Abstract
Background
Tim-3/Galectin-9 is involved in the immune escape of many pathogens. However, the role of Tim-3/Galectin-9 in persistent infection of Echinococcus multilocularis (Em), which is related to immune escape, is still unclear.
Objective
To investigate the role of Tim-3/Galectin-9 and related cytokines in mice with persistent infection of Em.
Methods
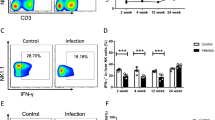
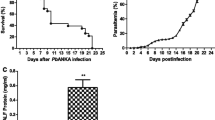
Em infection model was established by injecting the protoscoleces. Serum was collected at days 2, 8, 30, 60, 90, 180 and 270 after infection. Lymphocytes were isolated from liver tissue samples with Ficoll. Tim-3 + CD4 + T percentage was analyzed by flow cytometry. CD4 + T cells were isolated from liver tissues of Em infected mice and cultured in vitro. The mRNA levels of Tim-3, Galectin-9, IFN-γ and IL-4 were detected by qRT-PCR. Cytokine levels in serum and culture supernatant (IFN-γ and IL-4) were analyzed by cytometric bead array.
Results
The expression of Tim-3 and Galectin-9 mRNA significantly increased after 30 days of infection, reached peak on day 90, and then decreased slightly on days 180–270. The expression of IFN-γ mRNA, increased on day 2 and 8 after infection, slightly decreased on days 30–60, and obvious decreased on days 90–270, but were still higher than those of the control group. The expression of IL-4 mRNA gradually increased along with the time of infection. In serum of Em infected mice, level of IFN-γ peaked at day 30 and then gradually decreased; whereas IL-4 level peaked at day 90 and then gradually decreased. In vitro experiment found that Tim-3/Galectin-9 directly caused the changes in the levels of IFN-γ and IL-4.
Conclusions
Tim-3/Galectin-9 signaling pathway may be involved in the development of persistent infection of Em by regulating the production of Th1 and Th2 cytokines.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Wen H, Xu MQ (2007) Practical Science of Echinococcosis. Science Press, Beijing, pp 15–19
Liance M, Bresson-Hadni S, Vuitton D, Bretagne S, Houin R (1990) Comparison of the viability and developmental characteristics of Echinococcus multilocularis isolates from human patients in France. Int J Parasitol 20:83–86
Koziol U, Rauschendorfer T, Zanon Rodríguez L, Krohne G, Brehm K (2014) The unique stem cell system of the immortal larva of the human parasite Echinococcus multilocularis. Evodevo 5:10
Kern P (2010) Clinical features and treatment of alveolar echinococcosis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 23:505–512
Wen H, Vuitton L, Tuxun T, Li J, Vuitton DA, Zhang W, McManus DP (2019) Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st Century.Clin Microbiol Rev32
Xu K, Ahan A (2020) A new dawn in the late stage of alveolar echinococcosis “parasite cancer”. Med Hypotheses 142:109735
Cho JL, Roche MI, Barry S, Brian S, Xavier RJ, Medoff BD (2012) Enhanced Tim3 activity improves survival after influenza infection. J Immunol 189:2879–2889
Li Y, Liu X, Zhu Y, Zhou X, Cao C, Hu X, Ma H, Wen H, Ma X, Ding JB (2013) Bioinformatic prediction of epitopes in the Emy162 antigen of Echinococcus multilocularis. Exp Ther Med 6:335–340
Mejri N, Hassen IE, Knapp J, Saidi M (2017) Impairment of Macrophage Presenting Ability and Viability by Echinococcus granulosus Antigens. Iran J Immunol 14:35–50
Pang N, Zhang F, Ma X, Zhu Y, Zhao H, Xin Y, Wang S, Chen Z, Wen H, Ding J (2014) TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway regulates Th17/Treg balance during Echinococcus multilocularis infection. Int Immunopharmacol 20:248–257
Infante-Duarte C, Kamradt T (1999) Th1/Th2 balance in infection. Springer Semin Immunopathol 21:317–338
Bellanger AP, Mougey V, Pallandre JR, Gbaguidi-Haore H, Godet Y, Millon L (2017) Echinococcus multilocularis vesicular fluid inhibits activation and proliferation of natural killer cells.Folia Parasitol (Praha)64
Liu X, Zhao H, Cao W, Liu Y, Zhang C, Lan X, Peng S, Wen H, Ding J, Ma X (2016) Bioinformatic prediction of the antigenic epitopes of recombinant ferritin of Echinococcus granulosus. Mol Med Rep 13:888–894
Zhang C, Wang J, Lü G, Li J, Lu X, Mantion G, Vuitton DA, Wen H, Lin R (2012) Hepatocyte proliferation/growth arrest balance in the liver of mice during E. multilocularis infection: a coordinated 3-stage course. PLoS ONE 7:e30127
Gooden MJ, Wiersma VR, Samplonius DF, Gerssen J, van Ginkel RJ, Nijman HW, Hirashima M, Niki T, Eggleton P, Helfrich W, Bremer E (2013) Galectin-9 activates and expands human T-helper 1 cells. PLoS ONE 8:e65616
La X, Zhang F, Li Y, Li J, Guo Y, Hui Z, Pang N, Ma X, Hao W, Fan H (2015) Upregulation of PD-1 on CD4 + CD25 + T cells is associated with immunosuppression in liver of mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis. Int Immunopharmacol 26:357–366
Sánchez-Fueyo A, Tian J, Picarella D, Domenig C, Zheng XX, Sabatos CA, Manlongat N, Bender O, Kamradt T, Kuchroo VK (2003) Tim-3 inhibits T helper type 1-mediated auto- and alloimmune responses and promotes immunological tolerance. Nat Immunol 4:1093–1101
Tang ZH, Liang S, Potter J, Jiang X, Mao HQ, Li Z (2013) Tim-3/galectin-9 regulate the homeostasis of hepatic NKT cells in a murine model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Immunol 190:1788–1796
Wu M, Zhu Y, Zhao J, Ai H, Gong Q, Zhang J, Zhao J, Wang Q, La X, Ding J (2015) Soluble costimulatory molecule sTim3 regulates the differentiation of Th1 and Th2 in patients with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:8812–8819
Hirashima M, Kashio Y, Nishi N, Yamauchi A, Imaizumi TA, Kageshita T, Saita N, Nakamura T (2002) Galectin-9 in physiological and pathological conditions. Glycoconj J 19:593–600
Li X, Chen Y, Xu L, Jin Z, Xu H, Teng G, Yu D (2017) Tim3/Gal9 interactions between T cells and monocytes result in an immunosuppressive feedback loop that inhibits Th1 responses in osteosarcoma patients. Int Immunopharmacol 44:153–159
Sabatos CA, Chakravarti S, Cha E, Schubart A, Sanchez-Fueyo A, Zheng XX, Coyle AJ, Strom TB, Freeman GJ, Kuchroo VK (2003) Interaction of Tim-3 and Tim-3 ligand regulates T helper type 1 responses and induction of peripheral tolerance. Nat Immunol 4:1102–1110
Wang F, He W, Yuan J, Wu K, Zhou H, Zhang W, Chen ZK (2008) Activation of Tim-3-Galectin-9 pathway improves survival of fully allogeneic skin grafts. Transpl Immunol 19:12–19
Zhang C, Shao Y, Yang S, Bi X, Li L, Wang H, Yang N, Li Z, Sun C, Li L, Lü G, Aji T, Vuitton DA, Lin R, Wen H (2017) T-cell tolerance and exhaustion in the clearance of Echinococcus multilocularis: role of inoculum size in a quantitative hepatic experimental model. Sci Rep 7:11153
Zhang F, Li S, Zhu Y, Zhang C, Li Y, Ma H, Pang N, An M, Wang H, Ding J (2018) Immunization of mice with egG1Y162-1/2 provides protection against Echinococcus granulosus infection in BALB/c mice. Mol Immunol 94:183–189
Bresson-Hadni S, Mantion GA, Vuitton DA (2007) From basic science to clinical practice. Echinococcosis of the liver. Blackwell Publishing Inc, Oxford-Malden, pp 1047–1057
Qi Y, Song XR, Shen JL, Xu YH, Shen Q, Luo QL, Zhong ZR, Wang W, Chu DY, Song WJ (2012) Tim-2 up-regulation and galectin-9-Tim-3 pathway activation in Th2-biased response in Schistosoma japonicum infection in mice. Immunol Lett 144:60–66
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Gu W, He L, Sun B (2014) Th1/Th2 cell’s function in immune system. Adv Exp Med Biol 841:45–65
Barathan M, Mohamed R, Vadivelu J, Li YC, Vignesh R, Krishnan J, Sigamani P, Saeidi A, Ram MR, Velu V (2017) CD8 + T cells of chronic HCV-infected patients express multiple negative immune checkpoints following stimulation with HCV peptides. Cell Immunol 313:1–9
Jiao Q, Qian Q, Zhao Z, Fang F, Hu X, An J, Jian W, Liu C (2016) Expression of human T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin-3 (TIM-3) and TIM-3 ligands in peripheral blood from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol Res 308:1–9
Moretto MM, Hwang S, Khan IA (2017) Downregulated IL-21 Response and T Follicular Helper Cell Exhaustion Correlate with Compromised CD8 T Cell Immunity during Chronic Toxoplasmosis. Front Immunol 8:1436
Ricken FJ, Nell J, Grüner B, Schmidberger J, Kaltenbach T, Kratzer W, Hillenbrand A, Hennebruns D, Deplazes P, Möller P (2017) Albendazole increases the inflammatory response and the amount of Em2-positive small particles ofEchinococcus multilocularis(spems) in human hepatic alveolar echinococcosis lesions.Plos Neglected Tropical Diseases11
Sada-Ovalle I, Chavez-Galan L, Torre-Bouscoulet L, Nava-Gamino L, Barrera L, Jayaraman P, Torres-Rojas M, Salazar-Lezama MA, Behar SM (2012) The Tim3-galectin 9 pathway induces antibacterial activity in human macrophages infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol 189:5896–5902
Dai SY, Nakagawa R, Itoh A, Murakami H, Kashio Y, Abe H, Katoh S, Kontani K, Kihara M, Zhang SL, Hata T, Nakamura T, Yamauchi A, Hirashima M (2005) Galectin-9 induces maturation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol 175:2974–2981
Yang S, Jin W, Chen F, Liu G, Weng Z, Chen J (2017) Elevated Galectin-9 Suppresses Th1 Effector Function and Induces Apoptosis of Activated CD4 + T Cells in Osteoarthritis. Inflammation 40:1–10
Zhu C, Anderson AC, Schubart A, Xiong H, Imitola J, Khoury SJ, Zheng XX, Strom TB, Kuchroo VK (2005) The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nat Immunol 6:1245–1252
Barrueto L, Caminero F, Cash L, Makris C, Lamichhane P, Deshmukh RR (2020) Resistance to Checkpoint Inhibition in Cancer Immunotherapy. Transl Oncol 13:100738
Dembele BP, Chagan-Yasutan H, Niki T, Ashino Y, Tangpukdee N, Shinichi E, Krudsood S, Kano S, Hattori T (2016) Plasma levels of Galectin-9 reflect disease severity in malaria infection. Malar J 15:403
Xiao S, Liu J, Huang S, Lu F (2016) Increased Gal-9 and Tim-3 expressions during liver damage in a murine malarial model. Parasitol Res 115:663–672
Steichen AL, Simonson TJ, Salmon SL, Metzger DW, Mishra BB, Sharma J (2015) Alarmin function of galectin-9 in murine respiratory tularemia. PLoS ONE 10:e0123573
Pang N, Zhang F, Ma X, Zhang Z, Zhao H, Xin Y, Wang S, Zhu Y, Wen H, Ding J (2014) Th9/IL-9 profile in human echinococcosis: their involvement in immune response during infection by Echinococcus granulosus. Mediators Inflamm 2014: 781649
Curran SA, Romano E, Kennedy MG, Hsu KC, Young JW (2014) Phenotypic and functional activation of hyporesponsive KIRnegNKG2Aneg human NK-cell precursors requires IL12p70 provided by Poly(I:C)-matured monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Cancer Immunol Res 2:1000–1010
Dong J, Yang XF, Wang LX, Wei X, Wang AH, Hao CQ, Shen HJ, Huang CX, Zhang Y, Lian JQ (2017) Modulation of Tim-3 Expression by Antigen-Dependent and -Independent Factors on T Cells from Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:98
Rubinstein MP, Su EW, Suriano S, Cloud CA, Andrijauskaite K, Kesarwani P, Schwartz KM, Williams KM, Johnson CB, Li M, Scurti GM, Salem ML, Paulos CM, Garrett-Mayer E, Mehrotra S, Cole DJ (2015) Interleukin-12 enhances the function and anti-tumor activity in murine and human CD8(+) T cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 64:539–549
Jeon WY, Shin IS, Shin HK, Lee MY (2015) Samsoeum water extract attenuates allergic airway inflammation via modulation of Th1/Th2 cytokines and decrease of iNOS expression in asthmatic mice. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:47
Zhang F, Ma X, Zhu Y, Wang H, Liu X, Zhu M, Ma H, Wen H, Fan H, Ding J (2014) Identification, expression and phylogenetic analysis of EgG1Y162 from Echinococcus granulosus. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:5655–5664
Zhang F, Pang N, Zhu Y, Zhou D, Zhao H, Hu J, Ma X, Li J, Wen H, Samten B, Fan H, Ding J (2015) CCR7(lo)PD-1(hi) CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T cells are positively correlated with levels of IL-21 in active and transitional cystic echinococcosis patients. BMC Infect Dis 15:457
Zhang F, Lu X, Guo N, Zhang Y, Ji P, Hu J, Zhang Z, Li J, Li F, Ding J (2016) The prediction of T- and B-combined epitope of Ag85B antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int J Clin Exp Med 9:1408–1421
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 81960373, 81460307, 81660343, 81160200, 81160202, 81060135] and Xinjiang Institute of Hydatid Disease [grant number XJDX0202-2010-04].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JBD and HNF conceived and designed the experiments. SYL, FBZ, YJZ and YJL performed the experiments. HNF, NNP and MTA analyzed the data. SYL, FBZ, HNF Fan and JBD wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were conducted according to the ethical guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee and were approved by the Ethical Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (License number: A-20130216-155).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Shaoyu Li, Yuejie Zhu and Song Wang authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Zhu, Y., Wang, S. et al. Tim-3/Galectin-9 signaling pathway is involved in the cytokine changes in mice with alveolar echinococcosis. Mol Biol Rep 49, 7497–7506 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07554-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07554-3