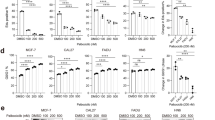
Abstract
Background
In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) with human papillomavirus (HPV)-negative, deregulation of cell cycle is partly due to inactivation of p16INK4 and overexpression of cyclin D1. Here we investigated the in vitro and in vivo effects of the CDK4/6 inhibitor Palbociclib alone or combined with EGFR inhibitor Cetuximab in HNSCC.
Methods and results
CCK-8, soft agar assay, colony formation assay, wound healing assay and transwell assay, β-galactosidase assay, western blotting, and cell-derived xenografts were used to investigated the in vitro and in vivo activity of drugs. Cell viability and colony formation decreased in a dose-dependent manner in Tu686, AMC-HN8, and Fadu cells under Palbociclib treatment. Palbociclib remarkably inhibited migration, invasion and the expression MMP-9 in HNSCC cells. Palbociclib also induced senescence. Palbociclib caused the dephosphorylation of RB but increased the cyclin D1 level in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, combination with Cetuximab could significantly prevent the induction of cyclin D1 and activation of EGFR signals from Palbociclib treatment. Nevertheless, only within the range of certain concentrations, a synergistic inhibitory effect on cell growth was observed when combined with Palbociclib and Cetuximab. Although the synergistic effect in Palbociclib/Cetuximab combined therapy was comparable to that in traditional chemotherapeutic regimens (cisplatin/Cetuximab) in Fadu tumor xenograft, the combination therapy was less active than Cetuximab monotherapy in Tu686 tumor xenograft.
Conclusion
In HPV-negative HNSCC, CDK4/6 inhibitor shows promising anti-tumor effects, which exhibits a synergistic effect when combined with EGFR inhibitor only in specific drug concentration and mouse model.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the conclusions of this study are obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71:7–33
Mody MD, Rocco JW, Yom SS, Haddad RI, Saba NF (2021) Head and neck cancer. Lancet 398:2289–2299
Vermorken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F, Remenar E, Kawecki A, Rottey S et al (2008) Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 359:1116–1127
Guigay J, Auperin A, Fayette J, Saada-Bouzid E, Lafond C, Taberna M et al (2021) Cetuximab, docetaxel, and cisplatin versus platinum, fluorouracil, and cetuximab as first-line treatment in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma (GORTEC 2014-01 TPExtreme): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. LANCET ONCOL 22:463–475
Vermorken JB, Herbst RS, Leon X, Amellal N, Baselga J (2008) Overview of the efficacy of cetuximab in recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in patients who previously failed platinum-based therapies. CANCER-AM CANCER SOC 112:2710–2719
Chaudhary S, Pothuraju R, Rachagani S, Siddiqui JA, Atri P, Mallya K et al (2021) Dual blockade of EGFR and CDK4/6 delays head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by inducing metabolic rewiring. CANCER LETT 510:79–92
van Caloen G, Schmitz S, El BM, Caignet X, Pyr DRS, Roger PP et al (2020) Preclinical activity of Ribociclib in squamous cell carcinoma of the Head and Neck. MOL CANCER THER 19:777–789
Turner NC, Slamon DJ, Ro J, Bondarenko I, Im SA, Masuda N et al (2018) Overall survival with Palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 379:1926–1936
Temam S, Kawaguchi H, El-Naggar AK, Jelinek J, Tang H, Liu DD et al (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor copy number alterations correlate with poor clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous cancer. J CLIN ONCOL 25:2164–2170
Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, Zhang HZ, Katz R, Hammond EH et al (2002) Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. CANCER RES 62:7350–7356
Adkins D, Ley J, Neupane P, Worden F, Sacco AG, Palka K et al (2019) Palbociclib and cetuximab in platinum-resistant and in cetuximab-resistant human papillomavirus-unrelated head and neck cancer: a multicentre, multigroup, phase 2 trial. LANCET ONCOL 20:1295–1305
Adkins DR, Lin JC, Sacco A, Ley J, Oppelt P, Vanchenko V et al (2021) Palbociclib and cetuximab compared with placebo and cetuximab in platinum-resistant, cetuximab-naive, human papillomavirus-unrelated recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomized, phase 2 trial. ORAL ONCOL 115:105192
Li RC, Du Y, Zeng QY, Tang LQ, Zhang H, Li Y et al (2016) Antibodies against Epstein-Barr Virus Glycoprotein gp42 for the diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. CLIN LAB 62:553–561
Hernandez-Perez M, El-hajahmad M, Massaro J, Mahalingam M (2012) Expression of gelatinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) and gelatinase activator (MMP-14) in actinic keratosis and in in situ and invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol 34:723–728
Mountzios G, Rampias T, Psyrri A (2014) The mutational spectrum of squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck: targetable genetic events and clinical impact. ANN ONCOL 25:1889–1900
Beck TN, Georgopoulos R, Shagisultanova EI, Sarcu D, Handorf EA, Dubyk C et al (2016) EGFR and RB1 as dual biomarkers in HPV-Negative Head and Neck Cancer. MOL CANCER THER 15:2486–2497
van Caloen G, Machiels JP (2019) Potential role of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. CURR OPIN ONCOL 31:122–130
Sathe A, Koshy N, Schmid SC, Thalgott M, Schwarzenbock SM, Krause BJ et al (2016) CDK4/6 inhibition controls proliferation of bladder Cancer and transcription of RB1. J Urol 195:771–779
Chen L, Pan J (2017) Dual cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition by PD-0332991 induces apoptosis and senescence in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Br J Pharmacol 174:2427–2443
Rubio C, Martinez-Fernandez M, Segovia C, Lodewijk I, Suarez-Cabrera C, Segrelles C et al (2019) CDK4/6 inhibitor as a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Advanced bladder Cancer independently of RB1 Status. CLIN CANCER RES 25:390–402
Gao Y, Shen J, Choy E, Mankin H, Hornicek F, Duan Z (2017) Inhibition of CDK4 sensitizes multidrug resistant ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel by increasing apoptosiss. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 40:209–218
Zhang J, Jin X, Fang S, Li Y, Wang R, Guo W et al (2004) The functional SNP in the matrix metalloproteinase-3 promoter modifies susceptibility and lymphatic metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma but not in gastric cardiac adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis 25:2519–2524
Kerkela E, Saarialho-Kere U (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor progression: focus on basal and squamous cell skin cancer. EXP DERMATOL 12:109–125
Liu F, Korc M (2012) Cdk4/6 inhibition induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances invasiveness in pancreatic cancer cells. MOL CANCER THER 11:2138–2148
Chou A, Froio D, Nagrial AM, Parkin A, Murphy KJ, Chin VT et al (2018) Tailored first-line and second-line CDK4-targeting treatment combinations in mouse models of pancreatic cancer. Gut 67:2142–2155
Coppe JP, Desprez PY, Krtolica A, Campisi J (2010) The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: the dark side of tumor suppression. Annu Rev Pathol 5:99–118
Gadsden NJ, Fulcher CD, Li D, Shrivastava N, Thomas C, Segall JE et al (2021) Palbociclib renders human papilloma virus-negative Head and Neck squamous cell Carcinoma Vulnerable to the Senolytic Agent Navitoclax. MOL CANCER RES 19:862–873
Yang C, Li Z, Bhatt T, Dickler M, Giri D, Scaltriti M et al (2017) Acquired CDK6 amplification promotes breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors and loss of ER signaling and dependence. Oncogene 36:2255–2264
Konecny GE, Winterhoff B, Kolarova T, Qi J, Manivong K, Dering J et al (2011) Expression of p16 and retinoblastoma determines response to CDK4/6 inhibition in ovarian cancer. CLIN CANCER RES 17:1591–1602
Burtness B, Bauman JE, Galloway T (2013) Novel targets in HPV-negative head and neck cancer: overcoming resistance to EGFR inhibition. LANCET ONCOL 14:e302–309
Kalish LH, Kwong RA, Cole IE, Gallagher RM, Sutherland RL, Musgrove EA (2004) Deregulated cyclin D1 expression is associated with decreased efficacy of the selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. CLIN CANCER RES 10:7764–7774
Goel S, Wang Q, Watt AC, Tolaney SM, Dillon DA, Li W et al (2016) Overcoming Therapeutic Resistance in HER2-Positive breast cancers with CDK4/6 inhibitors. Cancer Cell 29:255–269
Modjtahedi H (2005) Molecular therapy of head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24:129–146
Chen H, Maul-Pavicic A, Holzer M, Huber M, Salzer U, Chevalier N et al (2022) Detection and functional resolution of soluble immune complexes by an FcgammaR reporter cell panel. EMBO MOL MED 14:e14182
van Caloen G, Schmitz S, van Marcke C, Caignet X, Mendola A, Pyr DRS et al (2021) Preclinical Evaluation of the Association of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor, Ribociclib, and Cetuximab in squamous cell carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Cancers (Basel) 13:1251
Gu Z, Shi C, Li J, Han Y, Sun B, Zhang W et al (2022) Palbociclib-based high-throughput combination drug screening identifies synergistic therapeutic options in HPV-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. BMC MED 20:175
Funding
This study was supported by the Medical Guidance Project of the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission [number 21Y11900300] and the National Key R&D Program of China [number 2020YFE0205500].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ruichen Li: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing-Original Draft; Qi Wang: Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing-Original Draft; Yang Zhao: Investigation, Formal analysis; Yi Zhu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing-Review & Editing; Xiaoshen Wang: Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing-Review & Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Animal studies were performed on the basis of the International Animal Care and Use Committee-approved protocol (IACUC). The research was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Eye & ENT Hospital of Fudan University (approval numbers: 2019062-1).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Wang, Q., Zhao, Y. et al. Palbociclib inhibits the progression of head and neck cancer and improves the Cetuximab response under specific condition in vitro and in vivo. Mol Biol Rep 51, 455 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09423-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09423-7