamvakaris I, Korogiannos A, Tsiambas E, Salemis N, Kyrgias G, Karameris A, Theocharis S (2017) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in non small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 37(4):1773–1778
Tripathi SK, Biswal BK (2021) SOX9 promotes epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance via targeting β-catenin and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. Life Sci 277:119608
Panda M, Biswal BK (2022) Evodiamine inhibits stemness and metastasis by altering the SOX9-β-catenin axis in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Cell Biochem 123(9):1454–1466
Jo A, Denduluri S, Zhang B, Wang Z, Yin L, Yan Z, Kang R, Shi LL, Mok J, Lee MJ, Haydon RC (2014) The versatile functions of Sox9 in development, stem cells, and human diseases. Genes Dis 1(2):149–161
Aguilar-Medina M, Avendano-Felix M, Lizarraga-Verdugo E, Bermudez M, Romero-Quintana JG, Ramos-Payan R, Ruiz-Garcia E, Lopez-Camarillo C (2019) SOX9 stem-cell factor: clinical and functional relevance in cancer. J Oncol 2019:6754040
Li XL, Chen XQ, Zhang MN, Chen N, Nie L, Xu M, Gong J, Shen PF, Su ZZ, Weng X, Tan JY, Zhao T, Zeng H, Zhou Q (2015) SOX9 was involved in TKIs resistance in renal cell carcinoma via Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(4):3871–3881
Wang Z, Xu X, Liu N, Cheng Y, Jin W, Zhang P, Wang X, Yang H, Liu H, Tu Y (2018) SOX9-PDK1 axis is essential for glioma stem cell self-renewal and temozolomide resistance. Oncotarget 9(1):192–204
Novikov NM, Zolotaryova SY, Gautreau AM, Denisov EV (2021) Mutational drivers of cancer cell migration and invasion. Br J Cancer 124(1):102–114
Liu L, Zhu H, Liao Y, Wu W, Liu L, Liu L, Wu Y, Sun F, Lin HW (2020) Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway reverses multi-drug resistance and EMT in Oct4(+)/Nanog(+) NSCLC cells. Biomed Pharmacother 127:110225
Amable L (2016) Cisplatin resistance and opportunities for precision medicine. Pharmacol Res 106:27–36
Sun CY, Zhang QY, Zheng GJ, Feng B (2019) Phytochemicals: current strategy to sensitize cancer cells to cisplatin. Biomed Pharmacother 110:518–527
Jiang ZB, Huang JM, Xie YJ, Zhang YZ, Chang C, Lai HL, Wang W, Yao XJ, Fan XX, Wu QB, Xie C, Wang MF, Leung EL (2020) Evodiamine suppresses non-small cell lung cancer by elevating CD8(+) T cells and downregulating the MUC1-C/PD-L1 axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):249
Su T, Yang X, Deng JH, Huang QJ, Huang SC, Zhang YM, Zheng HM, Wang Y, Lu LL, Liu ZQ (2018) Evodiamine, a novel NOTCH3 methylation stimulator, significantly suppresses lung carcinogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Front Pharmacol 9:434
Zhong ZF, Tan W, Wang SP, Qiang WA, Wang YT (2015) Anti-proliferative activity and cell cycle arrest induced by evodiamine on paclitaxel-sensitive and -resistant human ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep 5:16415
Hu T, Li Z, Gao CY, Cho CH (2016) Mechanisms of drug resistance in colon cancer and its therapeutic strategies. World J Gastroenterol 22(30):6876–6889
Alan Mitteer R, Wang Y, Shah J, Gordon S, Fager M, Butter PP, Jun Kim H, Guardiola-Salmeron C, Carabe-Fernandez A, Fan Y (2015) Proton beam radiation induces DNA damage and cell apoptosis in glioma stem cells through reactive oxygen species. Sci Rep 5:13961
Lee YJ, Lee GJ, Yi SS, Heo SH, Park CR, Nam HS, Cho MK, Lee SH (2016) Cisplatin and resveratrol induce apoptosis and autophagy following oxidative stress in malignant mesothelioma cells. Food Chem Toxicol 97:96–107
Lee H, Lee D, Kang KS, Song JH, Choi YK (2018) Inhibition of intracellular ROS accumulation by formononetin attenuates cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells. Int J Mol Sci 19(3):813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030813
He W, Xia Y, Cao P, Hong L, Zhang T, Shen X, Zheng P, Shen H, Liang G, Zou P (2019) Curcuminoid WZ35 synergize with cisplatin by inducing ROS production and inhibiting TrxR1 activity in gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):207
Lai X, Li Q, Wu F, Lin J, Chen J, Zheng H, Guo L (2020) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition and metabolic switching in cancer: lessons from somatic cell reprogramming. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:760
Kim EK, Choi EJ, Debnath T (2016) Role of phytochemicals in the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis. Food Funct 7(9):3677–3685
Hong Z, Wang Z, Zhou B, Wang J, Tong H, Liao Y, Zheng P, Jamshed MB, Zhang Q, Chen H (2020) Effects of evodiamine on PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol 56(3):783–793
Zhao S, Xu K, Jiang R, Li DY, Guo XX, Zhou P, Tang JF, Li LS, Zeng D, Hu L, Ran JH, Li J, Chen DL (2020) Evodiamine inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the hippo-yes-associated protein signaling pathway. Life Sci 251:117424
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, Odisha, India, for providing laboratory and equipment facilities to carry out the research.
Funding
MP’s research was funded by grants from the Department of Science and Technology, Science and Engineering Research Board (DST, SERB), New Delhi, India (Grant Number: ECR/2016/000792), and the Department of Science and Technology, Odisha, India (Grant no-1201). SB was supported by a grant from the University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India (Grant Number: 997/(CSIR-UGC NET JUNE 2019)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MP: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, and writing–original draft, BKB: investigation and supervision, SB: formal analysis and writing–review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, M., Biswal, S. & Biswal, B.K. Evodiamine potentiates cisplatin-induced cell death and overcomes cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting SOX9-β‐catenin axis. Mol Biol Rep 51, 523 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09477-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09477-7