Abstract
Background
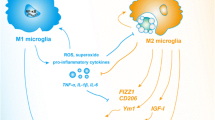
Growing evidence indicates that cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptor activation inhibits neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Nonetheless, the precise mechanisms of CB2 receptor-mediated neuroprotection have not been fully elucidated. The differentiation of microglia from the M1 to M2 phenotype plays a vital role in neuroinflammation.
Methods
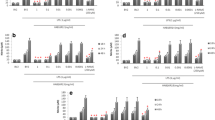
In the present study, we investigated the effect of CB2 receptor activation on the M1/M2 phenotypic transformation of microglia treated with 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+). The M1 phenotype microglia markers, including inducible nitric oxide (iNOS), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and CD86, and the M2 phenotype microglia markers, including arginase-1 (Arg-1), IL-10, and CD206, were detected by western blots and flow cytometry. The levels of phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) were determined by Western blots. Subsequent addition of Nrf2 inhibitors initially revealed the specific mechanism by which CB2 receptors affect phenotypic changes in microglia.
Results
Our results showed that pretreatment with JWH133 significantly inhibited the MPP+-induced up-regulation of M1 phenotype microglia markers. Meanwhile, JWH133 increased the levels of M2 phenotype microglia markers. JWH133-mediated effects were blocked by co-treatment with AM630. Mechanism studies found that MPP+ treatment downregulated PI3K, Akt phosphorylated proteins, and nuclear Nrf2 protein. JWH133 pretreatment promoted PI3K/Akt activation and facilitated nuclear translocation of Nrf2, which was reversed by the PI3K inhibitor. Further studies showed that Nrf2 inhibitors inverted the effect of JWH133 on microglia polarization.
Conclusion
The results indicate that CB2 receptor activation promotes MPP+-induced microglia transformation from M1 to M2 phenotype through PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The present work did not create or analyze new data, so no data sharing was applicable.
References
Forno LS (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:259–272
Skaper SD, Giusti P, Facci L (2012) Microglia and mast cells: two tracks on the road to neuroinflammation. FASEB J 26:3103–3117
Kam TI, Hinkle JT, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2020) Microglia and astrocyte dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 144:105028
Sugama S, Takenouchi T, Cho BP, Joh TH, Hashimoto M, Kitani H (2009) Possible roles of microglial cells for neurotoxicity in clinical neurodegenerative diseases and experimental animal models. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 8:277–284
Martinez FO, Gordon S (2014) The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep 6:13
Cassano T, Calcagnini S, Pace L, De Marco F, Romano A, Gaetani S (2017) Cannabinoid receptor 2 signaling in neurodegenerative Disorders: from pathogenesis to a Promising Therapeutic Target. Front Neurosci 11:30
Lisboa SF, Gomes FV, Guimaraes FS, Campos AC (2016) Microglial cells as a link between Cannabinoids and the Immune Hypothesis of Psychiatric Disorders. Front Neurol 7:5
Tao Y, Li L, Jiang B, Feng Z, Yang L, Tang J, Chen Q, Zhang J, Tan Q, Feng H, Chen Z, Zhu G (2016) Cannabinoid receptor-2 stimulation suppresses neuroinflammation by regulating microglial M1/M2 polarization through the cAMP/PKA pathway in an experimental GMH rat model. Brain Behav Immun 58:118–129
Zhao Y, Zhang Q, Xi J, Xiao B, Li Y, Ma C (2015) Neuroprotective effect of fasudil on inflammation through PI3K/Akt and Wnt/beta-catenin dependent pathways in a mice model of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:2354–2364
Galan-Ganga M, Del Rio R, Jimenez-Moreno N, Diaz-Guerra M, Lastres-Becker I (2020) Cannabinoid CB2 receptor modulation by the transcription factor NRF2 is specific in Microglial cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40:167–177
de Oliveira MR, Ferreira GC, Schuck PF (2016) Protective effect of carnosic acid against paraquat-induced redox impairment and mitochondrial dysfunction in SH-SY5Y cells: role for PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Toxicol In Vitro 32:41–54
Wu Q, Ma Y, Liu Y, Wang N, Zhao X, Wen D (2020) CB2R agonist JWH-133 attenuates chronic inflammation by restraining M1 macrophage polarization via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in diet-induced obese mice. Life Sci 260:118424
Popiolek-Barczyk K, Rojewska E, Jurga AM, Makuch W, Zador F, Borsodi A, Piotrowska A, Przewlocka B, Mika J (2014) Minocycline enhances the effectiveness of nociceptin/orphanin FQ during neuropathic pain. Biomed Res Int 2014:762930
Zhao S, Wang M, Ma Z (2021) Therapeutic potential of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res Bull 169:1–7
More SV, Kumar H, Kim IS, Song SY, Choi DK (2013) Cellular and molecular mediators of neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease, Mediators Inflamm, Doi 10.1155/2013/952375
Lu Y, Zhou M, Li Y, Li Y, Hua Y, Fan Y (2021) Minocycline promotes functional recovery in ischemic stroke by modulating microglia polarization through STAT1/STAT6 pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 186:114464
Du RH, Sun HB, Hu ZL, Lu M, Ding JH, Hu G (2018) Kir6.1/K-ATP channel modulates microglia phenotypes: implication in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis 9:404
Castillo PE, Younts TJ, Chavez AE, Hashimotodani Y (2012) Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 76:70–81
Javed H, Azimullah S, Haque ME, Ojha SK (2016) Cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptors activation protects against oxidative stress and Neuroinflammation Associated Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Rotenone Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Front Neurosci 10:321
Gubellini P, Kachidian P (2015) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: an updated overview. Rev Neurol (Paris) 171:750–761
He Q, Wang Q, Yuan C, Wang Y (2017) Downregulation of mir-7116-5p in microglia by MPP(+) sensitizes TNF-alpha production to induce dopaminergic neuron damage. Glia 65:1251–1263
Huang H, Gao Y, Nie K, Wang L (2021) [Macrophage migration inhibitory factor meditates MPP+/MPTP-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia cells]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 41:972–979
Zhou P, Weng R, Chen Z, Wang R, Zou J, Liu X, Liao J, Wang Y, Xia Y, Wang Q (2016) TLR4 Signaling in MPP(+)-Induced Activation of BV-2 Cells, Neural Plast https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5076740
Ma L, Jia J, Liu X, Bai F, Wang Q, Xiong L (2015) Activation of murine microglial N9 cells is attenuated through cannabinoid receptor CB2 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 458:92–97
Dong W, Luo B, Qiu C, Jiang X, Shen B, Zhang L, Liu W, Zhang W (2020) TRIM3 attenuates apoptosis in Parkinson’s disease via activating PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Aging 13:735–749
Li J, Cheng X, Fu D, Liang Y, Chen C, Deng W, He L (2022) Autophagy of spinal Microglia affects the activation of Microglia through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Neuroscience 482:77–86
Zhong Y, Cai X, Ding L, Liao J, Liu X, Huang Y, Chen X, Long L (2022) Nrf2 inhibits the progression of Parkinson’s disease by upregulating AABR07032261.5 to repress pyroptosis. J Inflamm Res 15:669–685
Subedi L, Lee JH, Yumnam S, Ji E, Kim SY (2019) Anti-inflammatory effect of sulforaphane on LPS-Activated Microglia potentially through JNK/AP-1/NF-kappaB inhibition and Nrf2/HO-1 activation, Cells 8(2): 194
Liao S, Wu J, Liu R, Wang S, Luo J, Yang Y, Qin Y, Li T, Zheng X, Song J, Zhao X, Xiao C, Zhang Y, Bian L, Jia P, Bai Y, Zheng X (2020) A novel compound DBZ ameliorates neuroinflammation in LPS-stimulated microglia and ischemic stroke rats: role of akt(Ser473)/GSK3beta(Ser9)-mediated Nrf2 activation. Redox Biol 36:101644
Wang N, Nie H, Zhang Y, Han H, Wang S, Liu W, Tian K (2022) Dexmedetomidine exerts cerebral protective effects against cerebral ischemic injury by promoting the polarization of M2 microglia via the Nrf2/HO-1/NLRP3 pathway. Inflamm Res 71:93–106
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports by the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2019GSF108095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors mentioned above participated in this work. MW: methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing: original draft. ML: methodology, formal analysis. ZM: writing: review & editing, funding acquisition, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors claim that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
All procedures were carried out in accordance with the National Institute of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Qingdao University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Liu, M. & Ma, Z. Cannabinoid type 2 receptor activation inhibits MPP+-induced M1 differentiation of microglia through activating PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signal pathway. Mol Biol Rep 50, 4423–4433 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08395-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08395-4