Abstract
Background
Continuing hyperglycemia causes and exacerbate oxidative stress. Betanin as the principal pigment of red beet root has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-diabetic properties. The purpose of this study was to investigate the potency of betanin on antioxidant defense in STZ-induced diabetic rats’ livers.
Methods
STZ at a single dose of 60 mg/kg body weight was intraperitoneally injected and betanin (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg/day) was administered orally for 28 days. Malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), protein carbonyl (PC) levels, and the enzyme activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalases and glutathione peroxidases (GPx) were evaluated in the liver. Furthermore, gene expression of Nrf2 and mentioned antioxidant enzymes were measured by Real-time PCR.
Results
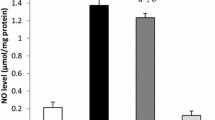
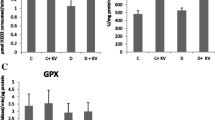
Betanin (10 and 20 mg/kg) significantly reduced PC levels and increased antioxidant enzyme activity in diabetic rats compared to the control diabetic group (P < 0.01). In comparison to the diabetic control group, all studied genes expression in diabetic rats were increased significantly with betanin at doses of 10 and 20 mg/kg (P < 0.02). The increase in gene expression at 20 mg/kg of betanin was significantly stronger than others (P < 0.015) except for the catalase (P = 0.201), that was almost the same. Moreover, treatment of diabetic rats with 20 mg/kg of betanin could significantly increase TAC levels (P < 0.05) and decrease MDA levels (P < 0.001) compared to diabetic control group.
Conclusions
Betanin could increase the antioxidant capacity of liver tissue associated with the Nrf2-mediated pathway in a dose-dependent manner.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data of present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes J, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, Cavan D, Shaw J, Makaroff L (2017) IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 128:40–50
Rahimi R, Nikfar S, Larijani B, Abdollahi M (2005) A review on the role of antioxidants in the management of diabetes and its complications. Biomed Pharmacotherapy 59(7):365–373
Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA, Grodsky GM (2002) Oxidative stress and stress-activated signaling pathways: a unifying hypothesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr reviews 23(5):599–622
Zhang P, Li T, Wu X, Nice EC, Huang C, Zhang Y (2020) Oxidative stress and diabetes: antioxidative strategies.Frontiers of medicine.:1–18
Ghasemi-Dehnoo M, Amini-Khoei H, Lorigooini Z, Rafieian-Kopaei M (2020) Oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetes mellitus. Asian Pac J Trop Med 13(10):431
Bhakkiyalakshmi E, Sireesh D, Rajaguru P, Paulmurugan R, Ramkumar KM (2015) The emerging role of redox-sensitive Nrf2–Keap1 pathway in diabetes. Pharmacol Res 91:104–114
Uruno A, Yagishita Y, Yamamoto M (2015) The Keap1–Nrf2 system and diabetes mellitus. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 566:76–84
Raish M, Ahmad A, Jardan YAB, Shahid M, Alkharfy KM, Ahad A, Ansari MA, Abdelrahman IA, Al-Jenoobi FI (2022) Sinapic acid ameliorates cardiac dysfunction and cardiomyopathy by modulating NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways in streptozocin induced diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacotherapy 145:112412
Yang G, Li Q, Peng J, Jin L, Zhu X, Zheng D, Zhang Y, Wang R, Song Y, Hu W (2021) Fucoxanthin regulates Nrf2 signaling to decrease oxidative stress and improves renal fibrosis depending on Sirt1 in HG-induced GMCs and STZ-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 913:174629
Al-Amarat W, Abukhalil MH, Althunibat OY, Alfwuaires MA, Alnamshan MM, Alqosaibi AI, Ahmeda AF, Kamel EM, Arab HH, Mahmoud AM (2021) Galangin attenuates liver injury, oxidative stress and inflammation, and upregulates Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Processes 9(9):1562
Elekofehinti OO, Adewumi NA, Iwaloye O (2021) Antidiabetic potential of Chromolaena Odorata leave extract and its effect on Nrf2/keap1 antioxidant pathway in the liver of diabetic-induced Wistar Rats.Advances in Traditional Medicine.:1–11
Jung K-A, Kwak M-K (2010) The Nrf2 system as a potential target for the development of indirect antioxidants. Molecules 15(10):7266–7291
Matzinger M, Fischhuber K, Heiss EH (2018) Activation of Nrf2 signaling by natural products-can it alleviate diabetes? Biotechnol Adv 36(6):1738–1767
Silva DVTd, Baiao DdS, Ferreira VF, Paschoalin VMF (2021) Betanin as a multipath oxidative stress and inflammation modulator: A beetroot pigment with protective effects on cardiovascular disease pathogenesis. Crit Reviews Food Sci Nutr 62(2):539–554
Krajka-Kuźniak V, Paluszczak J, Szaefer H, Baer-Dubowska W (2013) Betanin, a beetroot component, induces nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2-mediated expression of detoxifying/antioxidant enzymes in human liver cell lines. Br J Nutr 110(12):2138–2149
Straub LG, Efthymiou V, Grandl G, Balaz M, Challa TD, Truscello L, Horvath C, Moser C, Rachamin Y, Arnold M (2019) Antioxidants protect against diabetes by improving glucose homeostasis in mouse models of inducible insulin resistance and obesity. Diabetologia 62(11):2094–2105
Kujawska M, Ignatowicz E, Murias M, Ewertowska M, Mikołajczyk K, Jodynis-Liebert J (2009) Protective effect of red beetroot against carbon tetrachloride-and N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced oxidative stress in rats. J Agricultural Food Chem 57(6):2570–2575
Zielińska-Przyjemska M, Olejnik A, Kostrzewa A, Łuczak M, Jagodziński PP, Baer‐Dubowska W (2012) The beetroot component betanin modulates ROS production, DNA damage and apoptosis in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Phytotherapy Res 26(6):845–852
Dhananjayan I, Kathiroli S, Subramani S, Veerasamy V (2017) Ameliorating effect of betanin, a natural chromoalkaloid by modulating hepatic carbohydrate metabolic enzyme activities and glycogen content in streptozotocin–nicotinamide induced experimental rats. Biomed Pharmacotherapy 88:1069–1079
Han J, Zhang Z, Yang S, Wang J, Yang X, Tan D (2014) Betanin attenuates paraquat-induced liver toxicity through a mitochondrial pathway. Food and chemical toxicology 70:100–106
Belhadj Slimen I, Najar T, Abderrabba M (2017) Chemical and antioxidant properties of betalains. J Agricultural Food Chem 65(4):675–689
Kanner J, Harel S, Granit R (2001) Betalains a new class of dietary cationized antioxidants. J Agricultural Food Chem 49(11):5178–5185
Motawi TK, Ahmed SA, El-Boghdady NA, Metwally NS, Nasr NN (2020) Impact of betanin against paracetamol and diclofenac induced hepato-renal damage in rats. Biomarkers 25(1):86–93
Abedimanesh N, Asghari S, Mohammadnejad K, Daneshvar Z, Rahmani S, Shokoohi S, Farzaneh AH, Hosseini SH, Jafari Anarkooli I, Noubarani M (2021) The anti-diabetic effects of betanin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through modulating AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Nutr Metabolism 18(1):1–13
Apak R, Güçlü K, Özyürek M (2005) Karademi˙ r SEn, Altun M. Total antioxidant capacity assay of human serum using copper (II)-neocuproine as chromogenic oxidant: the CUPRAC method. Free radical research 39(9):949–961
Pisoschi AM, Negulescu GP (2011) Methods for total antioxidant activity determination: a review. Biochem Anal Biochem 1(1):106
Yan Lj (2018) Redox imbalance stress in diabetes mellitus: Role of the polyol pathway. Anim models experimental Med 1(1):7–13
Martinez RM, Longhi-Balbinot DT, Zarpelon AC, Staurengo-Ferrari L, Baracat MM, Georgetti SR, Sassonia RC, Verri WA, Casagrande R (2015) Anti-inflammatory activity of betalain-rich dye of Beta vulgaris: effect on edema, leukocyte recruitment, superoxide anion and cytokine production. Archives of pharmacal research 38(4):494–504
Madadi E, Mazloum-Ravasan S, Yu JS, Ha JW, Hamishehkar H, Kim KH (2020) Therapeutic application of betalains: a review. Plants 9(9):1219
Mahami N, Abedimanesh N, Asghari S, Mohammadnejad K, Eskandari MR, Nejadebrahimi Z, Ahangar H, Nedaei K, Fathi M, Noori E, Motlagh B (2022) Effects of betanin on AMPK, Sirtuin1, and Sirtuin6 gene expression and inflammatory cytokines levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with coronary artery disease. Nutrition & Food Science
Alatawi FS, Faridi UA, Alatawi MS (2018) Effect of treatment with vitamin D plus calcium on oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Saudi Pharm J 26(8):1208–1213
Kamata K, Kobayashi T (1996) Changes in superoxide dismutase mRNA expression by streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Br J Pharmacol 119(3):583
Saravanan G, Ponmurugan P (2011) Ameliorative potential of S-allyl cysteine on oxidative stress in STZ induced diabetic rats. Chemico-biological Interact 189(1–2):100–106
Goth L, Eaton JW (2000) Hereditary catalase deficiencies and increased risk of diabetes. The Lancet 356(9244):1820–1821
Quine SD, Raghu PS (2005) Effects of (-)-epicatechin, a flavonoid on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in streptozotocin-induced diabetic liver, kidney and heart. Pharmacol Rep 57(5):610–615
Tiwari BK, Pandey KB, Abidi A, Rizvi SI (2013) Markers of oxidative stress during diabetes mellitus. Journal of biomarkers. 2013
Masola B, Oguntibeju OO, Oyenihi AB (2018) Centella asiatica ameliorates diabetes-induced stress in rat tissues via influences on antioxidants and inflammatory cytokines. Biomed Pharmacotherapy 101:447–457
Sindhu RK, Koo JR, Roberts CK, Vaziri ND (2004) Dysregulation of hepatic superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in diabetes: response to insulin and antioxidant therapies. Clin experimental Hypertens 26(1):43–53
Sadi G, Bozan D, Yildiz HB (2014) Redox regulation of antioxidant enzymes: post-translational modulation of catalase and glutathione peroxidase activity by resveratrol in diabetic rat liver. Mol Cell Biochem 393(1):111–122
Fang S, Cai Y, Li P, Wu C, Zou S, Zhang Y, Lin X, Guan M (2019) Exendin-4 alleviates oxidative stress and liver fibrosis by activating Nrf2/HO-1 in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Nan fang yi ke da xue xue bao = Journal of Southern Medical University 39(4):464–470
Ebokaiwe AP, Ijomone OM, Griffin S, Ehiri RC, Obeten KE, Nwankwo JO, Ejike CE, Keck CM (2019) Nanosized selenium and Loranthus micranthus leaves ameliorate streptozotocin-induced hepato-renal dysfunction in rats via enhancement of antioxidant system, regulation of caspase 3 and Nrf2 protein expression. Pharmanutrition 9:100150
Jiménez-Osorio AS, Gonzalez-Reyes S, Pedraza-Chaverri J (2015) Natural Nrf2 activators in diabetes. Clin Chim acta 448:182–192
Zambrano V, Bustos R, Mahn A (2019) Insights about stabilization of sulforaphane through microencapsulation. Heliyon 5(11):e02951
Ayala A, Muñoz MF, Argüelles S (2014) Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity. 2014
Boarescu P-M, Boarescu I, Pop RM, Roşian ŞH, Bocșan IC, Rus V, Mada RO, Popa ID, Neagu N, Bulboacă AE (2022) Evaluation of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers, Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, and Histological Changes in Experimental Hypertension, Dyslipidemia, and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci 23(3):1438
Ramakrishna V, Jailkhani R (2008) Oxidative stress in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) patients. Acta Diabetol 45(1):41–46
Zare-Mirzaie A, Kazeminezhad B, Ghouchani MA (2018) The correlation between serum vitamin D level and Total antioxidant capacity in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects in Iran. Iran J Pathol 13(2):212
Khaki A, KHAKI A, Nouri M, AHMADI AHR, Rastgar H, Rezazadeh S, FATHI AF, Ghanbari M (2009) Evaluation effects of Quercetin on liver apoptosis in streptozotocininduced diabetic rat.
Samimi F, Baazm M, Eftekhar E, Jalali Mashayekh F (2019) Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Liver Total Oxidant/Antioxidant Status in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats. J Arak Univ Med Sci 22(4):28–39
El-Baz FK, Salama A, Salama RA (2020) Dunaliella salina attenuates diabetic neuropathy induced by STZ in rats: involvement of thioredoxin. BioMed research international. 2020
Acknowledgements
We thank the Vice Chancellor for Research of Zanjan University of Medical Sciences for the financial support.
Funding
The present study was funded by the Vice Chancellor for Research of Zanjan University of Medical Sciences and Student Research Committee of Zanjan University of Medical Sciences (Grants no. A-12-1125-6 and A-12-1125-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MM, E SH, M N, M T were involved in data collection and performance of experiment. N A and MR E were involved in conceptualization, formal analysis, data curation, methodology, writing original draft and review and editing and visualization. H KH, M F, J M contributed in investigation and validation. K M contributed in writing original draft and review. B M contributed in methodology, editing, supervision and project administration. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures were according to the Ethics Committee of Zanjan University of Medical Sciences (IR.ZUMS.REC.1398.475).
Consent for publication
No personal data is noted herein.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mousavi, M., Abedimanesh, N., Mohammadnejad, K. et al. Betanin alleviates oxidative stress through the Nrf2 signaling pathway in the liver of STZ-induced diabetic rats. Mol Biol Rep 49, 9345–9354 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07781-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07781-8