Abstract
Background
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is among the main complications of diabetes mellitus and has been a major factor of renal failure. This study was designed to address the association between beta-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-17, and IL-33 and the development of DN.
Methods
In this study, 20 healthy volunteers and 100 patients were enrolled. According to their biochemical markers, the patients were categorized into five groups: diabetic, chronic renal disease, diabetic chronic renal disease, end-stage renal disease, and diabetic end-stage renal disease.
Results
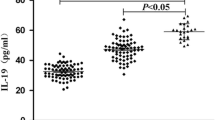
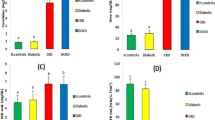
Our results showed a noticeable elevation in IL-1β and IL-17 levels and a reduction in IL-33 and Bcl-2 levels in all investigated groups compared with those in the healthy group. Positive correlations were found between IL-1β and fasting blood sugar and between creatinine levels and IL-17, HbA1c%, and sodium levels. However, negative correlations were found between IL-33 and urea and sodium concentrations and between Bcl-2 and HbA1c% and creatinine levels.
Conclusions
The present data revealed a marked relationship between Bcl-2, IL-1β, IL-17, and IL-33 levels and the onset and progression of DN. Understanding the molecular pathways of these processes could be translated into the development of therapeutic strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Shahbazian H, Rezaii I (2013) Diabetic kidney disease; review of the current knowledge. J Ren Inj Prev 2(2):73–80
Gheith O, Farouk N, Nampoory N, Halim MA, Al-Otaibi T (2016) Diabetic kidney disease: worldwide difference of prevalence and risk factors. J Nephropharmacol 5(1):49–56
Taha H, Mahmoud HH, Soliman AS, Taha MM, Mohammed RA (2019) The Association between Highly Sensitive C-Reactive Protein and Interleukin-18 with Nephropathy in a Sample of Type 1 Diabetic Egyptian Patients. Med J Cairo Univ 87(4):2393–2402
Qin J, Peng Z, Yuan Q, Li Q et al (2019) AKF-PD alleviates diabetic nephropathy via blocking the RAGE/AGEs/NOX and PKC/NOX Pathways. Sci Rep 9(1):4407
Donate-Correa J, Ferri CM, Sánchez-Quintana F et al (2021) Inflammatory Cytokines in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiologic and Therapeutic Implications. Front Med (Lausanne) 7:628289
Donate-Correa J, Víctor G, Tagua VG et al (2019) Pentoxifylline for Renal Protection in Diabetic Kidney Disease. A Model of Old Drugs for New Horizons. J Clin Med 8:287
Zhang G, Lv Z, Zhao Y et al (2012) Inhibitory effect of tumor necrosis factor–α on the basolateral Kir4.1/Kir5.1 channels in the thick ascending limb during diabetes. Exp Ther Med 22:1242
Abdel-Moneim A, Bakery HH, Allam G (2018) The potential pathogenic role of IL-17/Th17 cells in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomed Pharmacother 101:287–292
Tang H, Liu N, Feng X et al (2021) Circulating levels of IL-33 are elevated by obesity and positively correlated with metabolic disorders in Chinese adults. J Transl Med 19(1):52
Opferman JT, Kothari A (2018) Anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members in development. Cell Death Differ 25:37–45
Wu N, Shen H, Liu H et al (2016) Acute blood glucose fluctuation enhances rat aorta endothelial cell apoptosis, oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in vivo. Cardiovasc Diabetol 15(1):109
Borkan SC (2016) The Role of BCL-2 Family Members in Acute Kidney Injury. Semin Nephrol 36(3):237–250
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Bonnemaison ML, Marks ES, Boesen EI (2017) Interleukin–1beta as a driver of renal NGAL production. Cytokine 91:38–43
Abdel-Moneim A, Mahmoud B, Sultan EA, Mahmoud R (2000) Associationof erythrocytes indices and interleukin-1 beta with metabolic syndrome components. UTMJ 97(1):6–13
Li J, Xu J, Qin X et al (2019) Acute pancreatic beta cell apoptosis by IL-1β is responsible for postburn hyperglycemia: Evidence from humans and mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1865(2):275–284
Lei Y, Devarapu SK, Motrapu M et al (2019) Interleukin-1β Inhibition for Chronic Kidney Disease in Obese Mice With Type 2 Diabetes. Front Immunol 10:1223
Pirklbauer M, Sallaberger S, Staudinger P et al (2021) Empagliflozin Inhibits IL-1β-Mediated Inflammatory Response in Human Proximal Tubular Cells. Int J Mol Sci 22(10):5089
Lei Y, Devarapu SK, Motrapu M, Cohen CD, Lindenmeyer MT, Moll S, Kumar SV, Anders HJ (2019) Interleukin-1β Inhibition for Chronic Kidney Disease in Obese Mice With Type 2 Diabetes. Front Immunol 10:1223
Palsamy P, Subramanian S (2011) Resveratrol protects diabetic kidney by attenuating hyperglycemia- mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammatory cytokines via Nrf2–Keap1 signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812(7):719–731
Chen C, Shao Y, Wu X, Huang C, Lu W (2016) Elevated Interleukin-17 Levels in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biochem Physiol 5:206–217
Cruz JA, Child EE, Amatya N et al (2017) Interleukin-17 signaling triggers degradation of the constitutive NF-κB inhibitor ABIN-1. Immunohorizons 1(7):133–141
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC (2017) NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2:17023
Iyoda M, Shibata T, Kawaguchi M et al (2010) IL-17A and IL-17F stimulate chemokines via MAPK pathways (ERK1/2 and p38 but not JNK) in mouse cultured mesangial cells: synergy with TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298:779–787
Ma J, Li YJ, Chen X, Kwan T, Chadban SJ, Wu H (2019) Interleukin 17A promotes diabetic kidney injury. Sci Rep 9(1):2264
Wen Y, Crowley SD (2018) Renal effects of cytokines in hypertension. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 27(2):70–76
Karbach S, Croxford AL, Oelze M et al (2014) Interleukin 17 drives vascular inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and arterial hypertension in psoriasis-like skin disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34(12):2658–2668
Madhur MS, Lob HE, McCann LA et al (2010) Interleukin 17 promotes angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular dysfunction. Hypertension 55(2):500–507
Nguyen H, Chiasson VL, Chatterjee P, Kopriva SE, Young KJ, Mitchell BM (2013) Interleukin-17 causes Rho-kinase-mediated endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 97(4):696–704
Norlander AE, Saleh MA, Kamat NV et al (2016) Interleukin-17A regulates renal sodium transporters and renal injury in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Hypertension 68(1):167–174
Peng X, Xiao Z, Zhang J, Li Y, Dong Y, Du J (2015) IL-17A produced by both 𝛄𝛅 T and Th17 cells promotes renal fibrosis via RANTES-mediated leukocyte infiltration after renal obstruction. J Pathol 235(1):79–89
Cortvrindt C, Speeckaert R, Moerman A, Delanghe JR, Speeckaert MM (2017) The role of interleukin-17A in the pathogenesis of kidney diseases. Pathology 49(3):247–258
Coto E, Gómez J, Suárez B et al (2015) Association between the IL17RA rs4819554 polymorphism and reduced renal filtration rate in the Spanish RENASTUR cohort. Hum Immunol 76(2–3):75–78
Linhartova PB, Kastovsky J, Lucanova S et al (2016) Interleukin-17A Gene Variability in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Periodontitis: Its Correlation with IL-17 Levels and the Occurrence of Periodontopathic Bacteria. Mediators Inflamm. : ID 2979846
Duan L, Huang Y, Su Q et al (2016) Potential of IL-33 for Preventing the Kidney Injury via Regulating the Lipid Metabolism in Gout Patients J Diabetes Res. : ID 1028401
Ferhat M, Robin A, Giraud S et al (2018) Endogenous IL-33 Contributes to Kidney Ischemia Reperfusion Injury as an Alarmin. J Am Soc Nephrol 29:1272–1288
Sabapathy V, Stremska ME, Mohammad S, Corey RL, Sharma PR, Sharma R (2019) Novel Immuno modulatory Cytokine Regulates Inflammation, Diabetes, and Obesity to Protect From Diabetic Nephropathy. Front Pharmacol 10:572
Stremska ME, Jose S, Sabapathy V et al (2017) IL233, a novel IL-2 and IL-33 hybrid cytokine, ameliorates renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 28:2681–2693
Nile CJ, Barksby E, Jitprasertwong P, Preshaw PM, Taylor JJ (2010) Expression and regulation of interleukin-33 in human monocytes. Immunology 130(2):172–180
Caner S, Usluoğulları CA, Balkan F, Büyükcam F, Kaya C, Saçıkara M, Koca C, Ersoy R, Çakır B (2014) Is IL-33 useful to detect early stage of renal failure? Ren Fail 36(1):78–80
Alabi TD, Brooks NL, Oguntibeju OO (2021) Leaf Extracts of Anchomanes difformis Ameliorated Kidney and Pancreatic Damage in Type 2 Diabetes. Plants (Basel) 10(2):300
Kale J, Osterlund EJ, Andrews DW (2018) BCL-2 family proteins: changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell Death Differ 25(1):65–80
Borkan SC (2016) The Role of BCL-2 Family Members in Acute Kidney Injury. Semin Nephrol 36(3):237–250
Bălăşescu E, Cioplea M, Brînzea A, Nedelcu R, Zurac S, Ion DA (2016) Immunohistochemical Aspects of Cell Death in Diabetic Nephropathy. Rom J Intern Med 54(1):54–62
Nour H, Zahran N, Abd Elhamid S et al (2016) The Role of BCL-2 and BAK Genes in Chronic Kidney Disease and Haemodialysis Patients. J glycom Metab 1(1):8–24
Borkan SC (2016) The Role of BCL-2 Family Members in Acute Kidney Injury. Semin Nephrol 36(3):237–250
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation and data collection and analysis were performed by Basant Mahmoud, Adel Abdel-Moneim, and Ahmed Nabil. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Basant Mahmoud, Adel Abdel-Moneim, and Ahmed Nabil, and all authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Hospital’s Ethics Committee, Beni Suef, Egypt, approved all procedures (BSU/2017/9). Written informed consent was given by all participants in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoud, B., Abdel-Moneim, A., Negeem, Z. et al. The relationship between B-cell lymphoma 2, interleukin-1β, interleukin-17, and interleukin-33 and the development of diabetic nephropathy. Mol Biol Rep 49, 3803–3809 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07221-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07221-7