Abstract
Background. Sargassum fusiforme
(S. fusiforme) is a brown alga that has been utilized as a medicine for a long time. Polysaccharides extracted from S. fusiforme demonstrate antitumor activities.
Methods
The impact of S. fusiforme polysaccharides (SFPS 191,212) on the proliferation, apoptosis, and cell cycle kinetics of B16F10 murine melanoma cells were thoroughly investigated in this work. The anticancer activities of the SFPS 191,212 compounds were assayed in the B16F10 cells at both transcriptional and translational levels.
Results
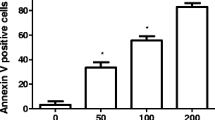
The compound exhibited concentration-dependent effects. Moreover, SPFS 191,212 increased the numbers of apoptotic cells and arrested the cell cycle in the S phase of the quantitative real-time PCR. From western blotting, it was verified that the SFPS 191,212 treatment improved the expression of Bax, Caspase-9, and Caspase-3 genes and proteins, while it reduced phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase and Bcl-2 genes and proteins, suggesting the involvement of mitochondria.
Conclusion
Overall, SFPS 191,212 can be further explored as a potential functional food or adjuvant agent for the prevention or treatment of melanoma.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Cooper AJ, Carlino MS, Kefford RF (2021) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Lancet 398(10304):1002–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01206-X
Leonardi GC, Falzone L, Salemi R, Zanghi A, Spandidos DA, McCubrey JA, Candido S, Libra M (2018) Cutaneous melanoma: from pathogenesis to therapy. Int J Oncol 52(4):1071–1080. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4287
Davis LE, Shalin SC, Tackett AJ (2019) Current state of melanoma diagnosis and treatment. Cancer Biol Ther 20(11):366–1379. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2019.1640032
Mishra A, Singh A, Kushwaha HR, Mishra A (2022) Cytotoxic effect of cobalt oxide–graphene oxide nanocomposites on melanoma cell line. J Exp Nanosci 17(1):509–521. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2022.2115483
Salaün H, de Koning L, Saint-Ghislain M, Servois V, Ramtohul T, Garcia A, Matet A, Cassoux N, Mariani P, Piperno-Neumann S, Rodrigues M (2022) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in metastatic uveal melanoma: a real-life, retrospective cohort of 47 patients. Oncoimmunology 11(1):2116845. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2022.2116845
Zhang SM, Cao S, Gong MY, Zhang WN, Zhang WF, Zhu ZE, Wu S, Yue YY, Qian WK, Ma QY, Wang SP, Wang Z (2022) Mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1 contributes to melanoma malignant progression through AKT/mTOR signaling. Cancer Biol Ther 23(1):336–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2022.2060015
Peng LX, Qiu JJ, Liu LD, Li XY, Liu XY, Zhang YJ (2022) Preparation of PEG/ZIF-8@HF drug delivery system for melanoma treatment via oral administration. Drug Deliv 29(1):1075–1085. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2022.2058649
Rousi EK, Kallionpaa RA, Kallionpaa RE, Juteau SM, Talve LAI, Hernberg MM, Vihinen PP, Kahari PP, Koskivuo IO (2022) Increased incidence of melanoma in children and adolescents in Finland in 1990–2014: nationwide re-evaluation of histopathological characteristics. Ann Med 54(1):244–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2022.2026001
Mohammed ER, Elmasry GF (2022) Development of newly synthesised quinazolinone-based CDK2 inhibitors with potent efficacy against melanoma. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 37(1):686–700. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2022.2036985
Hell T, Dobrzynski M, Groflin F, Reinhardt JK, Durr L, Pertz O, Hamburger M, Garo E (2022) Flavonoids from Ericameria nauseosa inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway in human melanoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother 156:113754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113754
Zhu S, Li X, Dang BR, Wu F, Wang CM, Lin CJ (2022) Lycium barbarum polysaccharide protects HaCaT cells from PM2.5-induced apoptosis via inhibiting oxidative stress, ER stress and autophagy. Redox Rep 27(1):32–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/13510002.2022.2036507
Ding HM, Chen XJ, Chen HM, Wang CS, Qian GY (2020) Effect of Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharide on apoptosis and its possible mechanism in human erythroleukemia cells. Chin J Nat Med 18(10):749–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1875-5364(20)60015-2
Zhao TX, Dong QY, Zhou HB, Yang HL (2022) Drying kinetics, physicochemical properties, antioxidant activity and antidiabetic potential of Sargassum fusiforme processed under four drying techniques. LWT Food Sci Technol 163:113578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113578
Wu SY, Liu J, Zhang Y, Song JX, Zhang ZS, Yang Y, Wu MJ, Tong HB (2022) Structural characterization and antagonistic effect against P-selectin-mediated function of SFF-32, a fucoidan fraction from Sargassum fusiforme. J Ethnopharmacol 295:115408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2022.115408
Wang L, Cui YR, Lee HG, Fu XT, Wang KQ, Xu JC, Gao X, Jeon YJ (2022) Fucoidan isolated from fermented Sargassum fusiforme suppresses oxidative stress through stimulating the expression of superoxidase dismutase and catalase by regulating Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol 209(Pt A):935–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.083
Ding HM, Fu RJ, Xie C, Wang CS, Qian GY (2021) Transcriptomic profile of human erythroleukemia cells in response to Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharide and its structure analysis. Chin J Nat Med 19(10):784–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1875-5364(21)60076-6
Wang L, Oh JY, Yang HW, Hyun JM, Ahn GN, Fu XT, Xu JC, Gao X, Cha SH, Jeon YJ (2023) Protective effect of Sargassum fusiforme fucoidan against ethanol-induced oxidative damage in in vitro and in vivo models. Polymers 15(8):1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081912
Du HF, Jin XD, Jin SZ, Zhang DL, Chen QD, Jin XA, Wang CS, Qian GY, Ding HM (2023) Anti-leukemia activity of polysaccharide from Sargassum fusiforme via the PI3K/AKT/BAD pathway in vivo and in vitro. Mar Drugs 21(5):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050289
Fan SR, Zhang JF, Nie WJ, Zhou WY, Jin LQ, Chen XM, Lu JX (2017) Antitumor effects of polysaccharide from Sargassum fusiforme against human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 102(1):53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.01.020
Zuo Y, Zhang CZ, Ren Q, Chen Y, Li X, Yang JR, Li HR, Tang WT, Ho HM, Sun C, Li MM, Ren B, Deng Y, Wang ML, Lu J (2022) Activation of mitochondrial-associated apoptosis signaling pathway and inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway by voacamine suppress breast cancer progression. Phytomedicine 99:154015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154015
Zhang Z, Feng Y, Li ZY, Cao XZ (2019) Antiproliferative and apoptotic activity of glycyrrhizinic acid in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells and evaluation of its effect on cell cycle, cell migration and m-TOR/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Arch Med Sci 15(1):174–182. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2018.79429
Wang YE, Xu K, Yue WH, Xu QM, You BG, Zhang MY, Zhu ZC, Yang SL, Liu YL, Li KP (2018) Hederacolchiside A1 suppresses proliferation of tumor cells by inducing apoptosis through modulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Chin Herb Med 10(2):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chmed.2018.03.007
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2022) Cancer statistics, 2022. CA: A Cancer. J Clin 72(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21708
Tewari D, Patni P, Bishayee A, Sah AN, Bishayee A (2022) Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: a novel therapeutic strategy. Semin Cancer Biol 80:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.008
Li F, Jiao X, Zhao J, Liao XJ, Wei YL, Li QH (2022) Antitumor mechanisms of an exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus fermentum on HT-29 cells and HT-29 tumor-bearing mice. Int J Biol Macromol 209(Pt A):552–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.023
Chen HL, Zhang L, Long XG, Li PF, Chen SC, Kuang W, Guo JM (2017) Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides inhibit VEGF-A-related angiogenesis and proliferation of lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Biomed Pharmacot 85(131):22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.131
Chen HJ, Cong QF, Du ZY, Liao WF, Zhang L, Yao YL, Ding K (2016) Sulfated fucoidan FP08S2 inhibits lung cancer cell growth in vivo by disrupting angiogenesis via targeting VEGFR2/VEGF and blocking VEGFR2/Erk/VEGF signaling. Cancer Lett 382(1):44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.020
Eskandari E, Eaves CJ (2022) Paradoxical roles of caspase-3 in regulating cell survival, proliferation, and tumorigenesis. J Cell Biol 221(6):e202201159. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202201159
Guo JM, Xing HJ, Cai JZ, Zhang HF, Xu SW (2021) H2S exposure-induced oxidative stress promotes LPS-mediated hepatocyte autophagy through the PI3K/AKT/TOR pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 209:111801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111801
Zhang CY, Lin TJ, Nie GH, Hu RM, Pi SX, Wei ZJ, Wang C, Xing CH, Hu GL (2021) Cadmium and molybdenum co-induce pyroptosis via ROS/PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. Environ Pollut 272:116403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116403
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was supported by the Ningbo Public Welfare Project (No. 2022S065), the Research Startup Project of the Advanced Talents of the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University (No. 2022KYQDJ-XF), the Medical and Health Research Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2022KY1145), and the Project of the Ningbo Leading Medical & Health Discipline (No. 2022-F23).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Feng Xu, Haomiao Ding, and Suling Xu contributed to the conception of the study. Feng Xu, Haomiao Ding, Zhifang Liu, Xinyu Jiang, Yizhao Ma, and Diancheng Wang performed the experiment. Suling Xu contributed significantly to the analysis and manuscript preparation. Feng Xu performed the data analysis and wrote the manuscript. Haomiao Ding helped perform the analysis with constructive discussion.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that they have no financial or personal ties to other parties that could be seen as influencing the results presented in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Feng Xu and Haomiao Ding contributed equally to this work.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Ding, H., Liu, Z. et al. Polysaccharide extracted from the Sargassum fusiforme induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of B16F10 melanoma cells through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Biol Rep 50, 6517–6528 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08570-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08570-7