Abstract
Background
Stomatitis is inflammation of the oral mucosa. Angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4) has pleiotropic functions both anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory properties. In the present study, we tested whether there is a correlation between increased ANGPTL4 expression and inflammation in stomatitis mice and the mechanisms involved.
Methods and Results
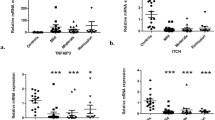
In this study, the oral mucosa of mice was burned with 90% phenol and intraperitoneal injection of 5-fluorouracil to establish the model of stomatitis mice. The pathological changes of stomatitis mice were observed by H&E staining of paraffin section. The expressions of cytokines and ANGPTL4 were detected by fluorescence quantitative PCR, and the protein levels of ANGPTL4 were detected by western blot. Compared with control group, the oral mucosal structure of model mice was damaged. The expression of ANGPTL4 were significantly increased concomitantly with elevated production of anti-inflammatory cytokine (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha) and pro-inflammatory cytokines [nuclear transcription factor-kappa B, interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-α] in mice with stomatitis.
Conclusions
This study suggests that ANGPTL4 may be a double-edged sword in multiple inflammatory responses in stomatitis mice.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All authors made sure that all data and materials as well as software application or custom code support their published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Bilodeau EA, Lalla RV (2000) Recurrent oral ulceration: etiology, classification, management, and diagnostic algorithm. Periodontol 80(1):49–60
Bateman E, Blijlevens N, Gibson RJ, Logan RM, Nair RG, Stringer AM, Yazbeck R, Elad S, Lalla RV (2013) Mucositis Study Group of Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer/International Society of Oral Oncology (MASCC/ISOO). Emerging evidence on the pathobiology of mucositis. Support Care Cancer 21(7):2075–2083
Abdullah Mustafa J (2013) Prevalence of recurrent aphthous ulceration experience in patients attending Piramird dental speciality in Sulaimani City. J Clin Exp Dent 5(2):e89-94
Paudel D, Kuramitsu Y, Uehara O, Morikawa T, Yoshida K, Giri S, Islam ST, Kitagawa T, Kondo T, Sasaki K, Matsuoka H, Miura H, Abiko Y (2022) Proteomic and microbiota analyses of the oral cavity during psychological stress. PLoS ONE 17(5):e0268155
Fujishiro M, Yahagi S, Takemi S, Nakahara M, Sakai T, Sakata I (2021) Pyridoxine stimulates filaggrin production in human epidermal keratinocytes. Mol Biol Rep 48(7):5513–5518
Grootaert C, Van de Wiele T, Verstraete W, Bracke M, Vanhoecke B (2012) Angiopoietin-like protein 4: health effects, modulating agents and structure-function relationships. Expert Rev Proteomics 9(2):181–199
Lei X, Shi F, Basu D, Huq A, Routhier S, Day R, Jin WJ (2011) Proteolytic processing of angiopoietin-like protein 4 by proprotein convertases modulates its inhibitory effects on lipoprotein lipase activity. J Biol Chem 286(18):15747–15756
Kersten S, Mandard S, Tan NS, Escher P, Metzger D, Chambon P, Gonzalez FJ, Desvergne B, Wahli W (2000) Characterization of the fasting-induced adipose factor FIAF, a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor target gene. J Biol Chem 275(37):28488–28493
Dao T, Gapihan G, Leboeuf C, Hamdan D, Feugeas JP, Boudabous H, Zelek L, Miquel C, Tran T, Monnot C, Germain S, Janin A, Bousquet G (2022) Expression of angiopoietin-like 4 fibrinogen-like domain (cANGPTL4) increases risk of brain metastases in women with breast cancer. Oncotarget 11(18):1590–1602
Li L, Chong HC, Ng SY, Kwok KW, Teo Z, Tan EHP, Choo CC, Seet JE, Choi HW, Buist ML, Chow VTK, Tan NS (2015) Angiopoietin-like 4 increases pulmonary tissue leakiness and damage during influenza pneumonia. Cell Rep 10(5):654–663
Qin L, Zhang R, Yang S, Chen F, Shi J (2019) Knockdown of ANGPTL-4 inhibits inflammatory response and extracellular matrix accumulation in glomerular mesangial cells cultured under high glucose condition. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47(1):3368–3373
Schumacher A, Denecke B, Braunschweig T, Stahlschmidt J, Ziegler S, Brandenburg LO, Stope MB, Martincuks A, Vogt M, Görtz D, Camporeale A, Poli V, Müller-Newen G, Brümmendorf TH, Ziegler P (2015) Angptl4 is upregulated under inflammatory conditions in the bone marrow of mice, expands myeloid progenitors, and accelerates reconstitution of platelets after myelosuppressive therapy. J Hematol Oncol 8:64
Masuko K (2017) Angiopoietin-like 4: a molecular link between insulin resistance and rheumatoid arthritis. J Orthop Res 35(5):939–943
Li L, Foo BJW, Kwok KW, Sakamoto N, Mukae H, Izumikawa K, Mandard S, Quenot JP, Lagrost L, Teh WK, Singh Kohli G, Zhu P, Choi H, Buist ML, Seet JE, Yang L, He F, Kwong Chow VT, Tan NS (2019) Antibody treatment against angiopoietin-like 4 reduces pulmonary edema and injury in secondary pneumococcal pneumonia. MBio 10(3):e02469-e12418
Jung KH, Son MK, Yan HH, Fang Z, Kim J, Kim SJ, Park JH, Lee JE, Yoon YC, Seo MS, Han BS, Ko S, Suh YJ, Lim JH, Lee DH, Teo Z, Wee JWK, Tan NS, Hong SS (2020) ANGPTL4 exacerbates pancreatitis by augmenting acinar cell injury through upregulation of C5a. EMBO Mol Med 12(8):e11222
Lan S, He Y, Tiheiran M, Liu W, Guo H (2021) The Angiopoietin-like protein 4: a promising biomarker to distinguish brucella spondylitis from tuberculous spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 40(10):4289–4294
Teratani T, Tomita K, Wada A, Sugihara N, Higashiyama M, Inaba K, Horiuchi K, Hanawa Y, Nishii S, Mizoguchi A, Tanemoto R, Ito S, Okada Y, Kurihara C, Akita Y, Narimatsu K, Watanabe C, Komoto S, Oike Y, Miura S, Hokari R, Kanai T (2021) Angiopoietin-like protein 4 deficiency augments liver fibrosis in liver diseases such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice through enhanced free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate cells. Hepatol Res 51(5):580–592
Lichtenstein L, Mattijssen F, de Wit NJ, Georgiadi A, Hooiveld GJ, van der Meer R, He Y, Qi L, Köster A, Tamsma JT, Tan NS, Müller M, Kersten S (2010) Angptl4 protects against severe proinflammatory effects of saturated fat by inhibiting fatty acid uptake into mesenteric lymph node macrophages. Cell Metab 12(6):580–592
Guo L, Li S, Zhao Y, Qian P, Ji F, Qian L, Wu X, Qian G (2015) Silencing angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4) protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulating SIRT1/NF-kB pathway. J Cell Physiol 230(10):2390–2402
Lan G, Xie W, Li L, Zhang M, Liu D, Tan YL, Cheng HP, Gong D, Huang C, Zheng XL, Yin WD, Tang CK (2016) MicroRNA-134 actives lipoprotein lipase-mediated lipid accumulation and inflammatory response by targeting angiopoietin-like 4 in THP-1 macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2472(3):410–417
Phua T, Sng MK, Tan EH, Chee DS, Li Y, Wee JW, Teo Z, Chan JS, Lim MM, Tan CK, Zhu P, Arulampalam V, Tan NS (2017) Angiopoietin-like 4 mediates colonic inflammation by regulating chemokine transcript stability via tristetraprolin. Sci Rep 7:44351
Cho DI, Kang HJ, Jeon JH, Eom GH, Cho HH, Kim MR, Cho M, Jeong HY, Cho HC, Hong MH, Kim YS, Ahn Y (2019) Antiinflammatory activity of ANGPTL4 facilitates macrophage polarization to induce cardiac repair. JCI Insight 4(16):e125437
Gruppen EG, Kersten S, Dullaart RPF (2018) Plasma angiopoietin-like 4 is related to phospholipid transfer protein activity in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects: role of enhanced low grade inflammation. Lipids Health Dis 17(1):60
Tanideh N, Namazi F, Andisheh Tadbir A, Ebrahimi H, Koohi-Hosseinabadi O (2014) Comparative assessment of the therapeutic effects of the topical and systemic forms of Hypericum perforatum extract on induced oral mucositis in golden hamsters. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 43(10):1286–1292
Sonis ST, Tracey C, Shklar G, Jenson J, Florine D (1990) An animal model for mucositis induced by cancer chemotherapy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 69(4):437–443
Tancharoen S, Shakya P, Narkpinit S, Dararat P, Kikuchi K (2018) Anthocyanins extracted from Oryza sativa L. prevent fluorouracil-induced nuclear factor-κB activation in oral mucositis: in vitro and in vivo studies. Int J Mol Sci 19(10):2981
Oteng AB, Ruppert PMM, Boutens L, Dijk W, van Dierendonck XAMH, Olivecrona G, Stienstra R, Kersten S (2019) Characterization of ANGPTL4 function in macrophages and adipocytes using Angptl4-knockout and Angptl4-hypomorphic mice. J Lipid Res 60(10):1741–1754
Georgiadi A, Wang Y, Stienstra R, Tjeerdema N, Janssen A, Stalenhoef A, van der Vliet JA, de Roos A, Tamsma JT, Smit JW, Tan NS, Müller M, Rensen PC, Kersten S (2013) Overexpression of angiopoietin-like protein 4 protects against atherosclerosis development. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(7):1529–1537
He Y, Yang W, Gan L, Liu S, Ni Q, Bi Y, Han T, Liu Q, Chen H, Hu Y, Long Y, Yang L (2021) Silencing HIF-1alpha aggravates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in vitro through inhibiting PPAR-alpha/ANGPTL4 singling pathway. Gastroenterol Hepatol 44(5):355–365
Blücher C, Iberl S, Schwagarus N, Müller S, Liebisch G, Höring M, Hidrobo MS, Ecker J, Spindler N, Dietrich A, Burkhardt R, Stadler SC (2020) Secreted factors from adipose tissue reprogram tumor lipid metabolism and induce motility by modulating PPARalpha/ANGPTL4 and FAK. Mol Cancer Res 18(12):1849–1862
Wu J, Niu P, Zhao Y, Cheng Y, Chen W, Lin L, Lu J, Cheng X, Xu Z (2019) Impact of miR-223-3p and miR-2909 on inflammatory factors IL-6, IL-1ss, and TNF-alpha, and the TLR4/TLR2/NF-kappaB/STAT3 signaling pathway induced by lipopolysaccharide in human adipose stem cells. PLoS ONE 14(2):e0212063
Koh HS, Chang CY, Jeon SB, Yoon HJ, Ahn YH, Kim HS, Kim IH, Jeon SH, Johnson RS, Park EJ (2015) The HIF-1/glial TIM-3 axis controls inflammation-associated brain damage under hypoxia. Nat Commun 6:6340
Mitchell JP, Carmody RJ (2018) NF-kappaB and the transcriptional control of inflammation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 335:41–84
Zhang M, Zhou J, Wang L, Li B, Guo J, Guan X, Han Q, Zhang H (2014) Caffeic acid reduces cutaneous tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), IL-6 and IL-1beta levels and ameliorates skin edema in acute and chronic model of cutaneous inflammation in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 37(3):347–354
Bougarne N, Weyers B, Desmet SJ, Deckers J, Ray DW, Staels B, De Bosscher K (2018) Molecular actions of PPAR alpha in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Endocr Rev 39(5):760–802
Aryal B, Rotllan N, Araldi E, Ramírez CM, He S, Chousterman BG, Fenn AM, Wanschel A, Madrigal-Matute J, Warrier N, Martín-Ventura JL, Swirski FK, Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C (2016) ANGPTL4 deficiency in haematopoietic cells promotes monocyte expansion and atherosclerosis progression. Nat Commun 7:12313
Ding S, Wu D, Lu Q, Qian L, Ding Y, Liu G, Jia X, Zhang Y, Xiao W, Gong W (2020) Angiopoietin-like 4 deficiency upregulates macrophage function through the dysregulation of cell-intrinsic fatty acid metabolism. Am J Cancer Res 10(2):595–609
Wee WKJ, Low ZS, Ooi CK, Henategala BP, Lim ZGR, Yip YS, Vos MIG, Tan WWR, Cheng HS, Tan NS (2022) Single-cell analysis of skin immune cells reveals an Angptl4-ifi20b axis that regulates monocyte differentiation during wound healing. Cell Death Dis 13(2):180
Funding
This study was supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (14JJ2079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the design of the study, analysis and discussion of the results, and review and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Ethical approval
Approval was obtained from Hunan Agricultural University ethics review board.
Consent to participate and for publication
The authors approved the manuscript to be submitted for consideration for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, MM., Wang, YS. & Xiao, HB. Dual roles of ANGPTL4 in multiple inflammatory responses in stomatitis mice. Mol Biol Rep 49, 9195–9204 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07745-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07745-y