Abstract
Background
Mannheimia haemolytica is one of the main agents of domestic pneumonic mannheimiosis, but a proper vaccine has not been explored in IRAN.
Methods and Results
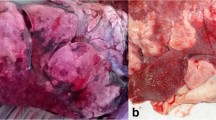
362 lung and nasal samples from sick domestic animal were detected by culture and PCR methods. Totally, 71 M. haemolytica isolates were identified in three main serotypes (A1, A2, and A6). Serotypes A2 (38/71; 54%) and A1 (25/71; 39%) were the most frequently detected, whereas the A6 serotype was detected with a frequency of less than 1% (1/71; 1%) and 7 isolates remained unknown (7/71; 10%). Subsequently, M. haemolytica vaccinal strain was developed and then formalin-killed vaccine was prepared. It provided the best protection against mannheimiosis in sheep which was proved by indirect ELISA.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that the efficacy and safety of vaccine strain are remarkable and may serve as a new therapeutic target in mannheimiosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zamri-Saad M, Azri A, Nurida A, Sheikh-Omar A (1994) Experimental respiratory infection of goats with Mycoplasma arginini and Pasteurella haemolytica A2. PERTANIKA 17:239–239
Jesse FFA, Chung ELT, Abba Y, Muniandy KV, Tan AHAR, Maslamany D, Bitrus AA, Lila MAM, Norsidin MJ (2019) Establishment of lung auscultation scoring method and responses of acute phase proteins and heat shock proteins in vaccinated and non-vaccinated goats. Trop Anim Health Prod 51(2):289–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-018-1683-7
Wilson BA, Ho M (2013) Pasteurella multocida: from zoonosis to cellular microbiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 26(3):631–655. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00024-13
Legesse A, Abayneh T, Mamo G, Gelaye E, Tesfaw L, Yami M, Belay A (2018) Molecular characterization of Mannheimia haemolytica isolates associated with pneumonic cases of sheep in selected areas of Central Ethiopia. BMC Microbiol 18(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-018-1338-x
Confer AW, Ayalew S (2018) Mannheimia haemolytica in bovine respiratory disease: immunogens, potential immunogens, and vaccines. Anim health Res reviews 19(2):79–99. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1466252318000142
Snyder E, Credille B (2020) Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida in Bovine Respiratory Disease: How Are They Changing in Response to Efforts to Control Them? Veterinary Clinics. Food Anim Pract 36(2):253–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvfa.2020.02.001
Jesse F, Boorei M, Chung E, Wan-Nor F, Lila M, Norsidin M, Isa K, Amira N, Maqbool A, Odhah M (2020) A review on the potential effects of Mannheimia haemolytica and its immunogens on the female reproductive physiology and performance of small ruminants. J Anim Health Prod 8(3):101–112. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.jahp/2020/8.3.101.112
Newsom I, Cross F (1932) Some bipolar organisms found in pneumonia in sheep. J Am Vet Med Assoc 80:711–719
Biberstein E, Gills M (1962) The relation of the antigenic types to the A and T types of Pasteurella haemolytica. J Comp Pathol Ther 72:316–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0368-1742(62)80036-8
Haig S-J (2011) Adherence of Mannheimia haemolytica to ovine bronchial epithelial cells. Bioscience Horizons 4(1):50–60. https://doi.org/10.1093/biohorizons/hzr007
Deressa A, Asfaw Y, Lubke B, Kyule M, Tefera G, Zessin K (2010) Molecular detection of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica in sheep respiratory infections in Ethiopia. J Appl Res Veterinary Med 8(2):101
Ferede Y, Mekuriaw S, Mazengia H, Amane A (2013) Sero-Typing and Evaluation of The Level of Protective Antibody Titer in Northwest Ethiopian Sheep Before And After Ovine Pasteurollosis Vaccination. Int J Pharma Med Biol Sci 2:57–64
Purdy CW, Raleigh RH, Collins JK, Watts JL, Straus DC (1997) Serotyping and enzyme characterization of Pasteurella haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida isolates recovered from pneumonic lungs of stressed feeder calves. Curr Microbiol 34(4):244–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900177
Dassanayake RP, Shanthalingam S, Herndon CN, Lawrence PK, Cassirer EF, Potter KA, Foreyt WJ, Clinkenbeard KD, Srikumaran S (2009) Mannheimia haemolytica serotype A1 exhibits differential pathogenicity in two related species, Ovis canadensis and Ovis aries. Vet Microbiol 133(4):366–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.07.015
Roehrig SC, Tran HQ, Spehr V, Gunkel N, Selzer PM, Ullrich HJ (2007) The response of Mannheimia haemolytica to iron limitation: implications for the acquisition of iron in the bovine lung. Vet Microbiol 121(3–4):316–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2006.12.013
Highlander SK (2001) Molecular genetic analysis of virulence in Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica. Front Biosci 6(September):D1128–D1150
Dassanayake RP, Shanthalingam S, Davis WC, Srikumaran S (2007) Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin-induced cytolysis of ovine (Ovis aries) leukocytes is mediated by CD18, the β subunit of β2-integrins. Microb Pathog 42(5–6):167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2007.01.002
Gioia J, Qin X, Jiang H, Clinkenbeard K, Lo R, Liu Y, Fox GE, Yerrapragada S, McLeod MP, McNeill TZ (2006) The genome sequence of Mannheimia haemolytica A1: insights into virulence, natural competence, and Pasteurellaceae phylogeny. J Bacteriol 188(20):7257–7266. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00675-06
Confer AW, Ayalew S, Panciera RJ, Montelongo M, Whitworth LC, Hammer JD (2003) Immunogenicity of recombinant Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 outer membrane protein PlpE and augmentation of a commercial vaccine. Vaccine 21(21–22):2821–2829. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-410X(03)00213-5
Shewen PE, Wilkie BN (1988) Vaccination of calves with leukotoxic culture supernatant from Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Vet Res 52(1):30
Katsuda K, Kamiyama M, Kohmoto M, Kawashima K, Tsunemitsu H, Eguchi M (2008) Serotyping of Mannheimia haemolytica isolates from bovine pneumonia: 1987–2006. Vet J 178(1):146–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.07.019
Sahay S, Natesan K, Prajapati A, Kalleshmurthy T, Shome BR, Rahman H, Shome R (2020) Prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida isolated from ovine respiratory infection: A study from Karnataka, Southern India. Veterinary World 13(9):1947. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2020.1947-1954
Amat S, Alexander TW, Holman DB, Schwinghamer T, Timsit E (2020) Intranasal bacterial therapeutics reduce colonization by the respiratory pathogen Mannheimia haemolytica in dairy calves. Msystems 5(2):e00629–e00619. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00629-19
Alexander TW, Cook SR, Yanke LJ, Booker CW, Morley PS, Read RR, Gow SP, McAllister TA (2008) A multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay for the identification of Mannheimia haemolytica, Mannheimia glucosida and Mannheimia ruminalis. Vet Microbiol 130(1–2):165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.01.001
Kumar J, Dixit SK, Kumar R (2015) Rapid detection of Mannheimia haemolytica in lung tissues of sheep and from bacterial culture. Veterinary World 8(9):1073. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2015.1073-1077
Hayati M, Shamseddini M, Tahamtan Y, Sadeghzadeh S, Manavian M, Nikoo D (2020) Isolation and Toxin Typing of Clostridium Perfringens From Sheep, Goats, and Cattle in Fars Province, Iran. Int J Enteric Pathog 8(3):89–93
Klima CL, Zaheer R, Briggs RE, McAllister TA (2017) A multiplex PCR assay for molecular capsular serotyping of Mannheimia haemolytica serotypes 1, 2, and 6. J Microbiol Methods 139:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2017.05.010
Stelma G Jr, Reyes A, Peeler J, Francis D, Hunt J, Spaulding P, Johnson C, Lovett J (1987) Pathogenicity test for Listeria monocytogenes using immunocompromised mice. J Clin Microbiol 25(11):2085–2089. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.25.11.2085-2089.1987
Melville-Smith ME, Seagroatt VA, Watkins JT (1983) A comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with the toxin neutralization test in mice as a method for the estimation of tetanus antitoxin in human sera. J Biol Stand 11(2):137–144
Bechmann G, Schöss P (1991) Detection of neutralizing antibodies against Pasteurella multocida toxin in swine with atrophic rhinitis. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr 98(8):310–312
Brogden KA, Lehmkuhl HD, Cutlip RC (1998) Pasteurella haemolytica complicated respiratory infections in sheep and goats. Vet Res 29(3–4):233–254
García-Alvarez A, Fernández-Garayzábal JF, Chaves F, Pinto C, Cid D (2018) Ovine Mannheimia haemolytica isolates from lungs with and without pneumonic lesions belong to similar genotypes. Vet Microbiol 219:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.04.012
Tabatabaei M, Abdollahi F (2018) Isolation and identification of Mannheimia haemolytica by culture and polymerase chain reaction from sheep’s pulmonary samples in Shiraz. Iran Veterinary World 11(5):636. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2018.636-641
Gharibi D, Ghorbanpoor M, Jabbari AR, Cid D (2021) Molecular characterization of Mannheimia haemolytica associated with ovine and caprine pneumonic lung lesions. Microb Pathog 153:104791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104791
Bemani E, Esmaeilzadeh S, Gharibi D, Ghorbanpoor M (2017) Immunohistochemical and bacteriological investigations of Mannheimia haemolytica in sheep bronchopneumonia. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg 23(1):7–14. https://doi.org/10.9775/kvfd.2016.15679
Marru HD, Anijajo TT, Hassen AA (2013) A study on Ovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: Isolation and Identification of Pasteurellae and their antibiogram susceptibility pattern in Haramaya District, Eastern Hararghe, Ethiopia. BMC Vet Res 9(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-6148-9-239
Biberstein E, Shreeve B, Thompson D (1970) Variation in carrier rates of Pasteurella haemolytica in sheep flocks: I. Normal flocks. J Comp Pathol 80(4):499–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9975(70)90046-0
Ackermann MR, Brogden KA (2000) Response of the ruminant respiratory tract to Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica. Microbes Infect 2(9):1079–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1286-4579(00)01262-4
Kaoud H, El-Dahshan A, Zaki M, Nasr SA (2010) Occurrence of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella trehalosi among ruminants in Egypt. New York Science Journal 3(5):135–141
Sisay T, Zerihun A (2003) Diversity of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella trehalosi serotypes from apparently healthy sheep and abattoir specimens in the highlands of Wollo, North East Ethiopia. Vet Res Commun 27(1):3–14
Hussain R, Mahmood F, Ali HM, Siddique AB (2017) Bacterial, PCR and clinico-pathological diagnosis of naturally occurring pneumonic pasturellosis (mannheimiosis) during subtropical climate in sheep. Microb Pathog 112:176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.09.061
Abed AH, El-Seedy FR, Hassan HM, Nabih AM, Khalifa E, Salem SE, Wareth G, Menshawy A (2020) Serotyping, genotyping and virulence genes characterization of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica Isolates Recovered from Pneumonic Cattle Calves in North Upper Egypt. Veterinary Sci 7(4):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7040174
Katsuda K, Kohmoto M, Mikami O (2013) Relationship between serotype and the antimicrobial susceptibility of Mannheimia haemolytica isolates collected between 1991 and 2010. Res Vet Sci 94(2):205–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2012.09.015
Al-Ghamdi GM, Ames TR, Baker JC, Walker R, Chase CC, Frank GH, Maheswaran SK (2000) Serotyping of Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica isolates from the upper Midwest United States. J Vet Diagn Invest 12(6):576–578. https://doi.org/10.1177/104063870001200617
Akan M, Öncel T, Sareyyüpoğlu B, Hazıroğlu R, Tel OY, Cantekin Z (2006) Vaccination studies of lambs against experimental Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica infection. Small Ruminant Research 65(1–2):44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2005.05.020
Roier S, Fenninger JC, Leitner DR, Rechberger GN, Reidl J, Schild S (2013) Immunogenicity of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica outer membrane vesicles. Int J Med Microbiol 303(5):247–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.05.001
Subramaniam R, Shanthalingam S, Bavananthasivam J, Kugadas A, Potter KA, Foreyt WJ, Hodgins DC, Shewen PE, Barrington GM, Knowles DP (2011) A multivalent Mannheimia-Bibersteinia vaccine protects bighorn sheep against Mannheimia haemolytica challenge. Clin Vaccine Immunol 18(10):1689–1694. https://doi.org/10.1128/CVI.05276-11
Confer AW, Ayalew S, Panciera RJ, Montelongo M, Wray JH (2006) Recombinant Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 outer membrane protein PlpE enhances commercial M. haemolytica vaccine-induced resistance against serotype 6 challenge. Vaccine 24(13):2248–2255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.11.036
Confer A, Clinkenbeard K, Gatewood D, Driskel B, Montelongo M (1997) Serum antibody responses of cattle vaccinated with partially purified native Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin. Vaccine 15(12–13):1423–1429. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-410X(97)84247-8
Kamaradin I-h, Assaw S, Sheikh HI, Abd Wahid ME (2021) Potential of Chlorella sp. exopolysaccharide as adjuvant for Mannheimia haemolytica A2 vaccine in rat model.Songklanakarin Journal of Science & Technology43(3)
Bowersock TL, Sobecki BE, Terrill SJ, Martinon NC, Meinert TR, Leyh RD (2014) Efficacy of a multivalent modified-live virus vaccine containing a Mannheimia haemolytica toxoid in calves challenge exposed with Bibersteinia trehalosi. Am J Vet Res 75(8):770–776. https://doi.org/10.2460/ajvr.75.8.770
Frank GH, Briggs RE, Duff GC, Loan RW, Purdy CW (2002) Effects of vaccination prior to transit and administration of florfenicol at time of arrival in a feedlot on the health of transported calves and detection of Mannheimia haemolytica in nasal secretions. Am J Vet Res 63(2):251–256. https://doi.org/10.2460/ajvr.2002.63.251
Acknowledgements
We thank the Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute (RVSRI), Shiraz, Iran for their support and Mr. S. Sadeghzadeh (Lab Animal Department) for his technical assistance. This study was supported by the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) and in part by Research Grant number 99013545.
Funding
This study was supported by the Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute and in part by Grant number 99013545.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors read and approved the final manuscript. YT designed the research work; HM, MH and ES performed the experiments; and HM wrote the manuscript and submitted the assembled sequence of M. haemolytica.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animal owner statement
Animal owners provided their verbal informed consent for injection of vaccine as well as for animal blood sampling. Blood samples were collected by veterinarians according to the guidelines on animal husbandry. The study protocol was approved by Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute animal house.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The experiments were performed in compliance with the principles of the Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute.
Consent to participate
All authors confirm that they have seen and have been given the opportunity to read the Article (as attached) to be published by Molecular Biology Reports.
Consent for publication
Anyone can read this paper published in the Molecular Biology Reports. We understand that readers may include not only medical professionals and scholarly researchers but also journalists and general members of the public.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Molaee, H., Tahamtan, Y., Saeednezhad, E. et al. Isolation of the various serotypes of Mannheimia haemolytica and preparation of the first vaccine candidate in Iran. Mol Biol Rep 49, 10367–10375 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07890-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07890-4