Abstract
Background
The combined restoration of tumor-suppressive microRNAs (miRs) has been identified as a promising approach for inhibiting breast cancer development. This study investigated the effect of the combined restoration of miR-424-5p and miR-142-3p on MCF-7 cells and compared the efficacy of the combined therapy with the monotherapies with miR-424-5p and miR-142-3p.
Methods
After transfection of miR-424-5p and miR-142-3p mimics into MCF-7 cells in the combined and separated manner, the proliferation of tumoral cells was assessed by the MTT assay. Also, the apoptosis, autophagy, and cell cycle of the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Western blot and qRT-PCR were used to study the expression levels of c-Myc, Bcl-2, Bax, STAT-3, Oct-3, and Beclin-1.
Results
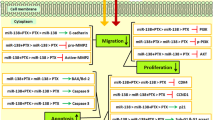
Our results have demonstrated that the combined restoration of miR-424-5p and miR-142-3p is more effective in inhibiting tumor proliferation via upregulating Bax and Beclin-1 and downregulating Bcl-2 and c-Myc. Besides, the combined therapy has arrested the cell cycle in the sub-G1 and G2 phases and has suppressed the clonogenicity via downregulating STAT-3 and Oct-3, respectively.
Conclusion
The combined restoration of miR-424-5p and miR-142-3p is more effective in inhibiting MCF-7 breast cancer development than monotherapies with miR-424-5p and miR-142-3p.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data would be available if requested by Editor or reviewers. They would be provided by Dr. Safaralizadeh (corresponding author).
References
Momenimovahed Z, Salehiniya H (2019) Epidemiological characteristics of and risk factors for breast cancer in the world. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press) 11:151–164
Yao H, He G, Yan S et al (2017) Triple-negative breast cancer: is there a treatment on the horizon? Oncotarget 8:1913–1924
Maeda H, Khatami M (2018) Analyses of repeated failures in cancer therapy for solid tumors: poor tumor-selective drug delivery, low therapeutic efficacy and unsustainable costs. Clin Transl Med 7:11
Ahangar NK, Hemmat N, Khalaj-Kondori M et al (2021) The regulatory cross-talk between microRNAs and novel members of the B7 family in human diseases: a scoping review. Int J Mol Sci 22(5):2652
Lin YC, Chen TH, Huang YM, Wei PL, Lin JC (2021) Involvement of microRNA in solid cancer: role and regulatory mechanisms. Biomedicines 9(4):343
Bertoli G, Cava C, Castiglioni I (2015) MicroRNAs: new biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics 5:1122–1143
Dastmalchi N, Safaralizadeh R, SM BK, et al (2021) An updated review of the cross-talk between micrornas and epigenetic factors in cancers. Curr Med Chem 28(42):8722–8732
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Ghasabi M et al (2019) miR-142-3p as tumor suppressor miRNA in the regulation of tumorigenicity, invasion and migration of human breast cancer by targeting Bach-1 expression. J Cell Physiol 234:9816–9825
Dastmalchi N, Safaralizadeh R, Baradaran B, Hosseinpourfeizi M, Baghbanzadeh A (2020) An update review of deregulated tumor suppressive microRNAs and their contribution in various molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Gene 729:144301
Mollaei H, Safaralizadeh R, Rostami Z (2019) MicroRNA replacement therapy in cancer. J Cell Physiol 234:12369–12384
Dastmalchi N, Hosseinpourfeizi MA, Khojasteh SMB, Baradaran B, Safaralizadeh R (2020) Tumor suppressive activity of miR-424-5p in breast cancer cells through targeting PD-L1 and modulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Life Sci 259:118239
Mansoori B, Duijf PH, Mohammadi A et al (2021) MiR-142-3p targets HMGA2 and suppresses breast cancer malignancy. Life Sci 276:119431
Zhou Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeshita F, Yamamoto T, Xiao Z, Ochiya T (2021) Delivery of miR-424-5p via extracellular vesicles promotes the apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 TNBC cells in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci 22:844
Xie D, Song H, Wu T et al (2018) MicroRNA-424 serves an anti-oncogenic role by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 1 in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep 40:3416–3426
Wang J, Wang S, Zhou J, Qian Q (2018) miR-424-5p regulates cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting doublecortin-like kinase 1 in basal-like breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 102:147–152
Liang L, Fu J, Wang S et al (2020) MiR-142-3p enhances chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells and inhibits autophagy by targeting HMGB1. Acta Pharm Sin B 10:1036–1046
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Gjerstorff MF et al (2019) miR-142-3p is a tumor suppressor that inhibits estrogen receptor expression in ER-positive breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 234:16043–16053
Zhou Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeshita F, Yamamoto T, Xiao Z, Ochiya T (2021) Delivery of miR-424–5p via extracellular vesicles promotes the apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 TNBC cells in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci 22(2):844
Zhao Y, Zhu C, Chang Q et al (2020) MiR-424-5p regulates cell cycle and inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting E2F7. PLoS ONE 15:e0242179
Derakhshani A, Rostami Z, Safarpour H et al (2021) From oncogenic signaling pathways to single-cell sequencing of immune cells: changing the landscape of cancer immunotherapy. Molecules 26:2278
Potter H (2003) Transfection by electroporation. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 9(9):3
Rodriguez-Barrueco R, Nekritz EA, Bertucci F et al (2017) miR-424(322)/503 is a breast cancer tumor suppressor whose loss promotes resistance to chemotherapy. Genes Dev 31:553–566
Tolosa L, Donato MT, Gomez-Lechon MJ (2015) General cytotoxicity assessment by means of the MTT assay. Methods Mol Biol 1250:333–348
Huang L, Jiang Y, Chen Y (2017) Predicting drug combination index and simulating the network-regulation dynamics by mathematical modeling of drug-targeted EGFR-ERK signaling pathway. Sci Rep 7:40752
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Gjerstorff MF et al (2019) miR-142–3p is a tumor suppressor that inhibits estrogen receptor expression in ER-positive breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 4(9):16043–16053
Redig AJ, McAllister SS (2013) Breast cancer as a systemic disease: a view of metastasis. J Intern Med 274:113–126
Mansoori B, Silvestris N, Mohammadi A et al (2021) miR-34a and miR-200c have an additive tumor-suppressive effect on breast cancer cells and patient prognosis. Genes 12:267
Mansoori B, Silvestris N, Mohammadi A et al (2021) miR-34a and miR-200c have an additive tumor-suppressive effect on breast cancer cells and patient prognosis. Genes (Basel) 12(2):267
Zhang T, Ji C, Shi R (2019) miR-142-3p promotes pancreatic beta cell survival through targeting FOXO1 in gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 12:1529–1538
Kastingschafer CS, Schafer SD, Kiesel L, Gotte M (2015) miR-142-3p is a novel regulator of cell viability and proinflammatory signalling in endometrial stroma cells. Reprod Biomed Online 30:553–556
Xie D, Song H, Wu T et al (2018) MicroRNA424 serves an antioncogenic role by targeting cyclindependent kinase 1 in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep 40:3416–3426
Dastmalchi N, Baradaran B, Banan Khojasteh SM, Hosseinpourfeizi M, Safaralizadeh R (2020) miR-424: a novel potential therapeutic target and prognostic factor in malignancies. Cell Biol Int 45(4):720–730
Dastmalchi N, Safaralizadeh R, Hosseinpourfeizi MA, Baradaran B, Khojasteh SMB (2021) MicroRNA-424-5p enhances chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to Taxol and regulates cell cycle, apoptosis, and proliferation. Mol Biol Rep 48:1345–1357
Valovka T, Schonfeld M, Raffeiner P et al (2013) Transcriptional control of DNA replication licensing by Myc. Sci Rep 3:3444
Shadbad MA, Hajiasgharzadeh K, Baradaran B (2020) Cross-talk between myeloid-derived suppressor cells and Mucin1 in breast cancer vaccination: on the verge of a breakthrough. Life Sci 258:118128
Zaytseva YY, Rychahou PG, Gulhati P et al (2012) Inhibition of fatty acid synthase attenuates CD44-associated signaling and reduces metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 72:1504–1517
Ma L, Li Z, Li W, Ai J, Chen X (2019) MicroRNA-142-3p suppresses endometriosis by regulating KLF9-mediated autophagy in vitro and in vivo. RNA Biol 16:1733–1748
Lu HT, Xu YQ, Wang H, Zhang XL (2020) miR-424-5p regulates apoptosis and cell proliferation via targeting Bcl2 in nucleus pulposus cells. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul) 24:136–142
Zhao FQ, Misra Y, Li DB et al (2018) Differential expression of Oct3/4 in human breast cancer and normal tissues. Int J Oncol 52:2069–2078
Karmakar S, Seshacharyulu P, Lakshmanan I et al (2017) hPaf1/PD2 interacts with OCT3/4 to promote self-renewal of ovarian cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 8:14806
Shen WW, Zeng Z, Zhu WX, Fu GH (2013) MiR-142-3p functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting CD133, ABCG2, and Lgr5 in colon cancer cells. J Mol Med (Berl) 91:989–1000
Marquez RT, Xu L (2012) Bcl-2: Beclin 1 complex: multiple, mechanisms regulating autophagy/apoptosis toggle switch. Am J Cancer Res 2:214–221
Gozuacik D, Akkoc Y, Ozturk DG, Kocak M (2017) Autophagy-regulating microRNAs and cancer. Front Oncol 7:65
Acknowledgements
We appreciated Immunology research center of Tabriz (IRC) for providing facilities.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ND acquired and analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript, RS designed the work, SMB and MH wrote and revised the manuscript, MA substantially revised the manuscript, BB, ShA, and AR drafted the work and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable. This project has not used any human or animal samples.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dastmalchi, N., Safaralizadeh, R., Khojasteh, S.M.B. et al. The combined restoration of miR-424-5p and miR-142-3p effectively inhibits MCF-7 breast cancer cell line via modulating apoptosis, proliferation, colony formation, cell cycle and autophagy. Mol Biol Rep 49, 8325–8335 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07646-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07646-0