Abstract
Background
Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A hypusine (eIF5AHyp) stimulates the translation of proline repeat motifs. Salt inducible kinase 2 (SIK2) containing a proline repeat motif is overexpressed in ovarian cancers, in which it promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Methods and results
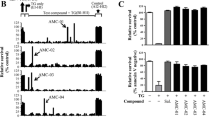
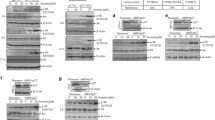
Western blotting and dual luciferase analyses showed that depletion of eIF5AHyp by GC7 or eIF5A-targeting siRNA downregulated SIK2 level and decreased luciferase activity in cells transfected with a luciferase-based reporter construct containing consecutive proline residues, whereas the activity of the mutant control reporter construct (replacing P825L, P828H, and P831Q) did not change. According to the MTT assay, GC7, which has a potential antiproliferative effect, reduced the viability of several ovarian cancer cell lines by 20–35% at high concentrations (ES2 > CAOV-3 > OVCAR-3 > TOV-112D) but not at low concentrations. In a pull-down assay, we identified eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) and 4E-BP1 (p4E-BP1) phosphorylated at Ser 65 as downstream binding partners of SIK2, and we validated that the level of p4E-BP1(Ser 65) was downregulated by SIK2-targeting siRNA. Conversely, in ES2 cells overexpressing SIK2, the p4E-BP1(Ser 65) level was increased but decreased in the presence of GC7 or eIF5A-targeting siRNA. Finally, the migration, clonogenicity, and viability of ES2 ovarian cancer cells were reduced by GC7 treatment as well as by siRNA for eIF5A gene silencing and siRNA for SIK2 and 4E-BP1 gene silencing. Conversely, those activities were increased in cells overexpressing SIK2 or 4E-BP1 and decreased again in the presence of GC7.
Conclusion
The depletion of eIF5AHyp by GC7 or eIF5A-targeting siRNA attenuated activation of the SIK2-p4EBP1 pathway. In that way, eIF5AHyp depletion reduces the migration, clonogenicity, and viability of ES2 ovarian cancer cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Gentz PM, Blatch GL, Dorrington RA (2009) Dimerization of the yeast eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A requires hypusine and is RNA dependent. FEBS J 276(3):695–706
Joe YA, Wolff EC, Park MH (1995) Cloning and expression of human deoxyhypusine synthase cDNA: structure-function studies with the recombinant enzyme and mutant proteins. J Biol Chem 270:22386–22392
Park JH, Aravind L, Wolff EC, Kaevel J, Kim YS, Park MH (2006) Molecular cloning, expression, and structural prediction of deoxyhypusine hydroxylase: a HEAT-repeat-containing metalloenzyme. PNAS 103:51–56
Shi XP, Yin KC, Ahem J, Davis LJ, Stern AM, Waxman L (1996) Effects of N 1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane, an inhibitor of deoxyhypusine synthase, on the growth of tumorigenic cell lines in culture. Biochem Biophys Acta 1310:119–126
Liu Y, Liu R, Fu P, Du F, Hong Y, Yao M, Zhang X, Zheng S (2015) N1-Guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane sensitizes estrogen receptor negative breast cancer cells to doxorubicin by preventing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 activation. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:2494–2503
Wang Z, Jiang J, Qin T, Xiao Y, Han L (2019) EIF5A regulates proliferation and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer through the sHH signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med 23:2678–2688
Saini P, Eyler DE, Green R, Dever TE (2009) Hypusine-containing protein eIF5A promotes translation elongation. Nature 459:118–121
Schuller AP, Wu Colin C-C, Dever TE, Buskirk A, Green R (2017) eIF5A functions globally in translation elongation and termination. Mol Cell 66:194–205
Gutierrez E, Shin BS, Woolstenhulme CJ, Kim JR, Saini P, Buskirk AR, Dever TE (2013) eIF5A promotes translation of polyproline motifs. Mol Cell 51(1):35–45
Pelechano V, Alepuz P (2017) eIF5A facilitates translation termination globally and promotes the elongation of many non-polyproline-specific tripeptide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 45:7326–7338
Bright NJ, Thornton C, Carling D (2009) The regulation and function of mammalian AMPK-related kinases. Acta Physiol 196(1):15–26
Katoh Y, Takemori H, Horike N, Doi J, Muraoka M, Min L, Okamoto M (2004) Salt-inducible kinase (SIK) isoforms: Their involvement in steroidogenesis and adipogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 217:109–112
Raab M, Rak M, Tesch R, Gasimli K, Becker S, Knapp S, Strebhardt K, Sanhaji M (2021) The small-molecule inhibitor MRIA9 reveals novel insights into the cell cycle roles of SIK2 in ovarian cancer cells. Cancers 13(15):3658
Ahmed AA, Lu Z, Jennings NB, Etemadmoghadam D, Capalbo L et al (2010) SIK2 is a centrosome kinase required for bipolar mitotic spindle formation that provides a potential target for therapy in ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell 18:109–121
Sun Z, Jiang Q, Li J, Guo J (2020) The potent roles of salt-inducible kinases (SIKs) in metabolic homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(150):1–15
Al-Hakim AK, Göransson O, Deak M, Toth R, Campbell DG et al (2005) 14-3-3 cooperates with LKB1 to regulate the activity and localization of QSK and SIK. J Cell Sci 118(23):5661–5673
Musa J, Orth MF, Dallmayer M, Baldauf M, Pardo C, Rotblat B, Kirchner T, Leprivier G, Grünewald TGP (2016) Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1): a master regulator of mRNA translation involved in tumorigenesis. Oncogene 35:4675–4688
Freire ER, Sturm NR, Campbell DA, de Melo Neto OP (2018) The role of cytoplasmic mRNA cap-binding protein complexes in Trypanosoma brucei and other Trypanosomatids. Pathogens 55:1–25
Pons B, Peg V, Vazquez-Sanchez MA, Lopez-Vicente L, Argelaguet E, Coch L, Martinez A, Hernandez-Losa J, Armengol G, Cajal SR (2011) The effect of p-4E-BP1 and p-eIF4E on cell proliferation in a breast cancer model. Int J Oncol 39:1337–1345
Qin X, Jiang B, Zhang Y (2016) 4E-BP1, a multifactor regulated multifunctional protein. Cell Cycle 15(6):781–786
Miao Y, Chen L, Shi C, Fan R, Chen P, Liu H, Xia A, Qian H (2017) Increased phosphorylation of 4E-binding protein 1 predicts poor prognosis for patients with colorectal cancer. Mol Med Rep 15:3099–3104
Corradetti MN, Inoki K, Bardeesy N, DePinho RA, Guan K-L (2004) Regulation of the TSC pathway by LKB1: evidence of a molecular link between tuberous sclerosis complex and Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Genes Dev 18(13):1533–1538
Shang ZF, Yu L, Li B, Tu WZ, Wang Y et al (2012) 4E-BP1 participates in maintaining spindle integrity and genomic stability via interacting with PLK1. Cell Cycle 11(18):3463–3471
Lee GK, Kim CW, Cho IH, Kim HY, Park JH (2023) Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A hypusine as a negative regulator of adenosine 2B receptor (A2bAR) through interaction with stem loop sequences within the A2bAR 3′-untranslated region. Mol Biol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08252-4
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9(7):671–675
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J, van Bree C (2006) Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc 2:2315–2319
Liang CC, Park AY, Guan JL (2007) In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc 2:329–333
Mémin E, Hoque M, Jain MR, Heller DS, Li H, Cracchiolo B, Hanauske-Abel HM, Pe’ery T, Mathews MB (2014) Blocking eIF5A modification in cervical cancer cells alters the expression of cancer-related genes and suppresses cell proliferation. Cancer Res 74:552–562
Mandal A, Mandal S, Park MH (2014) Genome-wide analyses and functional classification of proline repeat-rich proteins: potential role of eIF5A in eukaryotic evolution. PLoS ONE 9:e111800
Sfakianos AP, Raven RM, Willis AE (2022) The pleiotropic roles of eIF5A in cellular life and its therapeutic in cancer. Biochem Soc Trans 50:1885–1895
Bandino A, Geerts D, Koster J, Bachmann AS (2014) Deoxyhypusine synthase (DHPS) inhibitor GC7 induces p21/Rb-mediated inhibition of tumor cell growth and DHPS expression correlates with poor prognosis in neuroblastoma patients. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 37:387–398
Zhang J, Li X, Liu X, Tian F, Zeng W, Xi X, Lin Y (2018) EIF5A1 promotes epithelial ovarian cancer proliferation and progression. Biomed Pharmacother 100:168–175
Xu G, Yu H, Shi X, Sun L, Zhou Q, Zheng D, Shi H, Li N, Zhang X, Shao G (2014) Cisplatin sensitivity is enhanced in non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating epithelial mesenchymal transition through inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2. BMC Pulm Med 14:174. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2466-14-174
Aziz SM, Worthen DR, Yatin MY, Ain KB, Crooke PA (1998) A Unique Interaction between polyamine and multidrug resistance (P-glycoprotein) transporters in cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells transfected with mouse mdr-1 gene. Biochem Pharmacol 56:181–187
Roh MS, Lee JH, Kang WK, Nam HY, Jung SB, Kim K, Lee EH, Park MI, Kim MS, Lee HW (2015) Phosphorylated 4E-binding protein 1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in small-cell lung cancer. Virchows Arch 467(6):667–673
Wang Z, Feng X, Molinolo AA, Martin D, Vitale-Cross L, Nohata N, Ando M, Wahba A, Amornphimoltham P, Wu X, Gilardi M, Allevato M, Wu V, Steffen DJ, Tofilon P, Sonenberg N, Califano J, Chen Q, Lippman SM, Gutkind JS (2019) 4E-BP1 is a tumor suppressor protein reactivated by mTOR inhibition in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 79:1438–1450
Chen F, Chen L, Qin Q, Sun X (2019) Salt-inducible kinase 2: an oncogenic signal transmitter and potential target for cancer therapy. Front Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00018
Fujimura K, Choi S, Wyse M, Strnadel J, Wright T, Klemke R (2015) Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (EIF5A) regulates pancreatic cancer metastasis by modulating RhoA and Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) protein expression levels. J Biol Chem 290:29907–29919
Liu RR, Lv YS, Tang YX, Wang YF, Chen XL, Zheng XX, Xie SZ, Cai Y, Yu J, Zhang XZ (2014) Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 regulates the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via pathways involving reactive oxygen species. Oncotarget. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8324
Nathaniel J, Hiu WC (2016) Perspective on targeting salt-inducible kinase 2 (SIK2) in ovarian cancer metastasis. Transl. Cancer Res. 5(6):S1270–S1273
Shi X, Yu X, Wang J, Bian S, Li Q, Fu F, Zou X, Zhang L, Bast RC Jr, Lu Z, Guo L, Chen Y, Zhou J (2022) SIK2 promotes ovarian cancer cell motility and metastasis by phosphorylating MYLK. Mol Oncol 16:2558–2574
Cai W, Ye Q, She QB (2014) Loss of 4E-BP1 function induces EMT and promotes cancer cell migration and invasion via cap-dependent translational activation of snail. Oncotarget 14:6015–6027
Chen Y, Wang J, Fan H, Xie J, Xu L, Zhou B (2017) Phosphorylated 4E-BP1 is associated with tumor progression and adverse prognosis in colorectal cancer. Neoplasma 64:787–794
Qu Y, Zhao R, Wang H, Chang K, Yang X, Zhou X, Dai B, Zhu Y, Shi G, Zhang H, Ye D (2016) Phosphorylated 4EBP1 is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep 6:23594. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23594
Jensen N, Cheung HW (2016) Perspective on targeting salt-inducible kinase 2 (SIK2) in ovarian cancer metastasis. Transl Cancer Res 5:S1270–S1273
Acknowledgements
GC7 (N1-guanyl-1,7-diamineoheptane) was a gift from Myung Hee Park (NIH/NIDCR, Bethesda, MD).
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2014R1A1A2058125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JHP conceived and designed the study. JHP and GKL performed the experiments and collected the data. JHP and GKL wrote the paper. JHP, GKL, and HYK analyzed the data. JHP and HYK reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, G.K., Kim, HY. & Park, J.H. Inhibiting eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) hypusination attenuated activation of the SIK2 (salt-inducible kinase 2)-p4E-BP1 pathway involved in ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration. Mol Biol Rep 50, 5807–5816 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08510-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08510-5