Abstract
Background
Eggplant is an important vegetable that has long been cultivated in different parts of Iran. The major objectives of the eggplant breeding program are to improve fruit quality, increase yield performance through heterosis breeding, and introduce abilities of pest and disease resistance from wild relatives. In order to select suitable parents for breeding purposes, with respect to the genetic and morphological diversity of eggplant cultivars, it is necessary to have sufficient knowledge of genetic diversity and classification of germplasms.
Methods
This experiment was conducted in a randomized block design at the Seed and Plant Improvement Institute (SPII) in Karaj, Iran. Here, morphological diversity was assessed among a collection of eggplants which comprised four Iranian lines and 13 non-Iranian genotypes. For this purpose, 16 morphological traits were analyzed in the plants. Given the weakness of morphological analysis in providing precise characterizations of genetic divergence, a molecular study was also carried out by using five Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) markers. In addition to the univariate analysis, the multi-descriptor variation was studied among the genotypes using two methods of multivariate analyses.
Results
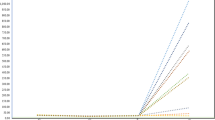
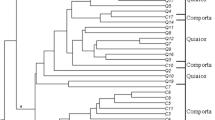
The genotypes differed significantly in terms of the morphological traits. The multivariate analyses of morphological data indicated that eggplants from two different origins were clearly differentiated. Three main clusters were distinguished by a morphological UPGMA dendrogram in which non-Iranian genotypes, with the exception of 11,212, constituted cluster I and required the maximum number of days to flower, days to fruit set, and days to first harvest. Cluster II was identified with two Iranian lines BJ30, Y60, and one non-Iranian genotype (11,212) which showed the highest values of stem diameter, fruit diameter, fruit length, fruit length-to-width ratio, number of fruits per plant, and yield. Cluster III comprised two Iranian lines, D1 and D7, and showed the maximum plant height, number of internodes, number of nodes, number of leaves, number of stems, fruit weight, and fruits weight per plant. The highest and lowest intra-cluster genetic distances were observed in cluster I and cluster II, respectively. Based on SSR analysis, high levels of similarity were detected between several genotypes, namely, Y60 and 13,411; BJ30 and 1111; D7 and 13,521; 21,881 and 13,421.
Conclusions
High levels of heterozygosity and polymorphism information content (PIC) were observed in this study. This not only indicated high levels of polymorphism and an equal distribution of the evaluated loci but also suggested that these genotypes can be considered for the development of diverse parental lines which are of interest in breeding programs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yousafi Q, Afzal M, Aslam M, Razaq M, Shahid M (2013) Screening of brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) varieties sown in autumn for resistance to cotton jassid, Amrasca Bigutulla Bigutulla (Ishida). Pakistan J Zoolo 45:897–902
Sifau MO, Ogunkanmi LA, Adekoya KO, Oboh BO, Ogundipe OT (2014) Partitioning and distribution of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) variation among eggplant Solanum L. in Southwest Nigeria International. J Gen Molecul Biol 6(1):1–7
Oladosu Y, Rafii MY, Arolu F, Chukwu SC, Salisu MA, Olaniyan BA, Fagbohun IK, Muftaudeen TK (2021) Genetic Diversity and Utilization of Cultivated Eggplant Germplasm in Varietal Improvement. Plants 10:1714
Portis E, Lanteri S, Barchi L, Portis F, Valente L, Toppino L, Acquadro A (2018) Comprehensive characterization of simple sequence repeats in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) genome and construction of a web resource. Front Plant Sci 9:401
Rahman MO, Rabbani MG, Yesmin R, Garvey EJ (2014) Genetic diversity of brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) through multivariate analysis. Int J Natur Soci Sci 1:85–93
Husnudin U, Daryono B, Purnomo P (2019) Genetic variability of Indonesian eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) based on ISSR markers.Biodivers J Biolo Diversity20(10)
Bashar A, Jahan N, Ali Ahmed F, Hossain MK, Alam N (2015) Morphological and phytochemical variation in eggplant (solanum melongena L.). Pharma Sci Moni 6(4):1–11
Kalloo G (1988) Vegetable Breeding Vol. II. Chapt1. Disease Resistance in Vegetable crops. CRS Press. Inc, Boca Raton, Florida
Munoz-Falcon EJ, Prohens J, Vilanova S, Ribas F, Castroc A, Nuez F (2009) Distinguishing a protected geographical indication vegetable (Almagro eggplant) from closely related varieties with selected morphological traits and molecular markers. J Sci Food Agri 89:320–328
Rad MRN, Poodineh M, Ghalandarzehi A, Abkhoo J (2016) Variability, heritability and association analysis in eggplant (Solanum melongena). J Agri Biologi Sci 10:464–468
Bagheri M (2017) Collection, conservation and breeding of Iranian eggplant landraces Advances in Genetics and Breeding of Capsicum and Eggplant. Editorial de la Universitat Politècnica de València, p 421
Musa I, Rafii MY, Ahmad K, Ramlee SI, Md-Hatta MA, Oladosu Y, Halidu J (2020) Effects of grafting on morphophysiological and yield characteristic of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) grafted onto wild relative rootstocks. Plants 9:1583
Adeniji OT, Kusolwa P, Reuben SWOM (2013) Morphologicaldescriptors and micro satellite diversity among scarlet eggplant groups. Afr Crop Sci J21:37–49
Begum F, Islam AKMA, Rasul MG, Mian MAK, Mofazzal M (2013) Morphological diversity of eggplant. J Food Agri 25:45–51
Cericola F, Portis E, Toppino L, Barchi L, Acciarri N, Ciriaci T, Sala T, Rotino GL, Lanteri S (2013) The Population Structure and Diversity of Eggplant from Asia and the Mediterranean Basin. PLoS ONE 8:1–16
Hurtado M, Vilanova S, Plazas M, Gramazio P, Fonseka HH, Fonseka R, Prohens J (2012) Diversity and Relationships of Eggplants from Three Geographically Distant Secondary Centers of Diversity. PLoS ONE 7:1–14
Li H, Chen H, Zhuang T, Chen J (2010) Analysis of genetic variation in eggplant and related Solanum species using sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. Scienta Horticultura (Amsterdam) 125:19–24
Reddy L, Chinnappareddy D, Hongasandra S, Reddy S, Kanupriya C, Chennareddy A, Singh TH (2012) SSR-Based DNA Barcodes as a Tool for Identification of Eggplant Genotypes. Int J Vegetable Sci 18:260–271
Kumar G, Meena BL, Kar R, Tiwari SK, Gangopadhyay KK, Bisht IS, Mahajan RK (2008) Morphological diversity in brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) germplasm accessions. Plant Genet. Res. 2008, 6:232–236
Hillis DM (1987) Molecular versus morphological approaches to systematics. Ann Rev Ecolog Sys18:23–42
Nunome T, Suwabe K, Ohyama A, Fukuoka H (2003) Characterization of Trinucleotide Microsatellites in Eggplant. BreedSci 83:77–83
Sakata Y, Nishio T, Matthews PJ (1991) Chloroplast DNA analysis of eggplant (Solanum melongena) and related species for their taxonomic affinity. Euphytica 55:21–26
Demir K, Bakır M, Sarıkamış G, Acunalp S (2010) Genetic diversity of eggplant (Solanum melongena) germplasm from Turkey assessed by SSR and RAPD markers. Gen Molecul Res 9:1568–1576
Mutlu N, Boyaci FH, Göçmen M, Abak K (2008) Development of SRAP, SRAP-RGA, RAPD and SCAR markers linked with a Fusarium wilt resistance gene in eggplant. Theori Appll Gen 117:1303–1312
Nunome T, Keizo I, Tatemi Y, Hirai M (2001) Mapping of fruit shape and color development traits in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Based on RAPD and AFLP markers. Breed Sci 51:19–26
Isshiki S, Iwata N, Khan MR (2008) ISSR variations in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and related Solanum species. Scientia Horticulturae (Amsterdam) 117:186–190
Caguiat XGI, Hautea DM (2014) Genetic diversity analysis of eggplant (solanum melongena L.) and related wild species in the Philippines using morphological and SSr markers. J Breed Gen 46:183–201
Liu J, Yang Y, Zhou X, Bao S, Zhuang Y (2018) Genetic diversity and population structure of worldwide eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) germplasm using SSR markers. Gen Resourse Crop Evolu 65:1663–1616
Mu JE, Vilanova S, Plazas M, Prohens J (2011) Diversity, relationships, and genetic fingerprinting of the Listada de Gandía eggplant landrace using genomic SSRs and EST-SSRs. Sci Hortic J 129:238–246
Nunome T, Negoro S, Kono I, Kanamori H, Miyatake K, Yamaguchi H, Ohyama A, Fukuoka H (2009) Development of SSR markers derived from SSR-enriched genomic library of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Theori Appll Gen 119:1143–1153
Vilanova S, Hurtado M, Cardona A, Plazas M, Gramazio P, Herraiz FJ, Andújar I, Prohens J (2014) Genetic Diversity and Relationships in Local Varieties of Eggplant from Different Cultivar Groups as Assessed by Genomic SSR Markers. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca 42:59–65
Powell W, Machray GC, Provar J (1996) Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci 1:0–7
Munoz-Falcon EJ (2008) Characterization, diversity, and relationships of the Spanish striped (Listada) eggplants : a model for the enhancement and protection of local heirlooms. Euphytica 164:405–419
Prohens J, Blanca JM, Nuez F (2005) Morphological and Molecular Variation in a Collection of Eggplants from a Secondary Center of Diversity: Implications for Conservation and Breeding. J Amer Soci Hortic Sci 130:54–63
Ronoh R, Linde M, Winkelmann T (2018) Morphological characterization, genetic diversity and population structure of African nightshades (section Solanum L.). GenResource Crop Evol 66:105–120
Mat Sulaiman NN, Rafii MY, Duangjit J, Ramlee SI, Phumichai C, Oladosu Y, Datta DR, Musa I (2020) Genetic Variability of Eggplant Germplasm Evaluated under Open Field and Glasshouse Cropping Conditions. Agronomy 10:436
Gramazio P, Chatziefstratiou E, Petropoulos C, Chioti V, Mylona P, Kapotis G, Vilanova S, Prohens J, Papasotiropoulos V (2019) Multi-Level Characterization of Eggplant Accessions from Greek Islands and the Mainland Contributes to the Enhancement and Conservation of this Germplasm and Reveals a Large Diversity and Signatures of Differentiation between both Origins. Agronomy 2019, 9: 887
Datta DR, Rafii MY, Misran A, Jusoh M, Yusuff O, Sulaiman NM, Momodu J (2021) Genetic diversity, heritability and genetic advance of Solanum melongena L. from three secondary centers of diversity. Bangladesh J Plant Taxonom 28:155–169
Furini A, Wunder J (2004) Analysis of eggplant (Solanum melongena) related germplasm: Morphological and AFLP data contribute to phylogenetic interpretation and germplasm utilization. Theor Appl Genet 108:197–208
Adeniji O, Aloyce A (2012) Farmer’s knowledge of horticultural traits and participatory selection of African eggplant varieties (Solanum aethiopicum) in Tanzania. Tropicultura 30:185–191
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical Taxonomy WH Freeman and Co. San Fransisco. 1–573
N’guessan OK, Marie AA, Léonard K, Doffou SA, Guy M (2020) Biodiverse J Biol Divers 21:8
Hassanzadeh Khankahdani H, Bagheri M, Khoshkam S (2022) Stability and Compatibility of some Iranian Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Lines using AMMI Method. Int J Hort Sci Technol 9(1):25–39
Husnudin UB, Daryono BS, Purnomo S (2019) Genetic variability of Indonesian eggplant (Solanum melongena) based on ISSR markers. Biodiversitas 20(10):3049–3055
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fallahi, F., Abdossi, V., Bagheri, M. et al. Genetic diversity analysis of Eggplant Germplasm from Iran: assessments by morphological and SSR markers. Mol Biol Rep 49, 11705–11714 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07768-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07768-5