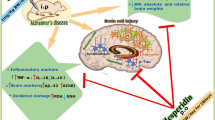
Abstract
Background
Neurological disorders result in not only a decline in the quality of life of patients but also a global economic burden. Therefore, protective medicine becomes more important for society. MK-801 is a chemical agent used to understand the etiology of behavioral disorders and brain degeneration in animal models. This study aims to determine whether N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is useful to treat brain degeneration caused by MK-801, an N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor antagonist.
Methods and results
Four groups were formed by dividing 24 male BALB/c mice into groups of six. The control group was given a saline solution (10 ml/kg-i.p.). MK-801 (1 mg/kg-i.p.) was given alone to one group, and it was given with NAC (100 mg/kg-i.p.) to another group, while the last group was given only NAC (100 mg/kg-i.p.). The administration of drugs lasted for fourteen days. After the behavioral tests (open field and elevated plus-maze), all animals were euthanised, and brain tissues were collected for real-time PCR, TAS-TOS analysis, hematoxylin-eosin, Kluver-Barrera, and TUNEL staining. In the MK-801 group, besides nuclear shrinkage in neurons, glial cell infiltration, vacuolization in cortical neurons, white matter damage, and apoptosis were observed.
Conclusion
In the mice given NAC as a protective agent, it was observed that behavioral problems improved, antioxidant levels increased, and nuclear shrinkage, glial cell infiltration, vacuolization in neurons, and white matter degeneration were prevented. Moreover, MBP expression increased, and the number of TUNEL-positive cells significantly decreased. As a result, it was observed that NAC may have a protective effect against brain degeneration.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used/analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sharma VK, Thakur G, Singh N, Garg S, Dhiman S, Gupta MH, Rahman A, Najda M, Walasek-Janusz M, Kamel GM, Albadrani, Muhammad F, Akhtar A, Saleem AE, Altyar (2021) Dysbiosis and Alzheimer’s Disease: a role for chronic stress? Biomolecules 11. 5:678Abdel-Daim
Knapp M, Wong G (2020) Economics and mental health: the current scenario. World Psychiatry 19(1):3–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20692
Arya A, Chahal R, Rao R, Rahman MH, Kaushik D, Akhtar MF, Saleem A, Khalifa SMA, El-Seedi HR, Kamel M, Albadrani GM, Abdel-Daim MM, Mittal V (2021) Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Potential of Various Sesquiterpene Analogues for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Biomolecules. Feb 25;11(3):350
Yu J, Qi D, Xing M, Li R, Jiang K, Peng Y, Cui D (2011) MK-801 induces schizophrenic behaviors through downregulating wnt signaling pathways in male mice. Brain Res 18:1385:281–292
Xiu Y, Kong XR, Zhang L, Qiu X, Chao FL, Peng C, Gao Y, Huang CX, Wang SR, Tang Y (2014) White matter injuries induced by MK-801 in a mouse model of schizophrenia based on NMDA antagonism. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 297(8):1498–1507
Xiu Y, Kong XR, Zhang L, Qiu X, Gao Y, Huang CX, Chao FL, Wang SR, Tang Y (2015) The myelinated fiber loss in the corpus callosum of mouse model of schizophrenia induced by MK-801. J Psychiatr Res 63:132–140
Bin-Jumah MN, Al-Huqail AA, Abdelnaeim N, Kamel M, Fouda MMA, Abulmeaty MMA, Saadeldin IM, Abdel-Daim MM (2021) Potential protective effects of Spirulina platensis on liver, kidney, and brain acrylamide toxicity in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int Jun 28(21):26653–26663
Kruk-Slomka M, Budzynska B, Slomka T, Banaszkiewicz I, Biala G (2016) The influence of the cb1 receptor ligands on the schizophrenia-like effects in mice induced by MK-801. Neurotox Res 30(4):658–676
Akosman SM, Turkmen R, Demirel HH (2021) Investigation of the protective effect of resveratrol in an MK-801-induced mouse model of schizophrenia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:65872–65884
Rosenbrock H, Dorner-Ciossek C, Giovannini R, Schmid B, Schuelert N (2022) Effects of the Glycine Transporter-1 inhibitor iclepertin (BI 425809) on sensory Processing, neural network function, and Cognition in Animal Models related to Schizophrenia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 382(2):223–232. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.121.001071
Zhang X, Boulton AA, Zuo DM, Yu PH (1996) MK-801 induces apoptotic neuronal death in the rat retrosplenial cortex: prevention by cycloheximide and R(-)-2-Hexyl-N-methylpropargylamine. J Neurosci Res 46:8289
Horvàth ZC, Czopf J, Buzsàki G (1997) MK-801-induced neuronal damage in rats. Brain Res 753:181–195
Kovacic P, Somanathan R (2010) Clinical physiology and mechanism of dizocilpine (MK-801) oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 3:113–122
Boggs JM (2006) Myelin basic protein: a multifunctional protein. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1945–1961
Matute C, Ransom BR (2012) Roles of white matter in central nervous system pathophysiologies. ASN Neuro 4(2):e00079. https://doi.org/10.1042/AN20110060
Xiang Z, Nesterov EE, Skoch J, Lin T, Hyman BT, Swager TM, Bacskai BJ, Reeves SA (2005) Detection of myelination using a novel histological probe. J Histochem Cytochem Dec; 53(12):1511–1516
Kipp M, Norkus A, Krauspe B, Clarner T, Berger K, van der Valk P, Amor S, Beyer C (2011) The hippocampal fimbria of cuprizone-treated animals as a structure for studying neuroprotection in multiple sclerosis. Inflamm Res Aug 60(8):723–726
Aziz AE, Sayed AE, Sallam RH, El Sayed NA NS (2021) Neuroprotective Effects of Telmisartan and Nifedipine Against Cuprizone-Induced demyelination and behavioral dysfunction in mice: roles of NF-κB and Nrf2. Inflamm Aug 44(4):1629–1642
Ye JN, Chen XS, Su L, Liu YL, Cai QY, Zhan XL, Xu Y, Zhao SF, Yao ZX (2013) Progesterone alleviates neural behavioral deficits and demyelination with reduced degeneration of oligodendroglial cells in cuprizone-induced mice. PLoS ONE 8(1):e54590
Lee HJ, Kang JS, Kim YI (2009) Citicoline protects against cognitive impairment in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J Clin Neurol. Mar;5(1):33 – 8. https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2009.5.1.33. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Erratum in: J Clin Neurol. 2009;5(2):104
Hesse A, Wagner M, Held J, Brück W, Salinas-Riester G, Hao Z, Waisman A, Kuhlmann T (2010) In toxic demyelination oligodendroglial cell death occurs early and is FAS independent. Neurobiol Dis Feb 37(2):362–369
Sharp FR, Jasper P, Hall J, Noble L, Sagar SM (1991) MK-801 and ketamine induce heat shock protein HSP72 in injured neurons in posterior cingulate and retrosplenial cortex. Ann Neurol 30(6):801–809
Ozyurt B, Ozyurt H, Akpolat N, Erdogan H, Sarsilmaz M (2007a) Oxidative stress in prefrontal cortex of rat exposed to MK-801 and protective effects of CAPE. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31(4):832–838
Ozyurt B, Sarsilmaz M, Akpolat N, Ozyurt H, Akyol O, Herken H, Kus I (2007b) The protective effects of omega – 3 fatty acids against MK-801-induced neurotoxicity in prefrontal cortex of rat. Neurochem Int 50(1):196–202
Ozyurt H, Ozyurt B, Sarsilmaz M, Kus I, Songur A, Akyol O (2014) Potential role of some oxidant/antioxidant status parameters in prefrontal cortex of rat brain in an experimental psychosis model and the protective effects of melatonin. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 18(15):2137–2144
Genius J, Geiger J, Dölzer AL, Benninghoff J, Giegling I, Hartmann AM, Möller HJ, Rujescu D (2013) Glutamatergic dysbalance and oxidative stress in in vivo and in vitro models of psychosis based on chronic NMDA receptor antagonism. PLoS One Jul 15(7):e59395. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059395PMID: 23869202; PMCID: PMC3711936
Scalley RD, Conner CS (1978) Acetaminophen poisoning: a case report of the use of acetylcysteine. Am J Hosp Pharm Aug 35(8):964–967
Dean O, Giorlando F, Berk M (2011) N-acetylcysteine in psychiatry: current therapeutic evidence and potential mechanisms of action. J Psychiatry Neurosci 36(2):78–86
Adair JC, Knoefel JE, Morgan N (2001) Controlled trial of N-acetylcysteine for patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. Oct 23;57(8):1515–1517
Farr SA, Poon HF, Dogrukol-Ak D, Drake J, Banks WA, Eyerman E, Butterfield DA, Morley JE (2003) The antioxidants alpha-lipoic acid and N-acetylcysteine reverse memory impairment and brain oxidative stress in aged SAMP8 mice. J Neurochem Mar 84(5):1173–1183
Dean O, van den Buuse M, Copolov D, Berk D, Bush A (2004) N-acetyl-cysteine treatment inhibits depletion of brain glutathione levels in rats: implications for schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 7(Supplement 2):S262–S262
Tardiolo G, Bramanti P, Mazzon E (2018) Overview on the effects of N-acetylcysteine in neurodegenerative diseases. MDPI Molecules. 23;3305.
Turkmen R, Birdane YO, Demirel HH, Yavuz H, Kabu M, Ince S (2019) Antioxidant and cytoprotective effects of N-acetylcysteine against subchronic oral glyphosate-based herbicide-induced oxidative stress in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:11427–11437
Himi T, Ikeda M, Yasuhara T, Murota SI (2003) Oxidative neuronal death caused by glutamate uptake inhibition in cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. Mar 1;71(5):679 – 88
Janáky R, Dohovics R, Saransaari P, Oja SS (2007) Modulation of [3H] dopamine release by glutathione in mouse striatal slices. Neurochem Res 32(8):1357–1364
Carlsson A (2006) The neurochemical circuitry of schizophrenia. Pharmacopsychiatry 39(Suppl 1):S10–S14
Berk M, Copolov D, Dean O, Lu K, Jeavons S, Schapkaitz I, Anderson-Hunt M, Judd F, Katz F, Katz P, Ording-Jespersen S, Little J, Conus P, Cuenod M, Do KQ, Bush AI (2008) N-acetyl cysteine as a glutathione precursor for schizophrenia–a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Biol Psychiatry. Sep 1;64(5):361-8
Lavoie S, Murray MM, Deppen P, Knyazeva MG, Berk M, Boulat O, Bovet P, Bush AI, Conus P, Copolov D, Fornari E, Meuli R, Solida A, Vianin P, Cuénod M, Buclin T, Do KQ (2008) Glutathione precursor, N-acetyl-cysteine, improves mismatch negativity in schizophrenia patients. Neuropsychopharmacol Aug 33(9):2187–2199 Epub 2007 Nov 14
Bulut M, Savas HA, Altindag A, Virit O, Dalkilic A (2009) Beneficial effects of N-acetylcysteine in treatment resistant schizophrenia. World J Biol Psychiatry 10(4 Pt 2):626–628
Mirzakhani N, Farshid AA, Tamaddonfard E, Imani M (2016) Study of the effects of n-acetylcysteine on functional, biochemical and ultrastructural evaluations of crushed sciatic nerve in the rat. J Urmia Univ Med Sci 27(4):266–276
Hichor M, Sundaram VK, Eid SA, Abdel-Rassoul R, Petit PX, Borderie D, Bastin J, Eid AA, Manuel M, Grenier J, Massaad C (2018) Liver X receptor exerts a protective effect against the oxidative stress in the peripheral nerve. Sci Rep Feb 6(1):2524. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20980-3
Zaki SM, Mohamed EA, Motawie AG, Abdel Fattah S (2018) N-acetylcysteine versus progesterone on the cisplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 77(2):234–245
Fukami G, Hashimoto K, Koike K, Okamura N, Shimizu E, Iyo M (2004) Effect of antioxidant N-acetyl-L-cysteine on behavioral changes and neurotoxicity in rats after administration of methamphetamine. Brain Res 1016(1):90–95
Taksande BG, Kotagale NR, Tripathi SJ, Ugale RR, Chopde CT (2009) Antidepressant like effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors involve modulation of imidazoline receptors by agmatine. Neuropharmacology 57(4):415–424
Akillioglu K, Babar Melik E, Kocahan S (2012) The investigation of neonatal MK-801 administration and physical environmental enrichment on emotional and cognitive functions in adult Balb/c mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 102:407–414
Gundersen HJ, Bagger P, Bendtsen TF, Evans SM, Korbo L, Marcussen N, Møller A, Nielsen K, Nyengaard JR, Pakkenberg B (1988) The new stereological tools: disector, fractionator, nucleator and point sampled intercepts and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS: acta pathologica, microbiologica. et Immunol Scand 96(10):857–881. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1699-0463.1988.tb00954.x
Erel O (2005) A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem 38:1103–1111
Erel O (2004) A novel automated method to measure total antioxidant response against potent free radical reactions. Clin Biochem 37:112–119
Walther S, Strik W (2012) Motor symptoms and schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 66:77–92
Karussis D (2014) The diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and the various related demyelinating syndromes: a critical review. J Autoimmun Feb-Mar; 48–49:134 – 42.
Sun Y, Ji J, Zha Z, Zhao H, Xue B, Jin L, Wang L (2021) Effect and mechanism of Catalpol on Remyelination via Regulation of the NOTCH1 Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol Feb 23:12:628209
Jatana M, Singh I, Singh AK, Jenkins D (2006) Combination of systemic hypothermia and N-acetylcysteine attenuates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res 59(5):684–689
Liang JQ, Chen X, Cheng Y (2022) Paeoniflorin rescued MK-801-Induced Schizophrenia-Like Behaviors in mice via oxidative stress pathway. Front Nutr Apr 27:9:870032. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.870032PMID: 35571896; PMCID: PMC9094402
Takadera T, Matsuda I, Ohyashiki T (1999) Apoptotic cell death and caspase-3 activation induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists and their prevention by insulin-like growth factor I. J Neurochem 73(2):548–556
Bozkurt NM, Unal G (2023) Vortioxetine improved negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia in subchronic MK-801 model in rats. Behav Brain Res 444:114365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114365
Bae HJ, Bae HJ, Kim JY, Park K, Yang X, Jung SY, Park SJ, Kim DH, Shin CY, Ryu JH (2023) The effect of lansoprazole on MK-801-induced schizophrenia-like behaviors in mice. Prog Neuro-psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 120:110646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2022.110646
Shi XJ, Du Y, Lei-Chen, Li XS, Yao CQ, Cheng Y (2022) Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) on the Schizophrenia model of animals. J Psychiatr Res 156:538–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2022.10.022
Lu C, Li S, Kang L, Li Q, Chen H, Lin Y, Zhang H, Tang Z, Bai M, Xiong P (2023) Aripiprazole combined with nerve growth factor improves cognitive function in mice with schizophrenia model. Neurosci Lett 812:137410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2023.137410
Patrono E, Hrůzova K, Svoboda J, Stuchlík A (2023) The role of optogenetic stimulations of parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the prefrontal cortex and the ventral hippocampus on an acute MK-801 model of schizophrenia-like cognitive inflexibility. Schizophr Res 252:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2022.12.047
Bonde C, Noraberg J, Zimmer J (2002) Nuclear shrinkage and other markers of neuronal cell death after oxygen-glucose deprivation in rat hippocampal slice cultures. Neurosci Lett. 12;327(1):49–52
Kim TW, Kang HS, Park JK, Lee SJ, Baek SB, Kim CJ (2014) Voluntary wheel running ameliorates symptoms of MK-801-induced schizophrenia in mice. Mol Med Rep 10:2924–2930
Olney JW, Labruyere J, Price MT (1989) Pathological changes induced in cerebrocortical neurons by phencyclidine and related drugs. Science 16(4910):1360–1362
Abd-Ellah HF, Abou-Zeid NRA, Nasr NM (2018) The possible protective effect of N-acetyl-L-cysteine and folic acid in combination against aspartame-induced cerebral cortex neurotoxicity in adult male rats: a light and transmission electron microscopic study. Ultrastruct Pathol 42(3):228–245
Haber M, James J, Kim J, Sangobowale M, Irizarry R, Ho J, Nikulina E, Grin’kina NM, Ramadani A, Hartman I, Bergold PJ (2018) Minocycline plus N-acteylcysteine induces remyelination, synergistically protects oligodendrocytes and modifies neuroinflammation in a rat model of mild traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38(8):1312–1326
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Scientific Research Project Coordination Unit at Afyon Kocatepe University (17.Kariyer.45).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The idea of the research was recommended by M.S.A, who also took part in the design of the study. M.S.A. and R.T. performed the experimental work and wrote/drafted/edited the manuscript and interpreted the results. M.S.A., R.T. and H.H.D. performed the laboratory analyses. All authors were involved in revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, and all authors approved the final version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The Animal Experiments Local Ethics Board, Afyon Kocatepe University, Afyon (Registration number: AKUHADYEK-189-17) has approved this study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sırrı Akosman, M., Türkmen, R. & Demirel, H.H. The protective effect of N-acetylcysteine against MK-801-induced neurodegeneration in mice. Mol Biol Rep 50, 10287–10299 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08881-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08881-9