Abstract
Objective
Previous studies have found that forkhead box o3 S574 phosphorylation status can regulate inflammation by inducing monocytes/macrophages apoptosis, and whether it directly affects the inflammatory response of monocytes has not been demonstrated. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of forkhead box o3 in inflammatory response of monocytes against lipopolysaccharide.
Methods
THP-1 cells were used to knock down or overexpress forkhead box o3 and its mutants, and then detect the activation of inflammatory cytokines expression and activation of nuclear factor kappa B after lipopolysaccharide treatment.
Results
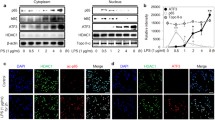
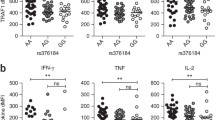
The present study demonstrated that lipopolysaccharide can up-regulate forkhead box o3 protein expression, especially the non-phosphorylated form at S574, in a post-transcriptional way. Knockdown of forkhead box o3 attenuated lipopolysaccharide mediated nuclear factor kappa B activation and downstream inflammatory cytokines expression. When overexpressing forkhead box o3, only non-phosphorylated S574A forkhead box o3 mutant enhanced lipopolysaccharide induced nuclear factor kappa B activation and inflammatory cytokines expression. Further studies have found that S574A forkhead box o3 may promote toll like receptor 4 expression through binding and accelerating its transcriptional activity from promoter.
Conclusion
There might be a positive feedback loop between lipopolysaccharide and forkhead box o3 in monocytes to promote the lipopolysaccharide mediated inflammatory response.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Salomao R, Brunialti MK, Rapozo MM, Baggio-Zappia GL, Galanos C, Freudenberg M (2012) Bacterial sensing, cell signaling, and modulation of the immune response during sepsis. Shock 38:227–242. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0b013e318262c4b0
Roh YS, Seki E (2013) Toll-like receptors in alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and carcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 28(Suppl 1):38–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.12019
Gomes JMG, Costa JA, Alfenas RCG (2017) Metabolic endotoxemia and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Metabolism 68:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2016.12.009
Huang Z, Kraus VB (2016) Does lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation have a role in OA? Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2015.158
Shi C, Pamer EG (2011) Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 11:762–774. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3070
Kawai T, Akira S (2007) Signaling to NF-kappaB by toll-like receptors. Trends Mol Med 13:460–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2007.09.002
van der Bruggen T, Nijenhuis S, van Raaij E, Verhoef J, van Asbeck BS (1999) Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha production by human monocytes involves the raf-1/MEK1-MEK2/ERK1-ERK2 pathway. Infect Immun 67:3824–3829. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.67.8.3824-3829.1999
Hambleton J, Weinstein SL, Lem L, DeFranco AL (1996) Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2774–2778. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.7.2774
Liu MK, Herrera-Velit P, Brownsey RW, Reiner NE (1994) CD14-dependent activation of protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinases (p42 and p44) in human monocytes treated with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol 153:2642–2652
Casey JR, Petranka JG, Kottra J, Fleenor DE, Rosse WF (1994) The structure of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor gene. Blood 84:1151–1156
Calissi G, Lam EW, Link W (2021) Therapeutic strategies targeting FOXO transcription factors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 20:21–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-020-0088-2
Luron L, Saliba D, Blazek K, Lanfrancotti A, Udalova IA (2012) FOXO3 as a new IKK-epsilon-controlled check-point of regulation of IFN-beta expression. Eur J Immunol 42:1030–1037. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201141969
Thompson MG, Larson M, Vidrine A, Barrios K, Navarro F, Meyers K, Simms P, Prajapati K, Chitsike L, Hellman LM, Baker BM, Watkins SK (2015) FOXO3-NF-kappaB RelA protein complexes reduce proinflammatory cell signaling and function. J Immunol 195:5637–5647. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1501758
Ouyang W, Beckett O, Ma Q, Paik JH, DePinho RA, Li MO (2010) Foxo proteins cooperatively control the differentiation of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 11:618–627. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1884
Loebel M, Holzhauser L, Hartwig JA, Shukla PC, Savvatis K, Jenke A, Gast M, Escher F, Becker SC, Bauer S, Stroux A, Beling A, Kespohl M, Pinkert S, Fechner H, Kuehl U, Lassner D, Poller W, Schultheiss HP, Zeller T, Blankenberg S, Papageorgiou AP, Heymans S, Landmesser U, Scheibenbogen C, Skurk C (2018) The forkhead transcription factor Foxo3 negatively regulates natural killer cell function and viral clearance in myocarditis. Eur Heart J 39:876–887. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx624
Litvak V, Ratushny AV, Lampano AE, Schmitz F, Huang AC, Raman A, Rust AG, Bergthaler A, Aitchison JD, Aderem A (2012) A FOXO3-IRF7 gene regulatory circuit limits inflammatory sequelae of antiviral responses. Nature 490:421–425. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11428
Li Z, Zhang H, Chen Y, Fan L, Fang J (2012) Forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a protein activates nuclear factor kappaB through B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 10 (BCL10) protein and promotes tumor cell survival in serum deprivation. J Biol Chem 287:17737–17745. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.291708
Li Z, Zhao J, Tikhanovich I, Kuravi S, Helzberg J, Dorko K, Roberts B, Kumer S, Weinman SA (2016) Serine 574 phosphorylation alters transcriptional programming of FOXO3 by selectively enhancing apoptotic gene expression. Cell Death Differ 23:583–595. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2015.125
Li Z, Zhao J, Zhang S, Weinman SA (2018) FOXO3-dependent apoptosis limits alcohol-induced liver inflammation by promoting infiltrating macrophage differentiation. Cell Death Discov 4:16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-017-0020-7
Bouzeyen R, Haoues M, Barbouche MR, Singh R, Essafi M (2019) FOXO3 transcription factor regulates IL-10 expression in mycobacteria-infected macrophages tuning their polarization and the subsequent adaptive immune response. Front Immunol 10:2922. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02922
Joseph J, Ametepe ES, Haribabu N, Agbayani G, Krishnan L, Blais A, Sad S (2016) Inhibition of ROS and upregulation of inflammatory cytokines by FoxO3a promotes survival against Salmonella typhimurium. Nat Commun 7:12748. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12748
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Dehner M, Hadjihannas M, Weiske J, Huber O, Behrens J (2008) Wnt signaling inhibits forkhead box O3a-induced transcription and apoptosis through up-regulation of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1. J Biol Chem 283:19201–19210. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M710366200
Cheong JK, Zhang F, Chua PJ, Bay BH, Thorburn A, Virshup DM (2015) Casein kinase 1alpha-dependent feedback loop controls autophagy in RAS-driven cancers. J Clin Invest 125:1401–1418. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI78018
Gao J, Yang X, Yin P, Hu W, Liao H, Miao Z, Pan C, Li N (2012) The involvement of FoxO in cell survival and chemosensitivity mediated by Mirk/Dyrk1B in ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol 40:1203–1209. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2011.1293
Greer EL, Oskoui PR, Banko MR, Maniar JM, Gygi MP, Gygi SP, Brunet A (2007) The energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase directly regulates the mammalian FOXO3 transcription factor. J Biol Chem 282:30107–30119. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M705325200
Chapuis N, Park S, Leotoing L, Tamburini J, Verdier F, Bardet V, Green AS, Willems L, Agou F, Ifrah N, Dreyfus F, Bismuth G, Baud V, Lacombe C, Mayeux P, Bouscary D (2010) IkappaB kinase overcomes PI3K/Akt and ERK/MAPK to control FOXO3a activity in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 116:4240–4250. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-12-260711
Kristof AS, Fielhaber J, Triantafillopoulos A, Nemoto S, Moss J (2006) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent suppression of the human inducible nitric-oxide synthase promoter is mediated by FKHRL1. J Biol Chem 281:23958–23968. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M513918200
Snoeks L, Weber CR, Turner JR, Bhattacharyya M, Wasland K, Savkovic SD (2008) Tumor suppressor Foxo3a is involved in the regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-8 in intestinal HT-29 cells. Infect Immun 76:4677–4685. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00227-08
Kruys V, Wathelet M, Poupart P, Contreras R, Fiers W, Content J, Huez G (1987) The 3’ untranslated region of the human interferon-beta mRNA has an inhibitory effect on translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:6030–6034
Han J, Huez G, Beutler B (1991) Interactive effects of the tumor necrosis factor promoter and 3’-untranslated regions. J Immunol 146:1843–1848
Cohen PS, Nakshatri H, Dennis J, Caragine T, Bianchi M, Cerami A, Tracey KJ (1996) CNI-1493 inhibits monocyte/macrophage tumor necrosis factor by suppression of translation efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3967–3971
Lee HY, Youn SW, Kim JY, Park KW, Hwang CI, Park WY, Oh BH, Park YB, Walsh K, Seo JS, Kim HS (2008) FOXO3a turns the tumor necrosis factor receptor signaling towards apoptosis through reciprocal regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and NF-kappaB. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.153304
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Senior Medical Talents Program of Chongqing for Young and Middle-aged (2019-181) and Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, SJZ, ZL and SW; methodology, SJZ and ZL; formal analysis, SJZ, ZL and SW; investigation, SJZ and ZL; writing—original draft preparation, SJZ; writing—review and editing, ZL, SW and SJZ. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Li, Z. & Weinman, S. FoxO3 might be involved in the inflammatory response of human monocytes to lipopolysaccharide through regulating expression of toll like receptor 4. Mol Biol Rep 49, 7611–7621 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07576-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07576-x